
SpaceX efficiently flew its eightieth “single-stick” Falcon 9 mission of 2023 late Friday, because the Hawthorne, Calif.-headquartered group gears up for a dramatic triple-header weekend, with a West Coast mission focused for late Saturday evening and the long-awaited second Built-in Flight Check (IFT-2) of the Starship/Tremendous Heavy stack standing prepared at Boca Chica, Texas, for liftoff early Saturday morning. Laden with 23 Starlink satellites, totaling 40,600 kilos (18,400 kilograms), Friday evening’s flight marked the 54th launch of greater than 1,700 of those flat-packed web communications satellites to date in 2023.

Climate circumstances for final evening’s opening launch try—which benefited from a raft of T-0 alternatives between 11 p.m. EST Friday and a couple of:59 a.m. EST Saturday—proved usually favorable, with a 60-percent chance of acceptability, enhancing to 90 p.c within the occasion of a 24-hour delay to Saturday night. A low that fashioned close to Miami was predicted to deliver robust onshore winds and precipitation by Friday morning, however forecasters on the forty fifth Climate Squadron at Patrick Area Power Base anticipated it to have shifted sufficiently far eastwards by Friday evening to not impression a launch try.
“The first concern for launch day will probably be liftoff winds, with an opportunity of Cumulus Cloud Rule violations as nicely,” famous the forty fifth. “By Saturday, the danger of a climate violation ought to decrease, as winds weaken and the mid and decrease ranges of the ambiance get drier.”

In readiness for launch, the Autonomous Spaceport Drone Ship (ASDS), “Simply Learn the Directions”, departed Port Canaveral final Monday, sure for a restoration place some 390 miles (630 kilometers) offshore within the Atlantic Ocean. Yesterday, the booster for SpaceX’s eightieth Falcon 9 mission of the yr—B1069, a car virtually misplaced on the shut of her maiden voyage, practically two years in the past—was transported out of storied Area Launch Advanced (SLC)-40 at Cape Canaveral Area Power Station, Fla., for her seventh launch of the yr and her eleventh outing in complete.
B1069 entered the fleet in December 2021, delivering the CRS-24 Cargo Dragon on the primary leg of its month-long trek to the Worldwide Area Station (ISS). However she was virtually misplaced in a hair-raising landing on the shut of her maiden voyage, which got here near seeing her miss the deck of the drone store and topple into the ocean.

The incident necessitated substantial repairs—together with a brand-new suite of Merlin 1D+ first-stage engines—earlier than B1069 re-entered service to log three missions within the second half of final yr: emplacing 54 Starlinks to orbit in August, Eutelsat’s Hotbird 13F geostationary communications satellite tv for pc in October and 40 broadband satellites in December for London, England-based OneWeb.
Up to now in 2023, she has now flown seven occasions, lifting six Starlink batches, totaling 232 satellites, to low-Earth orbit, in addition to the dual-stacked SES-18 and SES-19 geostationary communications satellites for Luxembourg-based supplier SES, again in March. Her March flight, which noticed her set a private better of solely 43 days between missions, additionally fashioned a part of a SpaceX in-house report of launching a pair of Falcon 9s inside solely 4 hours and 12 minutes of one another.
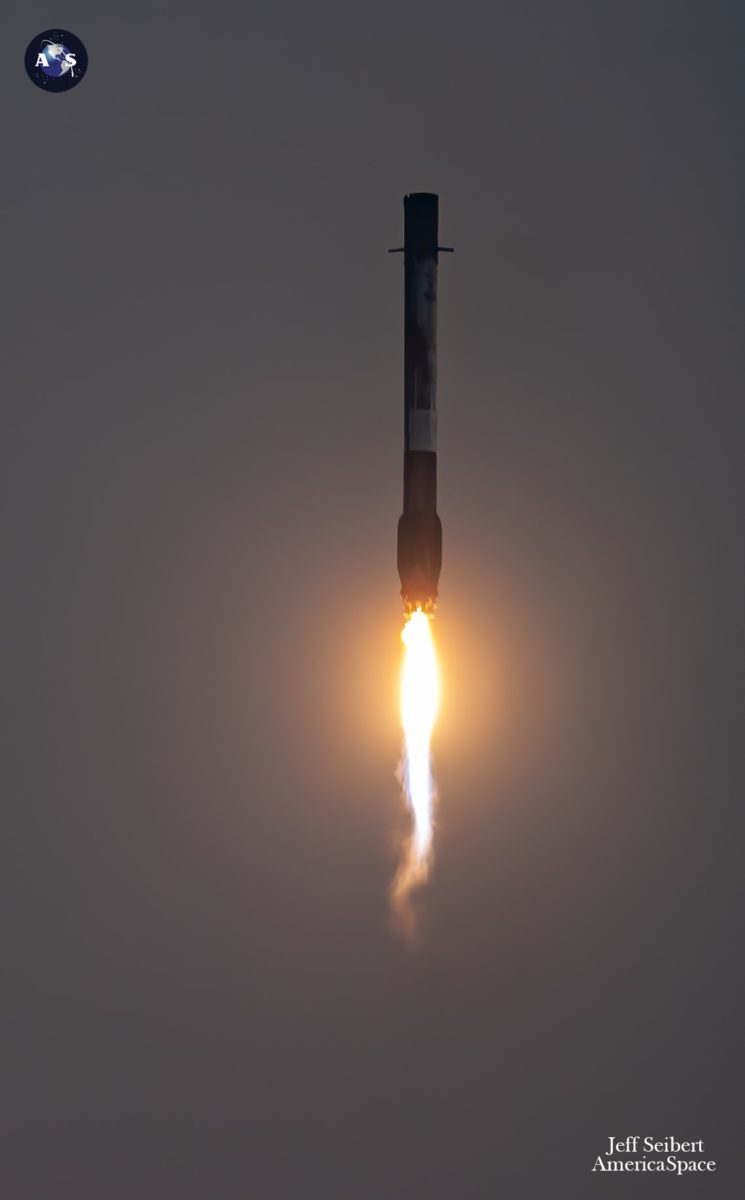

SpaceX groups opted to purpose for a T-0 level later in final evening’s window, inflicting B1069 to truly go airborne at 12:05 a.m. EST, pushing it squarely into the opening minutes of Saturday morning. Powering into the post-midnight darkness, the 230-foot-tall (70-meter) Falcon 9 carried out with attribute perfection, as B1069’s 9 Merlin 1D+ engines burned furiously for two.5 minutes, forward of the separation of the booster and a dramatic return to land on JRTI’s expansive deck.
In the meantime, the one Merlin 1D+ Vacuum engine of the Falcon 9’s second stage executed a normal six-minute “burn” to insert the 23 Starlinks into orbit, deploying the stack at 65 minutes after launch. As a community, Starlink facilitates high-speed and low-latency web provision to over 60 sovereign nations and worldwide markets in North and South America, Europe, Asia, Oceania and Africa. Up to now in November, Europe’s Georgia, Africa’s Benin and Asia’s Maldives have joined the community.
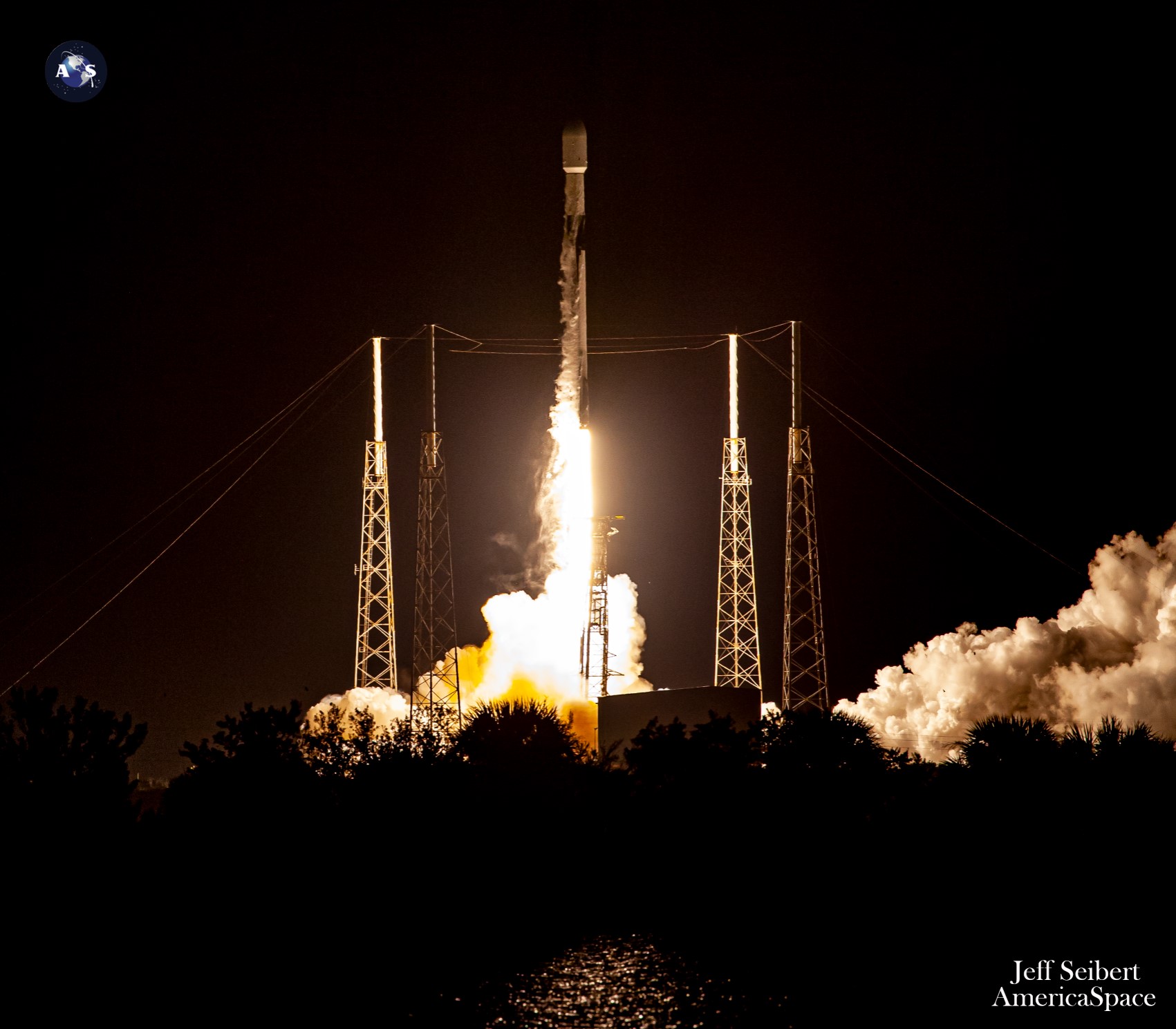

The Starlink “V2 Mini” satellites, first flown in February, boast three to 4 occasions better “usable” bandwidth than earlier Starlink iterations. “V2 Minis embody key applied sciences—similar to extra highly effective phased-array antennas and the usage of E-Band for backhaul—which is able to permit Starlink to supply 4x extra capability per satellite tv for pc than earlier iterations,” SpaceX defined. “Amongst different enhancements, V2 Minis are outfitted with new argon Corridor thrusters for on-orbit maneuvering.”
Florida-based intercity operator Brightline adopted Starlink on its trains earlier in 2023, the primary passenger rail service on the planet to take action. Moreover, El Salvador’s Ministry of Schooling has begun integrating Starlink functionality into its colleges to assist shut the digital divide between city and distant rural communities and 50 Rwandan colleges are actually related by way of Starlink’s high-speed web service.

With final evening’s launch, SpaceX has logged 80 missions utilizing 15 single-stick Falcon 9s, one among which has flown eight occasions. 4 new boosters entered the fleet between January and August, with over 1,700 Starlinks efficiently deployed on 54 missions.
Added to that record, Falcon 9s lofted eight geostationary communications satellites, 4 multi-payload Transporter rideshares, three crewed and uncrewed Dragon flights to the Worldwide Area Station (ISS), two missions of the Tranche 0 Transport and Monitoring Layer (TTL) for the Area Growth Company (SDA) and Europe’s Euclid deep-space observatory. That flotilla of flights noticed SpaceX’s turnaround and reusability statistics bounce incrementally, because the group flew its first eight-launch month in March and its first nine-launch month in August and noticed boosters log record-setting sixteenth, seventeenth and 18th missions.
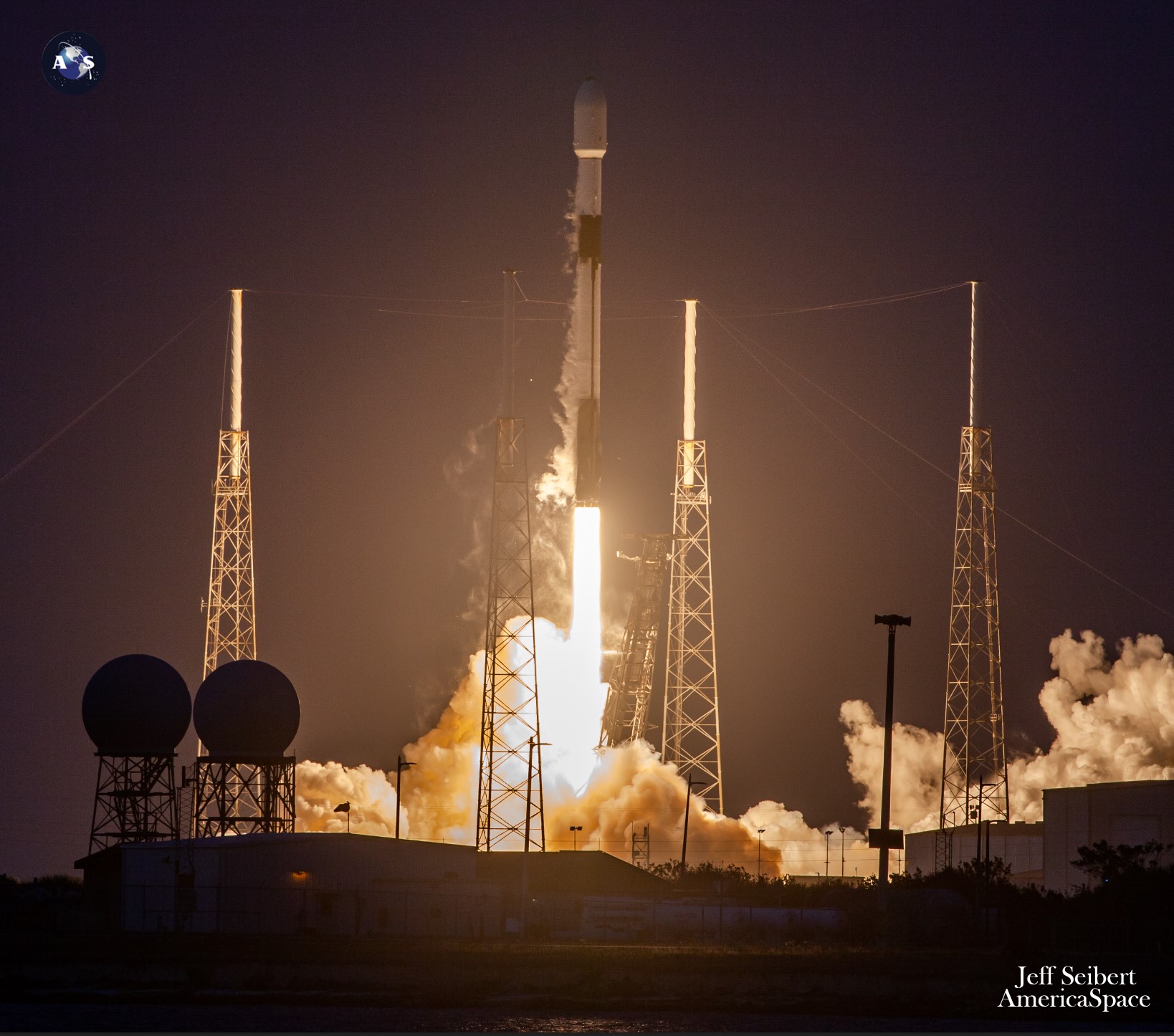

Late Saturday evening, SpaceX goals to fly the veteran B1063 booster from Area Launch Advanced (SLC)-4E at Vandenberg Area Power Base, Calif., laden with one other 23 Starlinks. Liftoff is at the moment focused for 10:55 p.m. PST Saturday (1:55 a.m. EST Sunday), with extra T-0 factors extending till 2:52 a.m. PST (5:52 a.m. EST) Sunday.
Flying its seventh time in 2023 and its fifteenth time throughout a three-year profession, B1063 is a devoted “Vandenberg Falcon”, having flown all however one among its missions from the mountain-ringed West Coast web site. Following tonight’s flight, the booster is concentrating on a touchdown on the “Of Course I Nonetheless Love You” drone ship, located offshore within the Pacific Ocean.
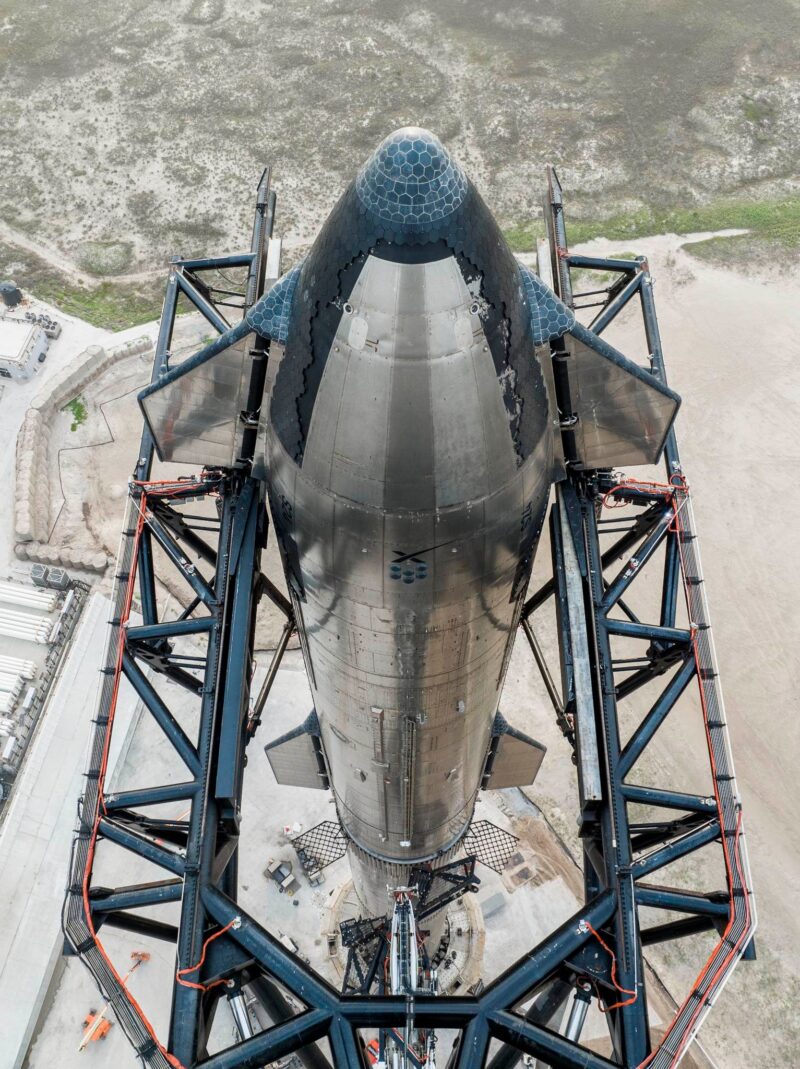

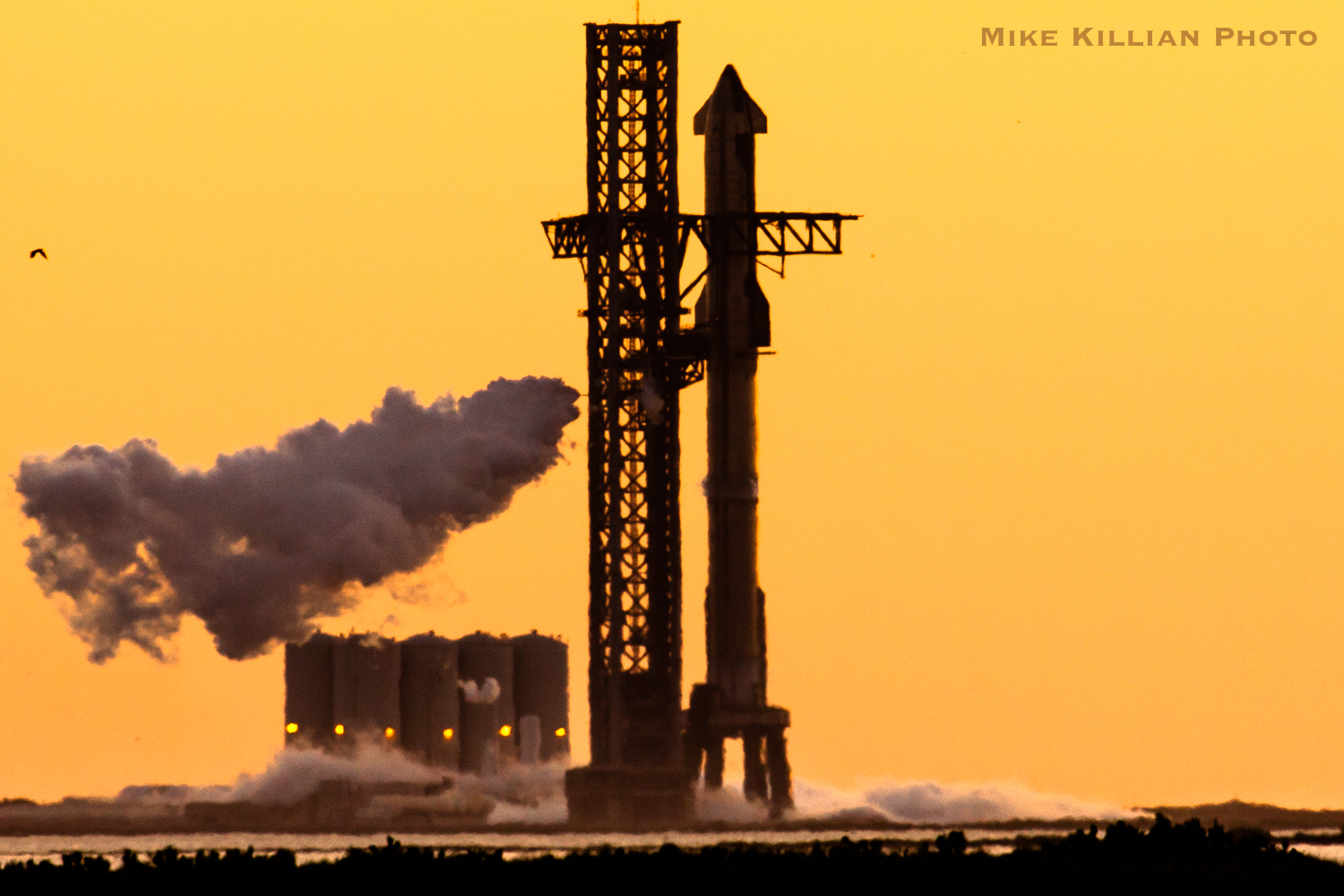
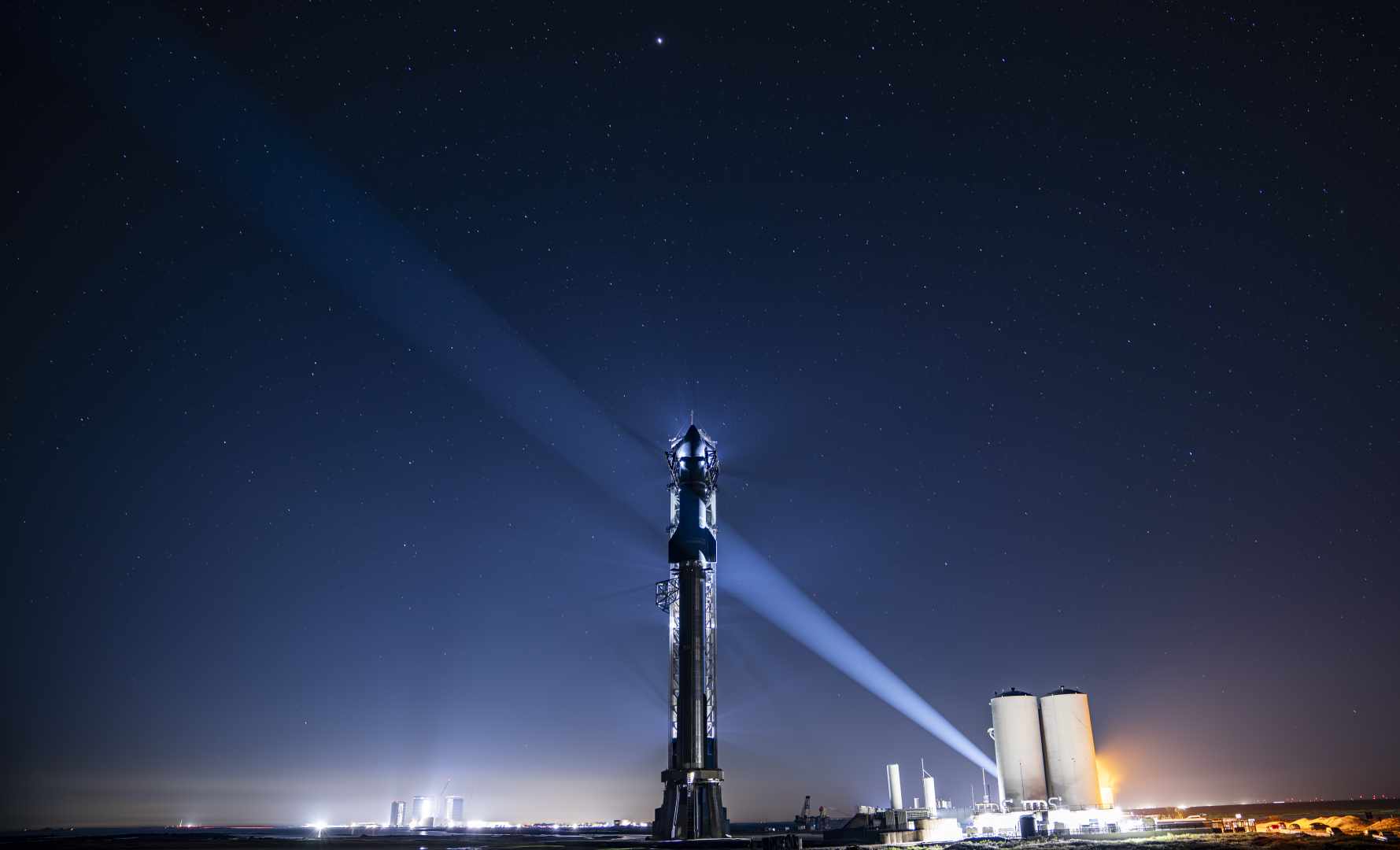
However for all of the drama these two missions have afforded and can afford, the actual spotlight of the weekend is the long-awaited second Built-in Flight Check (IFT-2) of the 394-foot-tall (120-meter) Starship/Tremendous Heavy stack out of Starbase in Boca Chica, Texas. As beforehand outlined by AmericaSpace, liftoff was initially focused throughout a two-hour “window” from 7 a.m. by 9 a.m. CST Friday, with Ship 25 hoisted atop Booster 9 on Thursday, however inside hours the try had been scrubbed, the Starship destacked and launch recycled to a backup alternative on Saturday morning.
“We have to change a grid-fin actuator,” tweeted SpaceX CEO Elon Musk on X. “Launch is postponed to Saturday.”
Late Friday evening, SpaceX reported the stack was “prepared on the launch pad” at Starbase, monitoring a slim 20-minute window, which opens at 7 a.m. CST Saturday.
“That is one other probability to place Starship in a real flight atmosphere, maximizing how a lot we study,” SpaceX tweeted. “Speedy iterative growth is important as we work to construct a totally reusable launch system able to carrying satellites, payloads, crew and cargo to quite a lot of orbits and Earth, lunar and Martian touchdown websites.”
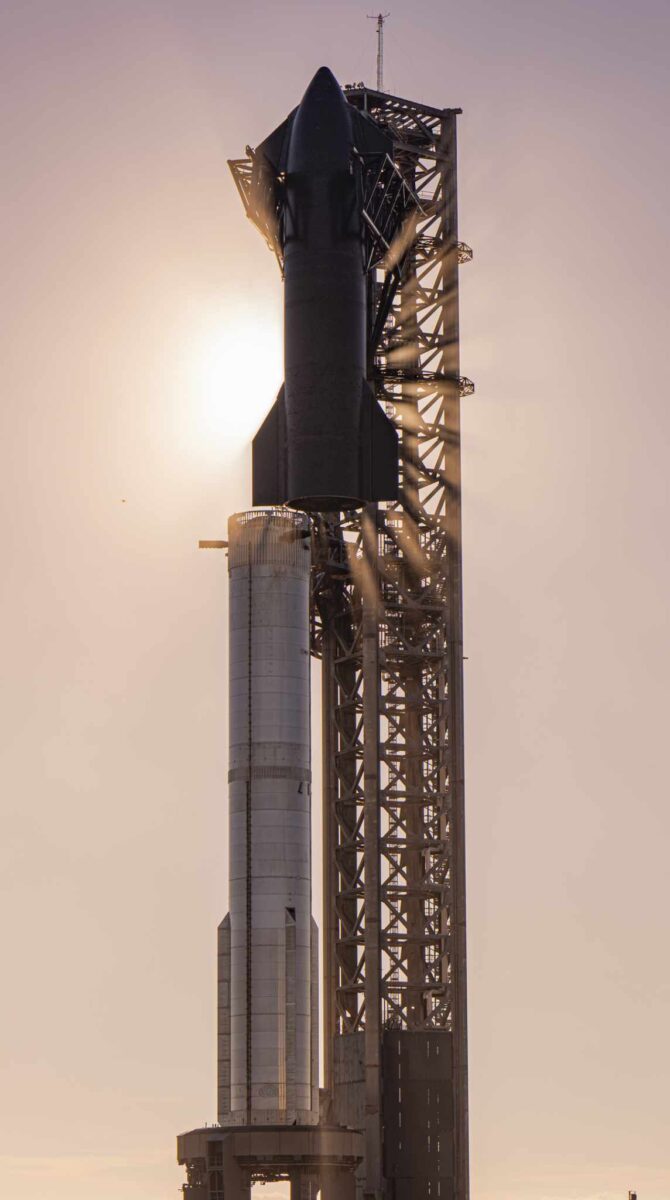

The long-awaited second outing of the 394-foot-tall (120-meter) booster comes after many weeks of hypothesis, with even SpaceX Senior Director of Human Spaceflight Packages Benji Reed remaining non-committal following questions on the post-Launch Readiness Evaluate (LRR) briefing forward of final week’s CRS-29 Cargo Dragon mission to the Worldwide Area Station (ISS). Mr. Reed indicated solely that SpaceX was aiming for a launch within the mid-November timeframe.
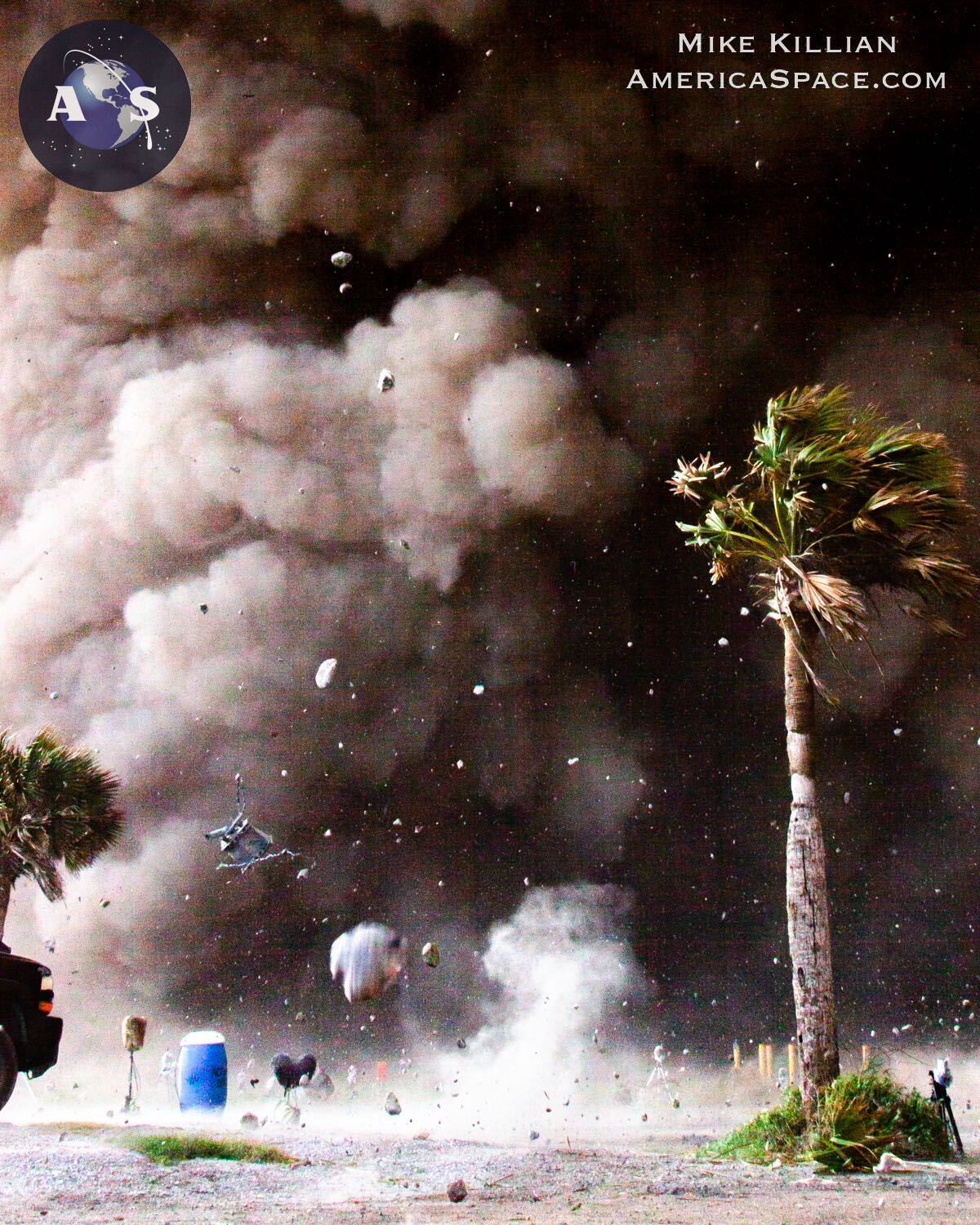
On its preliminary launch in April, the Starship/Tremendous Heavy ascended from Boca Chica underneath 16.7 million kilos (7.5 million kilograms) of thrust from its 33 Raptor engines, the best liftoff impulse of any orbital-class booster in historical past. However after struggling a number of engine failures instantly after liftoff, the behemoth was remotely destroyed at an altitude of about 24 miles (39 kilometers) by the Autonomous Flight Security System (AFSS) and a subsequent Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) investigation into the mishap was anticipated to take a number of months to finish.
In response to SpaceX, “quite a few classes” had been realized from April’s mishap, which—along with the lack of the car at altitude—additionally produced substantial injury to the Boca Chica launch amenities. Efforts have been applied “considerably reinforce” the pad foundations and combine a water-cooled metal flame deflector, along with different upgrades. A brand new digital Thrust Vector Management (TVC) system will function “fewer potential factors of failure” and better power effectivity over conventional hydraulic techniques.
Extra not too long ago, in July the second Starship booster (Booster 9) was transported to the pad for exams, with an expectation that it’s going to loft Ship 25 on a transatmospheric flight carefully mirroring the trajectory envisaged for its unsuccessful April mission. It underwent a profitable Static Hearth Check a number of weeks later and in late October SpaceX groups carried out a single-engine check to reveal Starship’s deorbit burn functionality and loaded your entire car with propellant in a flight-like launch-day rehearsal.

At T-2 hours tomorrow morning, the SpaceX Launch Director will conduct a ballot of the group, forward of authorizing the loading of greater than ten million kilos (4.5 million kilograms) of liquid oxygen and liquid methane into the tanks of the Tremendous Heavy and Starship. Fueling of the booster will begin at T-97 minutes, with that of the Starship anticipated to be underway by T-77 minutes.
Chill-down of the Raptor engines on each levels will happen at T-19 minutes and 40 seconds. Three seconds previous to liftoff, the Tremendous Heavy’s Raptors will ignite, with “Pleasure Assured” at T-0.

The 233-foot-tall (71-meter) Tremendous Heavy will elevate the stack uphill for the opening two minutes and 39 seconds of flight, earlier than the Starship’s personal Raptors ignite in a so-called “Scorching Staging” separation occasion. “Starship and Tremendous Heavy are being upgraded to make use of a separation technique known as scorching staging,” SpaceX tweeted earlier this summer season, “the place Starship’s second-stage engines will ignite to push the ship away from the booster.”
Returning homeward, the discarded Tremendous Heavy will execute a 54-second boostback burn, slowing to transonic speeds at 6.5 minutes after liftoff, then performing an 18-second touchdown burn for a vertical splashdown within the Gulf of Mexico, some 20 miles (32 kilometers) off the Texas Coast, somewhat greater than eight minutes into the mission.
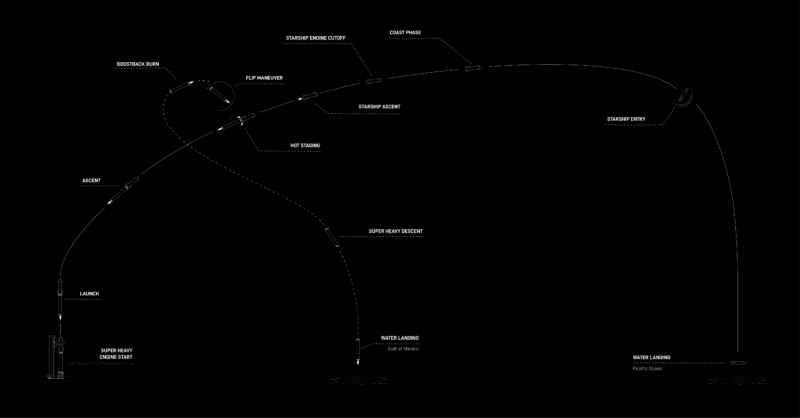
In the meantime, after separation from the booster, the Starship will ignite its Raptor engines for rather less than six minutes, earlier than shutting down and coasting three-quarters of the best way across the planet for the subsequent 68 minutes. Just like the Tremendous Heavy, it’s not meant for restoration on this inaugural check flight and can splash down—for what SpaceX describes hopefully as “an thrilling touchdown”—within the Pacific Ocean, doubtless about 60 miles (100 kilometers) northwest of Kauai in Hawaii.

