
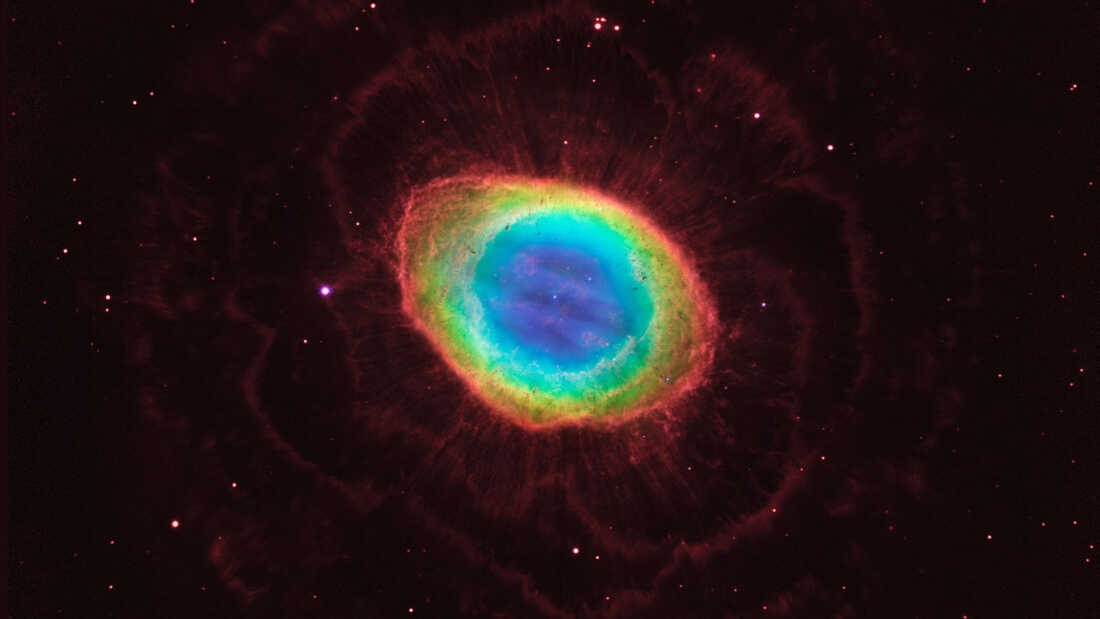
The well-known Ring Nebula is seen in good new readability, because of a brand new James Webb Area Telescope picture launched by researchers within the JWST Ring Nebula Imaging Challenge. The picture was processed by Roger Wesson, based on Western College in Ontario.
NASA/ESA/CSA
disguise caption
toggle caption
NASA/ESA/CSA

The well-known Ring Nebula is seen in good new readability, because of a brand new James Webb Area Telescope picture launched by researchers within the JWST Ring Nebula Imaging Challenge. The picture was processed by Roger Wesson, based on Western College in Ontario.
NASA/ESA/CSA
Gone are the times when the Ring Nebula regarded type of like a bagel, or a jelly doughnut, an enormous astronomical blob holding the secrets and techniques of a dying star.
The brand new pictures of the well-known Ring Nebula from NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope are mesmerizing, with glowing rings of gasoline and wispy trails emanating from the core. We will see it in additional readability than ever, together with hundreds of clumps that make up its principal ring.
“We all the time knew planetary nebulae had been fairly. What we see now could be spectacular,” Albert Zijlstra, an astrophysics professor on the College of Manchester, mentioned in a statement about the new image.
The picture was launched by a global workforce of researchers, together with specialists from the U.Okay., France, Canada, the U.S. and different international locations. It has given them rather a lot to review.
“The high-resolution pictures not solely showcase the intricate particulars of the nebula’s increasing shell but additionally reveal the interior area across the central white dwarf in beautiful readability,” mentioned Mike Barlow, lead scientist of the JWST Ring Nebula Challenge.
The brand new picture reveals vibrant colours and new element
“Similar to fireworks, completely different chemical components within the nebula emit gentle of particular colours,” as College Faculty London states. That does greater than produce eye-popping scenes in area; it additionally lets astronomers research the chemical make-up and evolution behind the spectacle.
Regardless of its identify, a planetary nebula is definitely the stays of a sun-like star. And the nearer astronomers look, the extra advanced planetary nebulae show to be, with quite a few clumps of gasoline and filaments radiating outward.
“Planetary nebulae had been as soon as regarded as quite simple objects, roughly spherical and with a single star at their centre,” mentioned Roger Wesson, a analysis affiliate at Cardiff University who led the picture evaluation. “Hubble confirmed that they had been rather more sophisticated than that, and with these newest pictures JWST is revealing but extra intricate element in these objects.”
For comparability to the brand new picture, this is a Hubble Area Telescope picture of the Ring Nebula that precipitated a stir 10 years in the past, when it confirmed extra complexity than had been seen earlier than:
The Ring Nebula is seen in a 2013 picture captured by NASA’s Hubble Area Telescope. A brand new picture has proven much more complexity throughout the well-known nebula.
NASA, ESA, C.R. Robert O’Dell, G.J. Ferland, W.J. Henney and M. Peimbert
disguise caption
toggle caption
NASA, ESA, C.R. Robert O’Dell, G.J. Ferland, W.J. Henney and M. Peimbert

The Ring Nebula is seen in a 2013 picture captured by NASA’s Hubble Area Telescope. A brand new picture has proven much more complexity throughout the well-known nebula.
NASA, ESA, C.R. Robert O’Dell, G.J. Ferland, W.J. Henney and M. Peimbert
You may see the Ring Nebula for your self
The Ring Nebula, also called Messier 57, is greater than 2,000 gentle years away, within the Lyra constellation. Found in 1779 by a French astronomer, it would not take a flowery instrument for an newbie astronomer to identify from their again yard.
“I first noticed the Ring Nebula as a child via only a small telescope,” mentioned astrophysicist Jan Cami of Western College in Ontario and the JWST Ring Nebula Imaging Challenge in a statement in regards to the new picture.
“I’d by no means have thought that at some point, I’d be a part of the workforce that might use probably the most highly effective area telescope ever constructed, to have a look at this object,” Cami mentioned.
If you wish to attempt to spot the Ring Nebula by yourself, you are in luck: Summer season is the perfect time to view it, and August is ideal, based on NASA. One solution to find Lyra is by in search of its vivid star, Vega.
The nebula is increasing as its star dies
“We’re witnessing the ultimate chapters of a star’s life, a preview of the solar’s distant future so to talk,” Barlow mentioned, including, “JWST’s observations have opened a brand new window into understanding these awe-inspiring cosmic occasions.”
The spectacle started round 4,000 years in the past, when the Nebula Ring’s central star, which was extra huge than our solar, expelled gases from its outer layers into area. For billions of years, the star had been changing hydrogen to helium — nevertheless it began to run low on gas.
“It then ballooned in dimension, changing into a crimson large,” based on NASA. “Throughout this section, the star shed its outer gaseous layers into area and started to break down as fusion reactions started to die out. A gusher of ultraviolet gentle from the dying star energized the gasoline, making it glow. The outer rings had been fashioned when faster-moving gasoline slammed into slower-moving materials.”
The nebula remains to be increasing — estimated at greater than 43,000 miles an hour, NASA says. It is anticipated to maintain that up for the subsequent 10,000 years or so.

