On Thursday (Aug. 17), astronomers introduced fairly an surprising replace about one in all our photo voltaic system’s ice giants, Neptune: It will seem that the azure world’s clouds have all however disappeared.
Principally, after taking a look at pictures taken of the planet between the years 1994 and 2022, the workforce observed a wierd sample starting in 2019. Across the planet’s mid-latitudes, cloud protection appeared to begin fading. Ultimately, all proof of clouds completely vanished.
“I used to be stunned by how shortly clouds disappeared on Neptune,” Imke de Pater, an emeritus professor of astronomy on the College of California, Berkeley and senior writer of a examine on the findings, said in a statement. “We primarily noticed cloud exercise drop inside a number of months.”
Intrigued by this discovery, de Pater and fellow researchers determined to dig deeper. And, positive sufficient, they got here up with a moderately fascinating rationalization. It is possible, the workforce suggests, that Neptune’s clouds are inextricably linked with the best way our solar behaves throughout its 11-year-long exercise cycle.
What do you imply it is the solar’s fault?
The photo voltaic cycle, in essence, refers back to the means our host star’s magnetic fields change over the course of time — particularly, over 11 years.
Regardless of what it appears to be like like, the solar is not precisely a blazing sizzling chunk of land. Relatively, it is extra of a large, orb-shaped ocean fabricated from charged particles, collectively often called plasma, which suggests its construction can typically movement round and mould itself over time. Along side such motion, the solar’s magnetic fields, instantly related to all these charged particles, get twisted up.
As these fields get tangled, they exert increasingly more “rigidity” on our host star, so to talk, till the yellow glowing ball cannot deal with it anymore. Then, each 11 years, form of as a reset, the solar’s magnetic fields flip, which means the north pole turns into the south pole and vice versa. From there, the saga repeats itself.
Associated: NASA’s New Horizons will examine Uranus from the rear (Neptune, too). Here is how one can assist
Throughout these 11 years, although, different sorts of issues occur as a result of magnetic area alterations, too. As an illustration, magnetic-field knots can result in an elevated quantity and depth of photo voltaic flares, that are extremely highly effective ejections of radiation out into area. These flares can typically be so robust they even intervene with Earth-orbiting satellites. And so they’re usually related to large eruptions of photo voltaic plasma often called coronal mass ejections, which may shower our planet with charged particles that create short-term mini-blips in communication strains.
However most significantly for the workforce’s Neptune evaluation, one phenomenon identified to occur throughout the photo voltaic cycle is that the solar emits a bunch of ultraviolet radiation as its magnetic fields transition. Contemplating how completely large the solar is, that radiation form of “floods” the remainder of the photo voltaic system, because the researchers put it.
And naturally, it is easy to consider that this entire scenario would possibly have an effect on a planet or two — together with Neptune, although the distant, windy planet sits some 2.8 billion miles (4.5 billion kilometers) from our beloved star.
The place does this go away Neptune?
To dissect the place Neptune’s clouds have gone, the workforce gathered 30 years of beautiful pictures of the planet taken by highly effective observatories, together with NASA’s Hubble Area Telescope and the W. M. Keck Observatory positioned in Hawaii.
What they discovered was that there appeared to be a transparent correlation between the variety of clouds on Neptune and the purpose at which our solar’s photo voltaic cycle discovered itself. Extra particularly, roughly two years after the cycle’s peak — aka, the primary occasion of magnetic area flipping — Neptune exhibited some strong cloud protection. It was solely after that peak when the clouds appeared to fade away above the planet’s hydrogen, helium and methane environment. (That methane content material is what makes Neptune look so very blue).
Probably, this implies the solar’s UV radiation — strongest at photo voltaic peak — could also be fostering a photochemical response, sparked by the absorption of vitality within the type of gentle, to provide Neptune’s cloudy cap.
And possibly that response takes one thing like, say, two years to take impact? This may clarify why, two years post-solar peak, the workforce witnessed Neptunian clouds galore.
“These exceptional information give us the strongest proof but that Neptune’s cloud cowl correlates with the solar’s cycle,” de Pater mentioned.
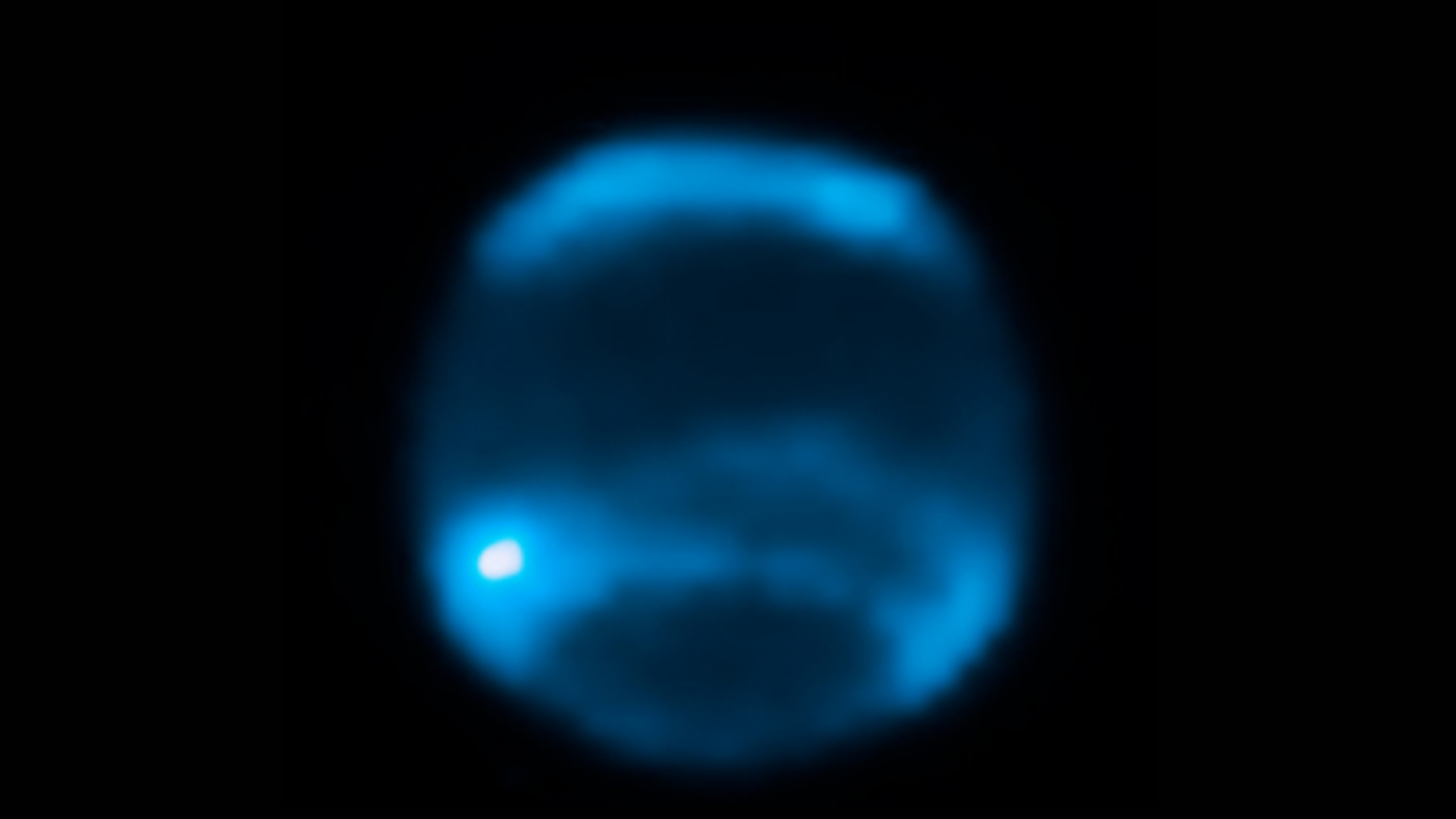
Moreover, the workforce noticed that the extra clouds there have been on this frozen blue world, the brighter it appeared to be, as a result of there was extra daylight reflecting off these clouds.
“Potential correlations of variations in Neptune’s brightness with altering seasons and the photo voltaic exercise cycle have been explored, however to date no single trigger has been recognized,” the examine authors wrote of their paper. “Whereas seasonal results are almost definitely necessary for the sluggish gradual modifications, secular variations in brightness should have a special origin.”
To get into a number of particulars, these outcomes are all of the consequence of taking a look at 2.5 cycles of cloud exercise recorded over the three-decade-long interval of Neptune observations the workforce laid out. And through this time, when it comes to that brightness discovering, the researchers say that the planet’s “reflectivity” elevated in 2002, dimmed in 2007, grew to become shiny once more in 2015, then darkened in 2020 — when the clouds appeared to have fully disappeared.
“Even now, 4 years later, the latest pictures we took this previous June nonetheless present the clouds have not returned to their former ranges,” Erandi Chavez, a graduate pupil on the Middle for Astrophysics, Harvard-Smithsonian and examine lead, mentioned within the statement. “That is extraordinarily thrilling and surprising, particularly since Neptune’s earlier interval of low cloud exercise was not practically as dramatic and extended.”
It is really fairly hanging that each one of those modifications are clearly seen within the pictures supplied by the workforce, additional underlining the significance of sustaining observatories resembling Keck and Hubble. “It’s fascinating to have the ability to use telescopes on Earth to review the local weather of a world greater than 2.5 billion miles away from us,” Carlos Alvarez, an astronomer at Keck Observatory and co-author of the examine, mentioned within the assertion.
Sooner or later, Alvarez and colleagues will proceed to observe Neptune’s cloud exercise to see when these cirrus-shaped options are on the return. Actually, over the previous couple of years, as photo voltaic UV rays have elevated a bit, they have been seeing some cloud resurgence already.
“We have now seen extra clouds in the latest Keck pictures that have been taken throughout the identical time NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope noticed the planet,” de Pater mentioned. “These clouds have been particularly seen at northern latitudes and at excessive altitudes, as anticipated from the noticed improve within the photo voltaic UV flux over the previous roughly two years.”
Don’t be concerned, Neptune: Your clouds shall return in due time.
A paper on these findings is available within the November concern of the journal Icarus.

