Credit score: NASA/ESA/JPL-Caltech
The following decade can be a crucial time for the exploration of Mars with the multi-agency Mars Pattern Return (MSR) being the marquee mission. The endeavor has been a long time within the making, however an impartial evaluation of the MSR structure raised some key questions concerning the feasibility and value.
An outline of that report and the way NASA intends to answer it was the main target of the autumn assembly of the Mars Exploration Program Evaluation Group (MEPAG) Steering Committee (SC). Members met nearly on Friday, Oct. 20, to debate the findings.
“Your complete planetary science group sees the worth of pattern return as a method of addressing excessive precedence science within the photo voltaic system,” mentioned Dr. Vicky Hamilton, the present SC chair and planetary geologist on the Southwest Analysis Institute. “And whereas the MSR stands out as the first mission that might show the feasibility of robotically deciding on and returning samples, it’s not the one vacation spot.”
“That mentioned, impartial of the scientific worth of pattern return, there are in fact sensible realities. And I believe that’s actually why we’re right here as we speak (Friday) and that’s as a result of doing pattern return is difficult,” Hamilton added. “There are technological hurdles, it’s going to value extra money than we’re accustomed to spending on the common Mars mission and there could also be adjustments to what we’ve turn out to be used to as our Mars Exploration Program.”
MSR will depend on parts from each NASA and the European House Company (ESA) amongst others. In Could 2023, NASA established its second Unbiased Evaluate Board (IRB-2) to comb via its portion of the plan and create a third-party analysis of the prices, technical saliency and the schedule set forth by NASA to make all of it occur.
Throughout his remarks on Friday, Orlando Figueroa, the IRB-2 chair, famous that this committee was shaped partly as a result of the previous MSR plans evaluated by the IRB-1 (chartered in 2020) had been discovered to be “nearly non-executable.”
“Technical points indicated to us that the early planning dates for a ’27 or ’28 launch had been merely not credible, a close to zero likelihood that we’d have the ability to do it,” Figueroa mentioned. “Shifting to 2030 gives a chance, and appears it’s attainable, however the President’s price range doesn’t fairly help that.”
Figueroa pointed to one of many key challenges for MSR: budgeting. As he referenced, the Biden Administration’s proposal for NASA’s price range in FY24 included about $3.4 billion for Planetary Science, a roughly 5.7 % enhance from FY23 funding ranges.
Of that, MSR could be allotted $949 million, up from $822.3 million the earlier yr. However with the one, two punch of ballooning mission prices and a Congress that would both freeze spending at FY23 ranges or cut back spending additional present value estimates are more likely to pose an enormous problem.
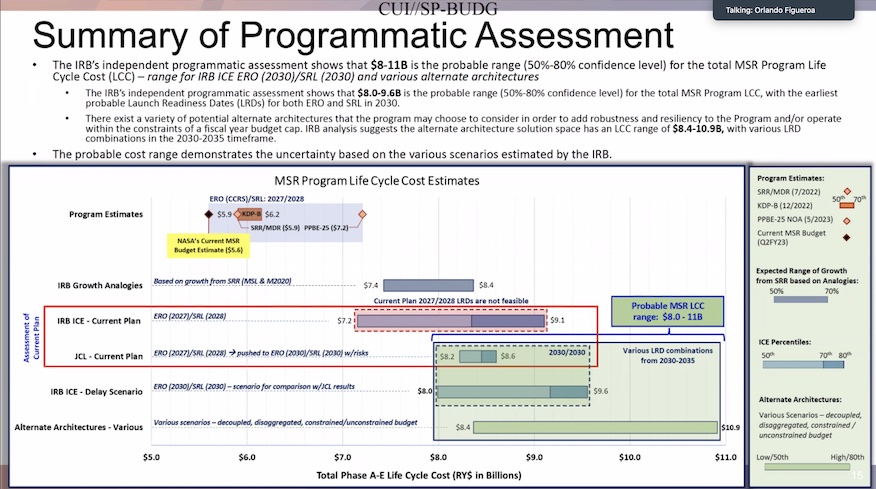
The IRB-2 report famous that as a way to hit a Launch Readiness Date (LRD) in 2030 for each the Pattern Retrieval Lander (SRL) and the Earth Return Orbiter (ERO), they would want to spend between $8-9.6 billion “with funding in extra of $1 billion per yr to be required for 3 or extra years beginning in 2025.”
“This pushes the expertise base of SMD (Science Mission Directorate). [James Webb Space Telescope] is the one massive mission or flagship mission of this sort that required excessive ranges of funding, however by no means exceeded $1 billion,” Figueroa mentioned. “So, this places quite a lot of stress on SMD, until there’s a reduction valve offered someplace and thus, one of many causes for the advice for the company to take a look at what different choices could also be obtainable.”
One of many choices, Figueroa mentioned, could be to place the launches of the SRL and the ERO on monitor for separate dates.
At present, the MSR structure consists of 4 essential buckets:
- Mars 2020/Perseverance
- Pattern assortment and storage
- Pattern Retrieval Lander (SRL) & Mars Ascent Automobile (MAV)
- Retrieve the collected samples and launch them into Mars orbit
- Earth Return Orbiter (ERO) & Seize Containment and Return System (CCRS)
- Seize and maintain onto samples in Mars orbit, endure decontamination and return samples to Earth
- Pattern Receiving Challenge
- Recuperate the samples on Earth and include them for preliminary pattern science and curation
One other suggestion within the report is to cross off the duty for ERO to the European House Company, noting that “This association will enable [Goddard Space Flight Center] to work with ESA and Airbus with out going via [Jet Propulsion Lab].”
“Different architectures, I alluded to them within the programmatic evaluation, they need to be examined with clear tips offered by NASA headquarters for what’s an inexpensive and sensible yearly price range constraint, as soon as once more acknowledging that the value tag of all of the choices that we look at had been within the $8-11 billion vary no matter architectural selections,” Figueroa mentioned.
“It might be nearer to the decrease finish or to the higher finish, relying on these selections, however it behooves the company to take a look at it rigorously, to be able to give you a sensible, technical and programmatic plan,” he added. “In our view, this mission shouldn’t be baselined till these issues are resolved as a result of in any other case, everybody resides underneath unrealistic expectations. That’s what put us on this state of affairs to start with.”

Managing nice expectations
NASA has fairly a little bit of headwind to face relating to charting a path ahead on MSR. Sandra Connelly, the deputy affiliate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, reiterated in her feedback that the mission stays a excessive precedence for NASA and said that in 2024, the company would “decide the price range alignment for the sustainable program.”
“It does should be sustainable fro ma value, schedule and technical perspective and finally, we’re gonna give attention to our partnerships with ESA and we’d like to verify we now have purchase in throughout the board,” Connelly mentioned.
Jeff Gramling, the MSR Program Director, mentioned as they navigate unknown price range constraints for FY24, they’re bringing Steve Tebow from the Utilized Physics Lab (APL) to be the chief engineer on the headquarters degree.
“He brings contemporary eyes and he’s the one which’s main the built-in staff. As we go off and take a look at methods to not solely add resiliency as Orlando spoke about, however how we additionally take a look at whether or not there are methods we are able to cut back value,” Gramling mentioned. “Orlando and his staff, as an example, explicitly mentioned we have to take a look at mission aspect phasing, as an example, to stay inside annual funding constraints. That’s one thing we’ll be .”
Dr. Lori Glaze, the director of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate’s Planetary Science Division, emphasised that having access to pristine samples from Mars is necessary in direction of the purpose of learning the present or former presence of water in addition to trying to find indicators of life.
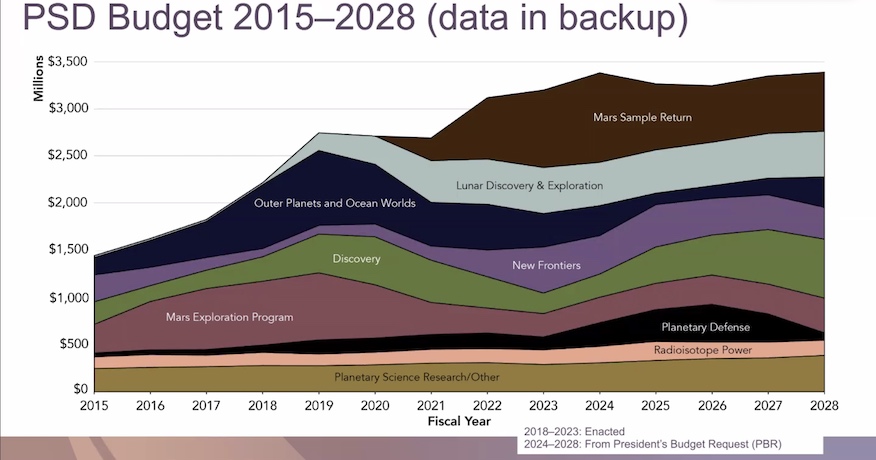
Whereas discussing the funding challenges that PSD faces, Glaze mentioned they might endeavor to stay to the steering of the decadal report and never let the MSR prices exceed 35 % of that workplace’s price range.
“I really discover that steering to be not solely actually sensible, however actually helpful. It’s actually one thing that Jeff Gramling and myself, in collaboration with Nicky Fox and Sandra on the SMD degree, have actually saved in thoughts as we take into consideration, you realize, how are we going to attain and execute Mars Pattern Return in order that it doesn’t affect, in a damaging means, the remainder of the planetary portfolio,” Glaze mentioned.
She added that an necessary job for them is to maintain what she termed “confirmed missions” on monitor. These missions which have handed affirmation critiques embrace Psyche, Europa Clipper, VIPER and the Close to Earth Objects (NEO) Surveyor missions. She mentioned these are ones which have agreements with Congress on each value and schedule.
Glaze mentioned they’re additionally making an attempt to guard the analysis and evaluation applications’ price range as they contemplate cost-cutting efforts. She reiterated a point from August that if the tighter federal budgets come to fruition, the New Frontiers program’s Announcement of Alternative (AO) would slip to no sooner than 2026.
“Discovery and SIMPLEx are additionally unlikely to be supplied so long as these budgets are actually tight. So, unlikely to return out over the following couple of years,” Glaze mentioned.
Connelly mentioned NASA intends to answer the suggestions of the IRB-2 report by the top of March 2024.

