
“T-30 seconds…”
The phrases of the launch commentator on the morning of 12 August 1993 have been calm and measured, as all eyes targeted upon shuttle Discovery as she entered the ultimate portion of the countdown to fly STS-51. The mission—a nine-day flight to deploy a NASA superior communications satellite tv for pc and launch and retrieve an ultraviolet telescope on a Shuttle Pallet Satellite tv for pc (SPAS), in addition to carry out a spacewalk—had already been postponed twice, with the astronauts aboard the car.
Poised to fly from historic Pad 39B at Florida’s Kennedy House Middle (KSC), it was hoped that at present could be third time fortunate for Commander Frank Culbertson, Pilot Invoice Readdy and Mission Specialists Jim Newman, Dan Bursch and Carl Walz. However the gremlins of ill-fortune nonetheless had yet one more card to play.
Thus far, every little thing had gone effectively. The 5 males had closed and locked their visors and their eyes have been targeted intently on their devices.
At T-5 minutes, Readdy switched on Discovery’s Auxiliary Energy Items (APUs), bringing life, muscle, and management to the hydraulic programs. The clock continued counting. At T-31 seconds, command of the countdown and all car crucial capabilities have been handed off to the shuttle’s on-board computer systems.

“T-10, 9, eight, seven…Go for Fundamental Engine Begin…”
Contained in the cabin, the astronauts felt the immense vibration as turbopumps awoke, liquid oxygen and hydrogen flooded into the combustion chambers of Discovery’s principal engines, they usually roared to life…and, all of sudden, mechanically shut down. The roar was changed by an ethereal silence, then the blaring of the grasp alarm.
“We now have a Fundamental Engine Cutoff. Safing in work…”

The communications loop from the Launch Management Middle (LCC) offered a flurry of messages, verifying that the engines have been in post-shutdown standby and requesting Readdy to close down the three APUs. No hearth detectors on Pad 39B had tripped in the course of the incident, which might later be traced to a defective fuel-flow sensor within the No. 2 engine.
The engine had posted a “main element failure,” brought on by the sensor glitch, about 0.6 seconds after ignition. “This situation,” famous NASA’s official STS-51 Mission Report, “brought on a miscompare which violated the Launch Commit Standards…On account of the failure, the engines have been shut down and safing actions have been initiated.”
Shortly thereafter, the 5 upset astronauts disembarked from Discovery. The principle engines have been changed and one other launch try was provisionally scheduled for 10 September, however this was itself slipped by two days, on account of the failure on 21 August of NASA’s Mars Observer, shortly earlier than its arrival on the Pink Planet.

Throughout the investigation into the Mars Observer loss, it was revealed that the spacecraft’s Switch Orbit Stage (TOS)—a near-identical booster to that of STS-51’s main payload, the $363 million Superior Communications Expertise Satellite tv for pc (ACTS)—exhibited a transistor failure. Throughout the further two days’ delay, engineers and managers verified there was no commonality between the Mars Observer fault and ACTS.
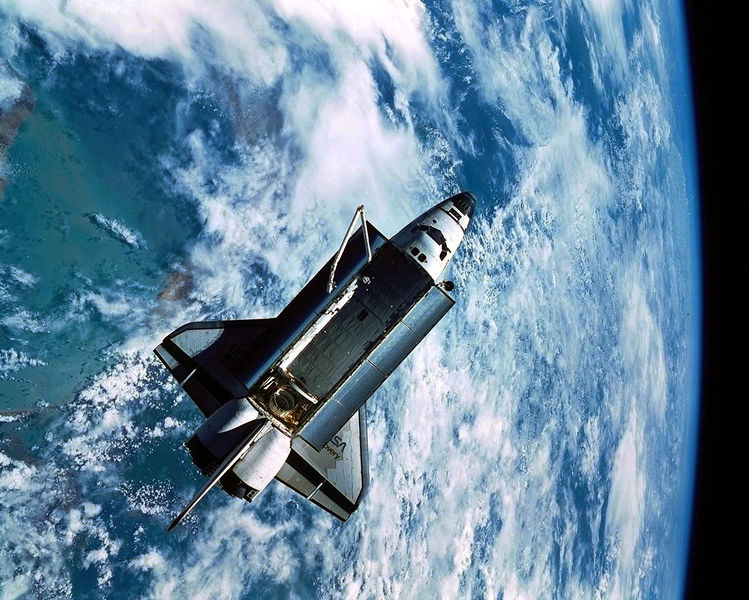
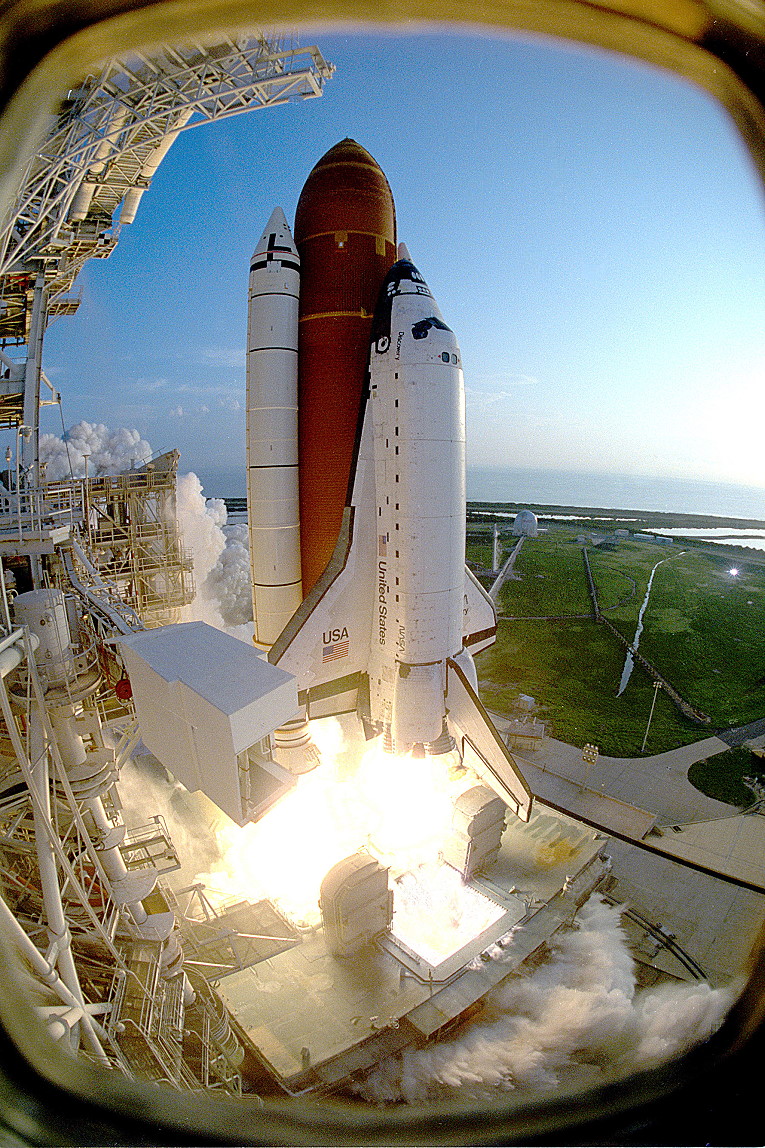
Liftoff of the long-delayed mission lastly befell at 7:45 a.m. EDT on the twelfth, and a nominal ascent positioned Discovery into the meant orbit. Years later, Newman recalled his first expertise of flying in house.
“Once we first acquired to orbit, it was exhilarating,” he informed a NASA interviewer. “I can bear in mind getting out of my seat and going to the home windows within the aft flight deck. The orbiter was upside-down, in order that we have been capable of look and see the Earth, ‘beneath’ us. For those who’ve ever seen the IMAX films, they nearly seize all of it, however to be floating—to be seeing the Earth with my very own eyes—was actually spectacular!”

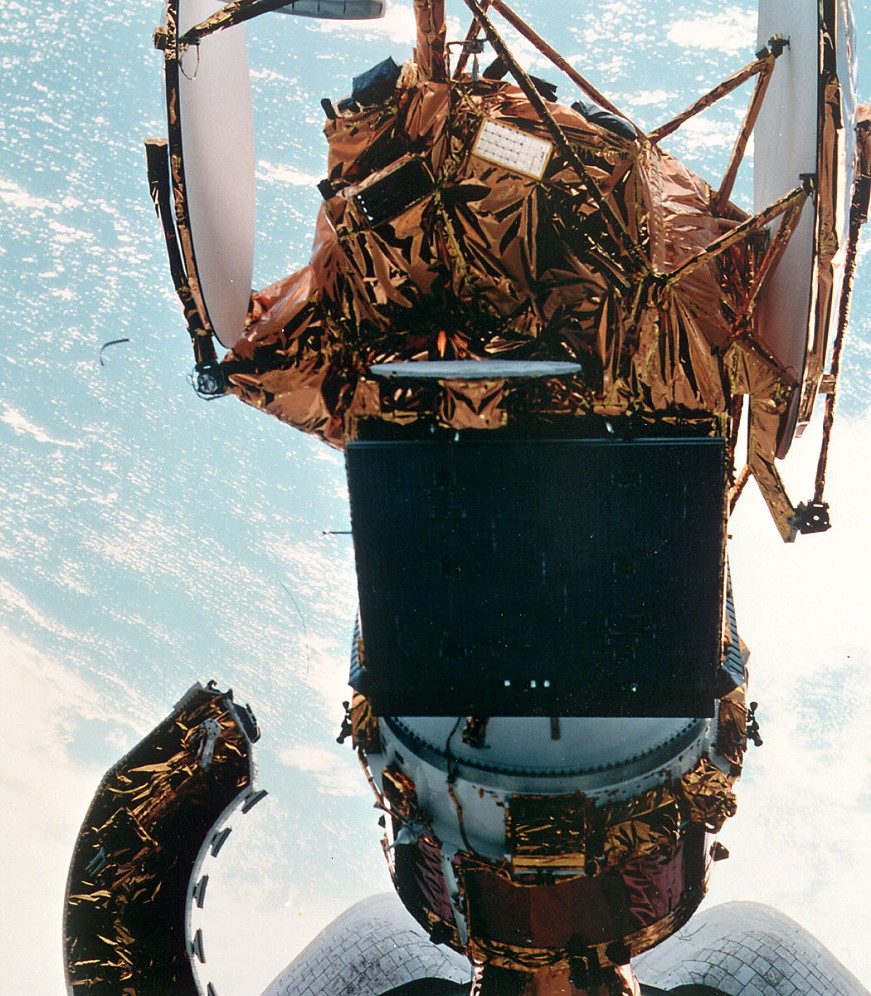
Inside two hours, the payload bay doorways have been open, exposing STS-51’s twin-satellite cargo. On the rear finish of the bay, the ACTS-TOS mixture represented some of the superior communications satellites ever inserted into orbit.
ACTS’ objective was to function a testbed for the event of high-risk superior communications satellite tv for pc applied sciences, using subtle antenna beams and on-board switching and processing programs and bringing collectively authorities, academia, and business. Particularly, the satellite tv for pc operated throughout three channels inside the 30/20 GHz Ka-band, which boasted 2.5 GHz of accessible spectrum—some 5 instances that out there at lower-frequency bands—and really high-gain, multiple-hopping beam antennas which permitted smaller-aperture Earth stations.
Connected to the bottom of ACTS was the TOS booster, making its second flight after Mars Observer and its first and solely flight aboard the shuttle. On STS-51, the TOS was tasked with delivering the payload into an elliptical geosynchronous switch orbit.

In readiness for the discharge of the payload, Discovery’s aft flight deck was a hive of exercise, with deployment anticipated eight hours after launch, on the sixth orbit. The astronauts checked out the TOS’ crucial programs and unlatched and rotated the higher ahead cradle into its “open” configuration, after which all the payload was elevated to an angle of 42 levels.
Nonetheless, deployment was postponed by one other orbit, when S-band forward-link communications with Mission Management have been misplaced. Flight controllers might obtain telemetry and voice communications from Discovery, however not vice-versa.
The astronauts adopted their malfunction protocols, waved off the deliberate deployment, and altered the S-band to a decrease frequency. This restored communications after 45 minutes.

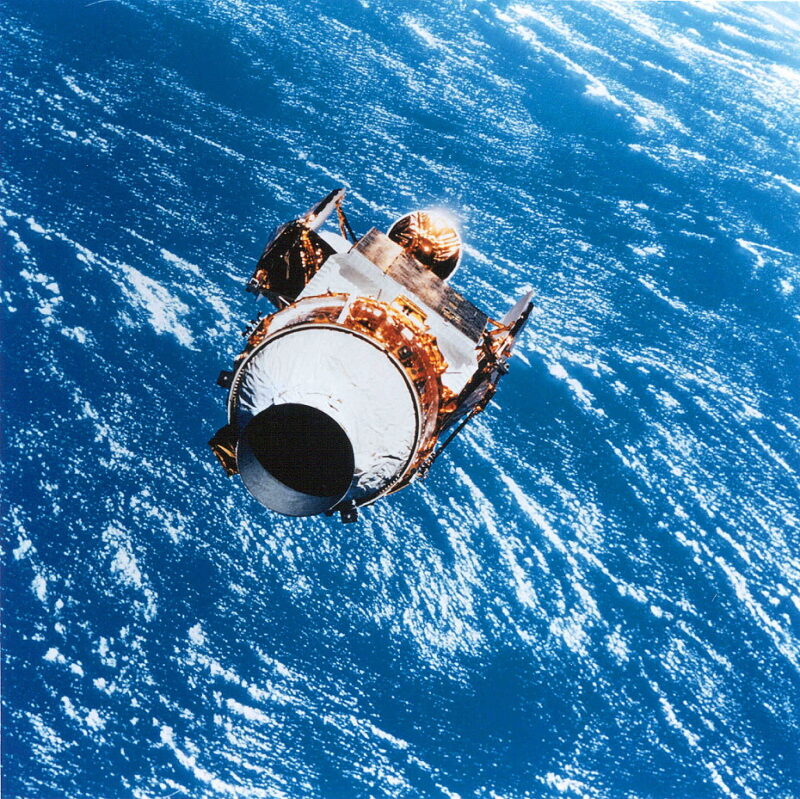
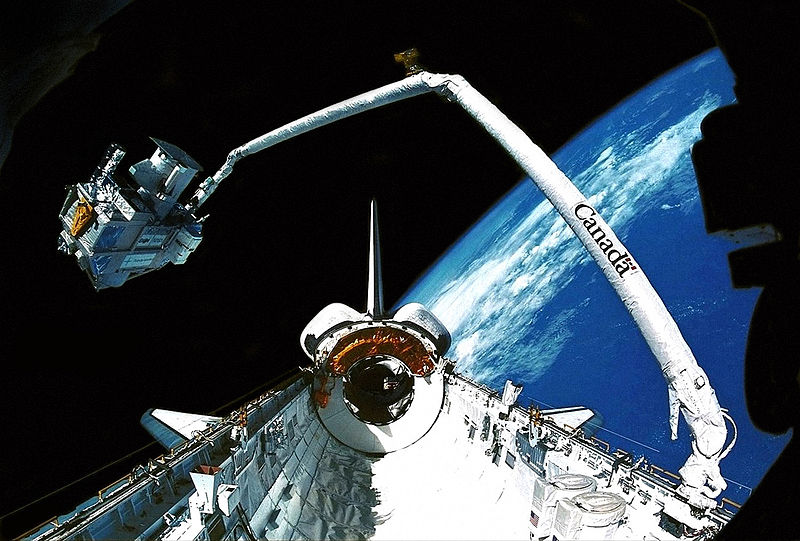
Deployment lastly befell at 5:13 p.m. EDT, about 9.5 hours into the mission. Beneath the path of Walz and Newman, a “Tremendous*Zip” separation mechanism was fired and comes on the aft cradle of the TOS pushed the payload away from the shuttle.
It later grew to become clear from video footage that in depth harm had been brought on to the increasing tube meeting and doublers on the Tremendous*Zip ring. Particles included sharp-edged steel and different non-metallic supplies, and effectively over half of the increasing tube meeting was recorded as being “not restrained to the airborne help gear.”
Investigations revealed that the first and backup separation “cords” of the Tremendous*Zip ring have been fired concurrently and, regardless of concern about potential harm to the orbiter, it was decided that the payload bay liners and thermal blankets might maintain impacts from the increasing tube meeting fragments in the event that they got here free throughout re-entry. In mid-October 1993, an investigative board was established by Jeremiah Pearson, NASA’s affiliate administrator for house flight, to determine the reason for the Tremendous*Zip incident.

Pearson’s board discovered a complete of 36 particles hits in Discovery’s mid-body and aft bulkhead areas, leading to tears, gouges, scratches, and the deposition of residue on a number of surfaces. One space of penetration handed by the aft bulkhead itself. “Not one of the particles hits had any impact in the course of the flight,” famous NASA’s post-flight abstract, “and all harm websites will likely be repaired throughout turnaround operations.”
With the deployment of ACTS behind them, the STS-51 astronauts pressed on with the rest of their mission, which, though scheduled for 9 days, was anticipated to be prolonged to a “extremely fascinating” 10 days. The crew’s second main payload was the German-built Shuttle Pallet Satellite tv for pc, which had flown on two earlier missions, however which was being carried for the primary time in its new “ASTRO-SPAS” configuration.
Not like its first-generation predecessor, ASTRO-SPAS had the potential to stay in autonomous free-flight for as much as ten days. Energy for the satellite tv for pc and its payloads got here from a brand new lithium-sulphate battery pack and exact attitude-control was offered by a three-axis-stabilised cold-gas system, a star tracker, and a space-borne global-positioning system (GPS) receiver.
The satellite tv for pc’s exact attitude-control capabilities enabled it to help delicate astronomical and Earth-observation sensors, with a number of missions deliberate. Two of those would carry a set of infrared telescopes and spectrometers to look at the higher ambiance, one was scheduled (however by no means flown) to reveal superior automated rendezvous and seize applied sciences in help of House Station Freedom, and two others—together with the ASTRO-SPAS aboard STS-51—carried the Orbiting and Retrievable Far and Excessive Ultraviolet Spectrometer (ORFEUS).
This instrument, with a big telescope, was designed to analyze very popular and really chilly matter within the universe, mixed with an Interstellar Medium Absorption Profile Spectrograph (IMAPS). Additionally affixed to the ASTRO-SPAS framework was a floor results pattern monitor to judge a number of future telescope materials samples and a distant IMAX digicam.
Because the mission progressed, not solely would the STS-51 astronauts efficiently deploy and retrieve ORFEUS, however they might additionally help an formidable spacewalk, throughout which Walz and Newman supported preparations for the daunting restore of the Hubble House Telescope (HST). In so doing, Frank Culbertson’s crew established their mission as one which demonstrated just about the entire shuttle’s myriad capabilities. And it demonstrated them in type.
The second a part of this text will seem tomorrow.

