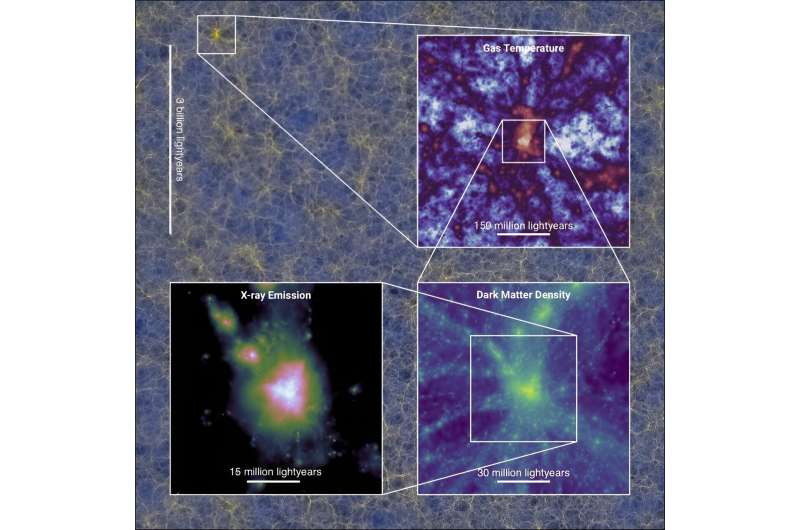
A world workforce of astronomers has carried out what’s believed to be the biggest ever cosmological pc simulation, monitoring not solely darkish but in addition extraordinary matter (corresponding to planets, stars and galaxies), giving us a glimpse into how our universe could have developed.
The FLAMINGO simulations calculate the evolution of all parts of the universe—extraordinary matter, darkish matter, and darkish power—in line with the legal guidelines of physics. Because the simulation progresses, digital galaxies and clusters of galaxies emerge. Three papers have been published in Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society: one describing the strategies, one other presenting the simulations and the third analyzing how nicely the simulations reproduce the large-scale construction of the universe.
Amenities such because the Euclid Area Telescope lately launched by the European Area Company (ESA) and NASA’s JWST gather spectacular quantities of knowledge on galaxies, quasars, and stars. Simulations corresponding to FLAMINGO play a key function within the scientific interpretation of the info by connecting predictions from theories of our universe to the noticed information.
In response to the idea, the properties of our whole universe are set by a couple of numbers referred to as ‘cosmological parameters’ (six of them within the easiest model of the idea). The values of those parameters will be measured very exactly in varied methods.
Certainly one of these strategies depends on the properties of the cosmic microwave background (CMB), a faint background glow left over from the early universe. Nonetheless, these values don’t match these measured by different strategies that depend on the way in which by which the gravitational power of galaxies bends gentle (lensing). These ‘tensions’ might sign the demise of the usual mannequin of cosmology—the chilly darkish matter mannequin.
The pc simulations could possibly reveal the reason for these tensions as a result of they’ll inform scientists about potential biases (systematic errors) within the measurements. If none of those show adequate to elucidate away the tensions, the idea shall be in actual bother.
To this point, the pc simulations used to match to the observations solely monitor chilly darkish matter. “Though the darkish matter dominates gravity, the contribution of extraordinary matter can not be uncared for,” says analysis chief Joop Schaye (Leiden College), “since that contribution may very well be much like the deviations between the fashions and the observations.”
The primary outcomes present that each neutrinos and extraordinary matter are important for making correct predictions, however don’t get rid of the tensions between the totally different cosmological observations.
Simulations that additionally monitor extraordinary, baryonic matter (also referred to as baryonic matter) are rather more difficult and require rather more computing energy. It is because extraordinary matter—which makes up solely sixteen % of all matter within the universe—feels not solely gravity but in addition gasoline strain, which might trigger matter to be blown out of galaxies by lively black holes and supernovae far into intergalactic area.
The energy of those intergalactic winds is determined by explosions within the interstellar medium and may be very tough to foretell. On prime of this, the contribution of neutrinos, subatomic particles of very small however not exactly recognized mass, can also be necessary however their movement has not been simulated to this point.
The astronomers have accomplished a collection of pc simulations monitoring construction formation in darkish matter, extraordinary matter, and neutrinos. Ph.D. pupil Roi Kugel (Leiden College) explains, “The impact of galactic winds was calibrated utilizing machine studying, by evaluating the predictions of plenty of totally different simulations of comparatively small volumes with the noticed lots of galaxies and the distribution of gasoline in clusters of galaxies.”
The researchers simulated the mannequin that finest describes the calibration observations with a supercomputer in several cosmic volumes and at totally different resolutions. As well as, they various the parameters of the mannequin, together with the energy of galactic winds, the mass of neutrinos, and the cosmological parameters in simulations of barely smaller however nonetheless giant volumes.
The most important simulation makes use of 300 billion decision parts (particles with the mass of a small galaxy) in a cubic quantity with edges of ten billion gentle years. That is believed to be the biggest cosmological pc simulation with extraordinary matter ever accomplished. Matthieu Schaller, of Leiden College, mentioned, “To make this simulation potential, we developed a brand new code, SWIFT, which effectively distributes the computational work over 30 thousand CPUs.”
The FLAMINGO simulations open a brand new digital window on the universe that can assist benefit from cosmological observations. As well as, the big quantity of (digital) information creates alternatives to make new theoretical discoveries and to check new information evaluation strategies, together with machine studying.
Utilizing machine studying, astronomers can then make predictions for random digital universes. By evaluating these with large-scale construction observations, they’ll measure the values of cosmological parameters. Furthermore, they’ll measure the corresponding uncertainties by evaluating with observations that constrain the impact of galactic winds.
Extra data:
Joop Schaye et al, The FLAMINGO mission: cosmological hydrodynamical simulations for large-scale construction and galaxy cluster surveys, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2023). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad2419
Roi Kugel et al, FLAMINGO: Calibrating giant cosmological hydrodynamical simulations with machine studying, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2023). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad2540
Ian G McCarthy et al, The FLAMINGO mission: revisiting the S8 pressure and the function of baryonic physics, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2023). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad3107
Quotation:
Astronomers perform largest ever cosmological pc simulation (2023, October 23)
retrieved 24 October 2023
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.

