NASA’s Juno spacecraft has noticed Jupiter’s winds penetrating the gasoline big’s ambiance. These findings may finally reveal extra about Jupiter’s mysterious, and fairly turbulent, inside.
What’s extra, the Jovian gravity knowledge collected by Juno confirmed a workforce of worldwide scientists that these atmospheric winds are whipping via the gasoline big planet in a “cylindrical” method, shifting parallel to the planet’s spin axis.
The NASA spacecraft has had a ringside seat to the violent goings-on in Jupiter’s ambiance since 2016, when it arrived on the largest planet in our photo voltaic system. Juno has dutifully made round 55 flybys of Jupiter and continues to make use of a set of science devices to see deep into the world’s ambiance, in addition to via floor clouds to look at the planet’s interior workings.
“As Juno’s journey progresses, we’re reaching scientific outcomes that actually outline a brand new Jupiter and that seemingly are related for all big planets, each inside our photo voltaic system and past,” Juno’s principal investigator, Scott Bolton, said in a statement. “The decision of the newly decided gravity subject is remarkably just like the accuracy we estimated 20 years in the past. It’s nice to see such settlement between our prediction and our outcomes.”
Associated: Proof of alien life could exist within the fractures of icy moons round Jupiter and Saturn
Measuring the winds of Jupiter
As Juno flies previous Jupiter at round 130,000 miles per hour (209,000 kilometers per hour) — which is round 85 occasions the highest pace of a fighter jet — NASA’s Deep House Community antennas monitor the spacecraft’s radio alerts, measuring tiny adjustments in velocity.
These shifts, which will be as small as 0.01 millimeters per second, come up as a result of variations within the planet’s gravity subject. And mapping these gravity variations basically lets researchers look into Jupiter’s ambiance.
This radio science method has already led to a slew of discoveries for Juno, together with the revelation that deep inside Jupiter lies a dilute core that will have been created when the planet suffered a large collision with a spherical physique way back. It has additionally allowed researchers to measure the depths of Jupiter’s varied zones and belts — extending from its cloud tops down round 1,860 miles (3,000 kilometers).
Settling a 20-year-long argument about Jupiter’s winds
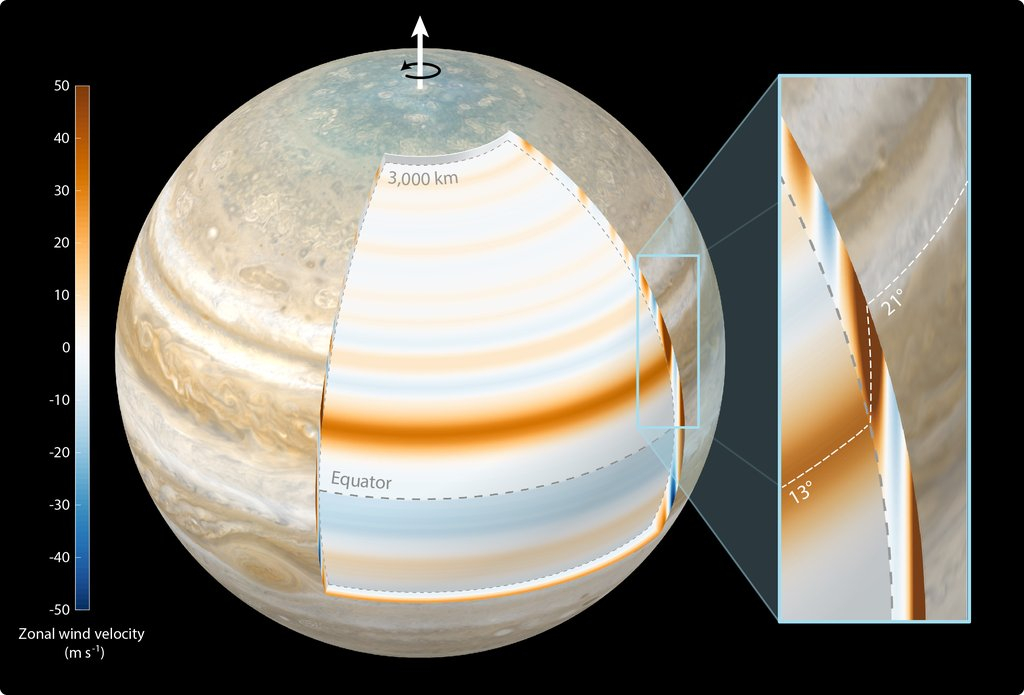
Modeling the cylindrical nature of Jupiter’s atmospheric winds required the workforce behind this analysis to invoke a step past radio measurements. They turned to a mathematical method beforehand used to mannequin gravitational variations and floor elevations of rocky planets like Earth. Making use of this mechanism to Juno’s knowledge delivered a decision of Jupiter’s winds 4 occasions better than what has been achieved beforehand by Jupiter missions Voyager and Galileo.
“We utilized a constraining method developed for sparse knowledge units on terrestrial planets to course of the Juno knowledge,” Ryan Park, Juno scientist and lead of the mission’s gravity science investigation, stated within the assertion. “That is the primary time such a method has been utilized to an outer planet.”
The measurements of Jupiter’s gravity subject aligned with 20-year-old fashions of Jupiter’s highly effective east-to-west zonal flows, which had prompt the winds prolong down from cloud-level zones and belts via the ambiance. As an alternative of extending in all instructions, nevertheless, the brand new measurements assist the concept these zonal flows transfer inward cylindrically, and are oriented alongside the course of Jupiter’s rotational axis.
This merely means with these new outcomes, Juno has settled a debate in regards to the deep atmospheric winds of Jupiter and their construction — a debate than first began within the Seventies.
“All 40 gravity coefficients measured by Juno matched our earlier calculations of what we count on the gravity subject to be if the winds penetrate inward on cylinders,” research lead creator and Juno co-investigator Yohai Kaspi stated. “Once we realized all 40 numbers precisely match our calculations, it felt like profitable the lottery.”
The method can now be utilized to planets exterior the photo voltaic system to construct a high-resolution image of their atmospheres as effectively.
As for Juno, its mission round Jupiter shall proceed, because it conducts a collection of flybys of the Jovian moon Io. On Dec. 30, the spacecraft will make its closest flyby of the volcanic moon, passing simply round 930 miles (1,500 kilometers) above its floor.
The Juno outcomes have been printed earlier this yr within the journal Nature Astronomy.

