By analyzing the information from the WALLABY pre-pilot survey, astronomers from the College of Western Australia and elsewhere, have inspected 78 candidate ultra-diffuse galaxies within the Eridanus supergroup. The examine was detailed in a paper revealed September 21 on the pre-print server arXiv.
Extremely-diffuse galaxies (UDGs) are extremely-low-density galaxies. The biggest UDGs have sizes just like the Milky Method, however have solely about 1% as many stars as our dwelling galaxy. The thriller of UDGs continues to be baffling scientists as they attempt to clarify why these faint however massive galaxies will not be ripped aside by the tidal discipline of their host clusters.
Widefield ASKAP L-band Legacy All-sky Blind surveY (WALLABY) is a next-generation survey of impartial hydrogen (H I) within the native universe, working on the Australian Sq. Kilometer Array Pathfinder (ASKAP). To date, it has accomplished pilot observations of the Hydra, Norma, and NGC 4636 fields. WALLABY early science research have been in a position to get better many gas-rich low-mass dwarf galaxies.
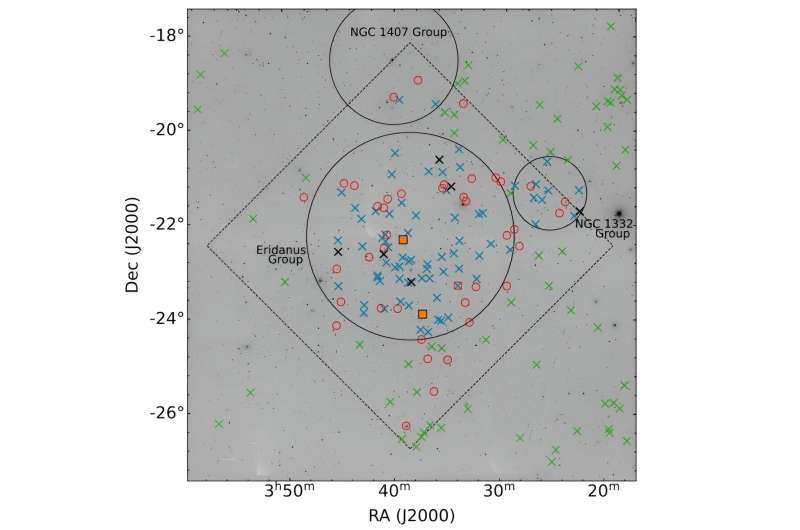
Not too long ago, a crew of astronomers led by Bi-Qing For, has analyzed the pre-pilot information from WALLABY to seek for impartial hydrogen in UDG candidates discovered within the Systematically Measuring Extremely-diffuse Galaxies survey (SMUDGes). They investigated candidate UDGs within the discipline of the Eridanus supergroup (positioned about 65 million gentle years away), which comprises a gaggle of galaxy teams that will ultimately merge to kind a cluster.
“On this paper, we current a pilot examine of H I content material of optically recognized UDG candidates within the WALLABY pre-pilot Eridanus discipline and focus on implications for his or her formation mechanisms,” the researchers defined.
For’s crew investigated the properties and derived the bodily parameters of 78 UDG candidates from the SMUDGes catalog. They discovered that six of them are putative UDGs, whereas the remainder are low-surface-brightness (LSB) dwarf galaxies.
In keeping with the examine, a lot of the galaxies within the investigated pattern have efficient radii smaller than 4,900 gentle years. They’re additionally typically low-mass, with lots lower than 100 million photo voltaic lots, and are largely purple in shade.
The astronomers famous that impartial hydrogen has been detected in solely one of many studied galaxies—in a LSB dwarf designated WALLABY J033408−232125. Due to this fact, they anticipate about 22 impartial hydrogen detections because the decrease restrict for the total WALLABY survey, noting that the detection fee must be greater within the remoted and free group environments.
As a part of the examine, the authors of the paper additionally investigated if tidal or ram-pressure stripping is a attainable formation mechanism for UDGs within the Eridanus supergroup.
“We discover a putative UDG (SMDG 0345097−223826) that might have been fashioned by way of tidal heating/interplay as it’s positioned on the tail finish of a stellar stream. If that was the case, this putative UDG would probably be a background UDG and wouldn’t be related to the Eridanus group,” the scientists concluded.
Extra data:
B. -Q. For et al, WALLABY Pre-Pilot Survey: Extremely-Diffuse Galaxies within the Eridanus Supergroup, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2309.11799
© 2023 Science X Community
Quotation:
Pre-pilot survey explores dozens of candidate ultra-diffuse galaxies (2023, September 28)
retrieved 28 September 2023
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.

