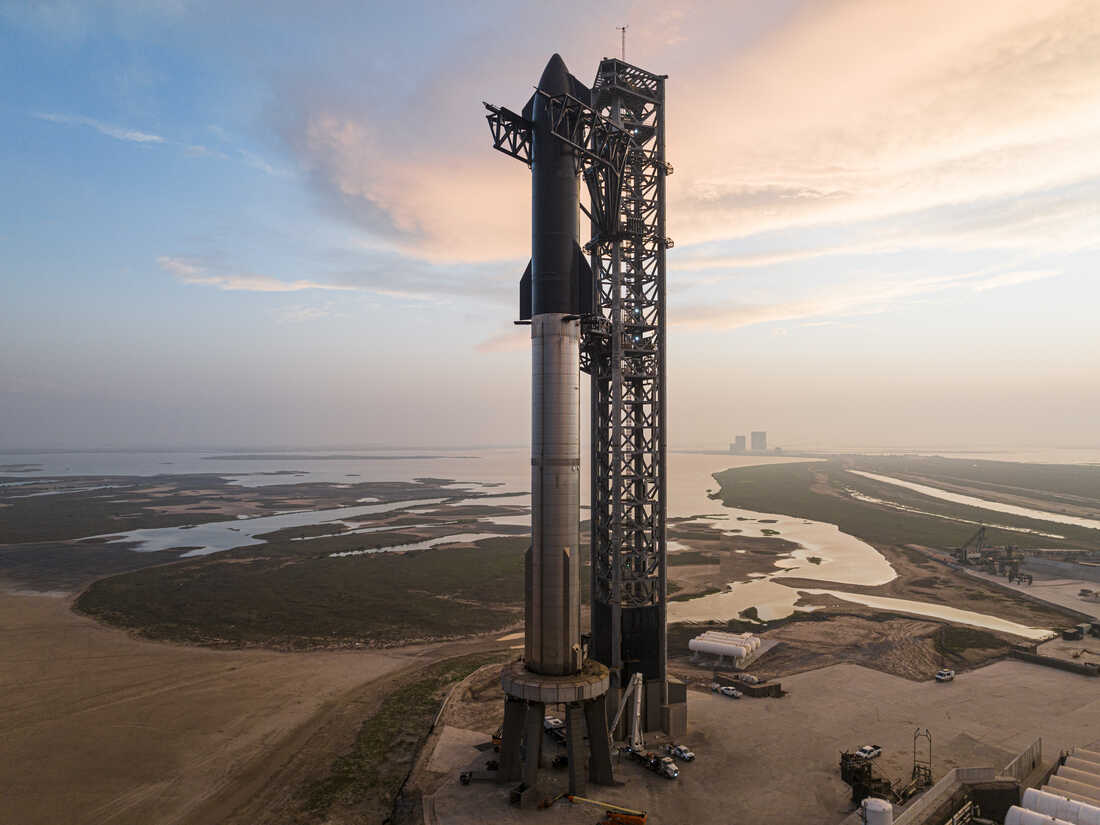

Starship is the biggest rocket ever constructed. Elon Musk hopes it can in the future carry individuals to Mars.
SpaceX
disguise caption
toggle caption
SpaceX
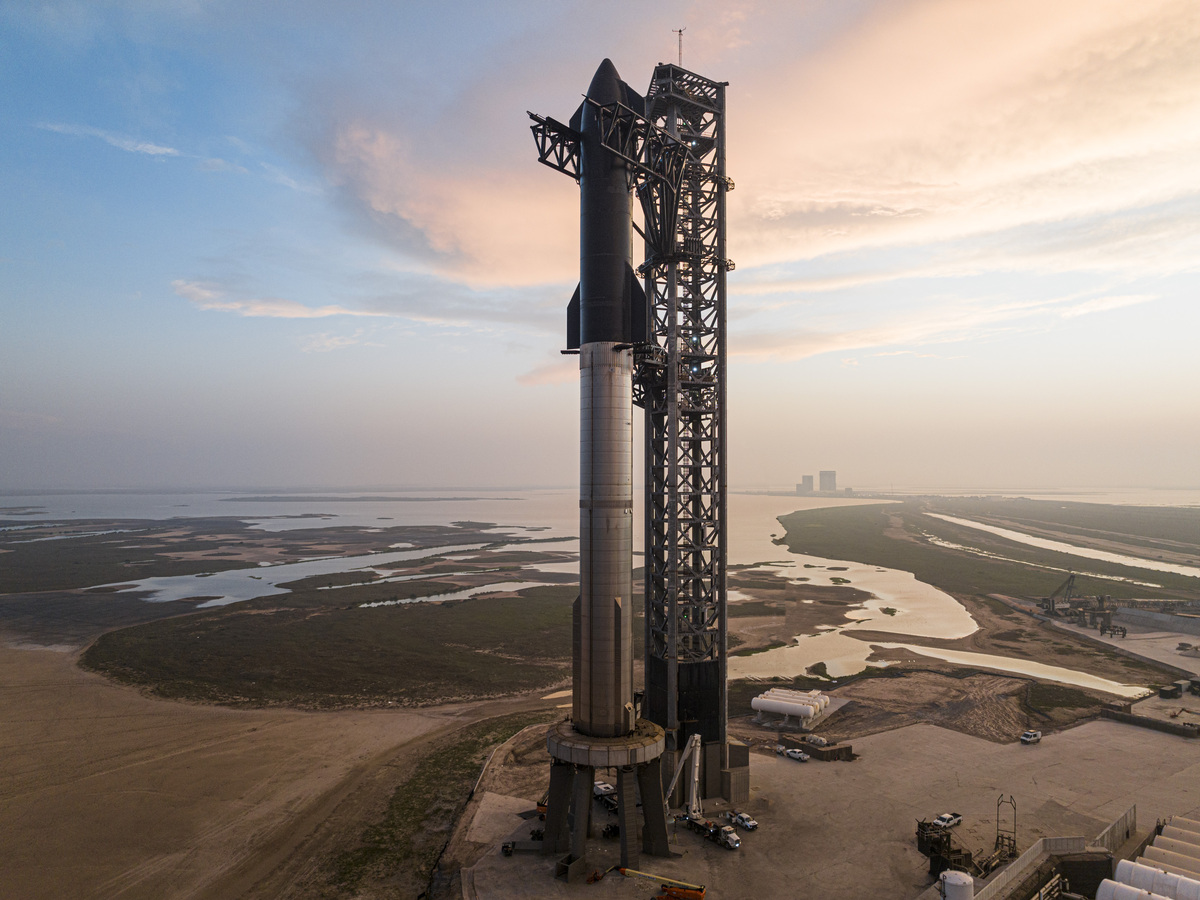

Starship is the biggest rocket ever constructed. Elon Musk hopes it can in the future carry individuals to Mars.
SpaceX
SpaceX is about to make its second try at launching the biggest rocket the world has ever seen. The stainless-steel monster, generally known as Starship, stands almost 400 ft tall. Its large first stage, recognized solely as “Tremendous Heavy,” is powered by 33 Raptor engines that should fireplace in good synchrony to hold Starship into orbit.
SpaceX founder Elon Musk hopes that Starship can in the future develop into an inexpensive, quickly reusable system that may jumpstart human exploration of the moon and Mars.

Right now’s check flight is a small first step. If it really works, Starship will launch from Texas, briefly enter area after which splash down within the Pacific Ocean close to Hawaii. However even that could be a troublesome objective to achieve. This is why.
Starship’s first flight in April didn’t go in response to plan
The primary check flight of any rocket goes to be powerful — and for its April 20 launch try, SpaceX tried to handle expectations. Considerably tongue-in-cheek, the official countdown timeline promised “pleasure assured” after the launch.
The rocket lifted off shortly after 8:30 a.m. native time. Virtually instantly it was clear that a number of the 33 engines within the first stage had failed, and because it climbed into the sky, additional engines flamed out.

Starship’s first launch try resulted in failure. The rocket spun uncontrolled earlier than exploding about 4 minutes after liftoff.
Eric Homosexual/AP
disguise caption
toggle caption
Eric Homosexual/AP

Starship’s first launch try resulted in failure. The rocket spun uncontrolled earlier than exploding about 4 minutes after liftoff.
Eric Homosexual/AP
Earlier than the Starship may separate from its booster, the complete rocket started spinning uncontrolled. It exploded roughly 4 minutes into flight.
Within the aftermath, it emerged that Starship’s flight termination system, which was designed to destroy the car if it went uncontrolled, had didn’t do its job. On high of that, the rocket’s first stage pulverized the concrete launch pad throughout liftoff, sending particulate mud and chunks of particles flying.
The failure of the pad specifically was embarrassing, says Jonathan McDowell, an astronomer on the Middle for Astrophysics, Harvard & Smithsonian. “This monumental rocket principally blew the pad aside and showered concrete over miles of Texas,” he says.
These rocketry goof-ups additionally caught the attention of presidency regulators. The Federal Aviation Administration grounded Starship pending a security and environmental assessment. Earlier this week, the regulator cleared SpaceX for a second strive, partially due to adjustments the corporate made to the design.
This time, SpaceX has made some main upgrades
First, engineers have added extra oomph to Starship’s self-destruct system. They’ve put in bigger explosive expenses that ought to be capable of destroy the beefy rocket, if it strays off track because it did again in April.
The corporate has additionally created a wholly new system for attaching the Starship to its booster rocket. It should enable the spacecraft to make use of its engines to separate from the booster throughout flight, and proceed its journey into orbit. That is assuming it really works: This so-called “scorching staging” technique is new to SpaceX, and is not used fairly often on American rockets.
Tremendous Heavy Booster 9 static fireplace efficiently lit all 33 Raptor engines, with all however two operating for the total length. Congratulations to the SpaceX crew on this thrilling milestone! pic.twitter.com/1hzs768vHg
— SpaceX (@SpaceX) August 25, 2023
Third, the Tremendous Heavy booster rocket getting used on this flight has some appreciable enhancements over the earlier one, the corporate claims. Most significantly, it makes use of {an electrical} mechanism to manage the thrust of its dozens of engines. That ought to make the spacecraft extra sturdy if a number of engines fail on the best way up.
Lastly, there is a massive improve to the launchpad, which acquired blasted within the first flight check. This time, SpaceX has put in a water deluge system that ought to maintain the pad from getting too scorching. Such methods are generally used for different launch pads.

Starship is a giant a part of SpaceX’s enterprise plans
SpaceX is investing closely in Starship. Musk has beforehand mentioned that the corporate has spent $2 billion this 12 months alone in growth.
The corporate has targeted on the mammoth rocket partially as a result of Starship is central to Musk’s dream of colonizing Mars. He hopes {that a} fleet of starships will in the future be capable of put sufficient provides into orbit to hold the primary settlers to the crimson planet.

The rocket can also be a giant a part of SpaceX’s enterprise with NASA. The area company has awarded round $4 billion in contracts to SpaceX in order that it could develop Starship right into a lunar lander. NASA plans on utilizing a model of the rocket for a few of its upcoming Artemis missions to the moon’s floor, which may begin as quickly as 2025.
Lastly, Starship has a vital function in SpaceX’s enterprise a lot nearer to earth. The corporate’s Starlink satellite tv for pc web system is awaiting a significant improve, however SpaceX’s present rockets aren’t large enough to hold the most recent, third era of Starlink satellites into orbit, in response to Chris Quilty, the president of Quilty Area, a non-public area analytics agency.
“Not solely is the event of Starship burning a ton of money, nevertheless it’s additionally holding again their means to launch these gen-3 satellites,” Quilty says.
Whether or not it really works is anybody’s guess
On this check flight, SpaceX hopes to take off from their launch website in Brownsville, Texas. From there the Starship will shoot out over the Gulf of Mexico, separate from its heavy booster and enter what McDowell describes as a “marginal orbit” that may ship it all over the world. It should then splash down off the coast of Hawaii.
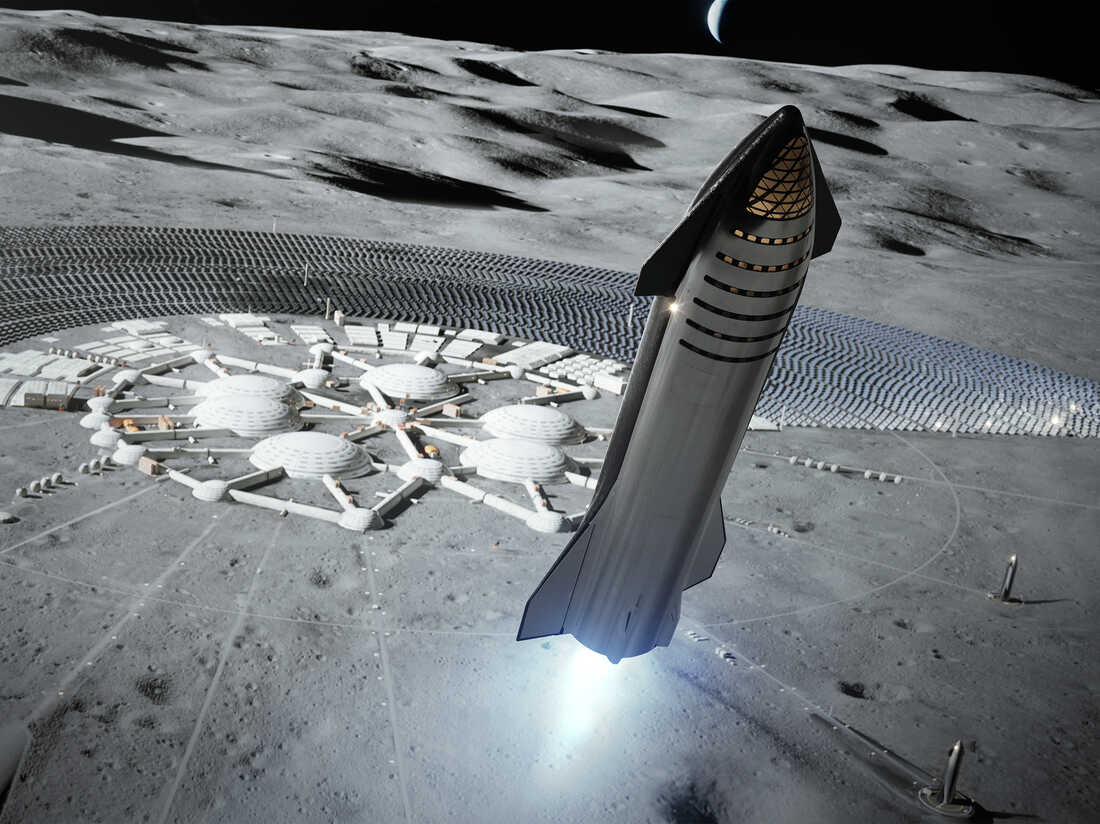
NASA is paying SpaceX billions to develop Starship right into a lunar touchdown craft, however first it has to show itself on Earth.
SpaceX
disguise caption
toggle caption
SpaceX
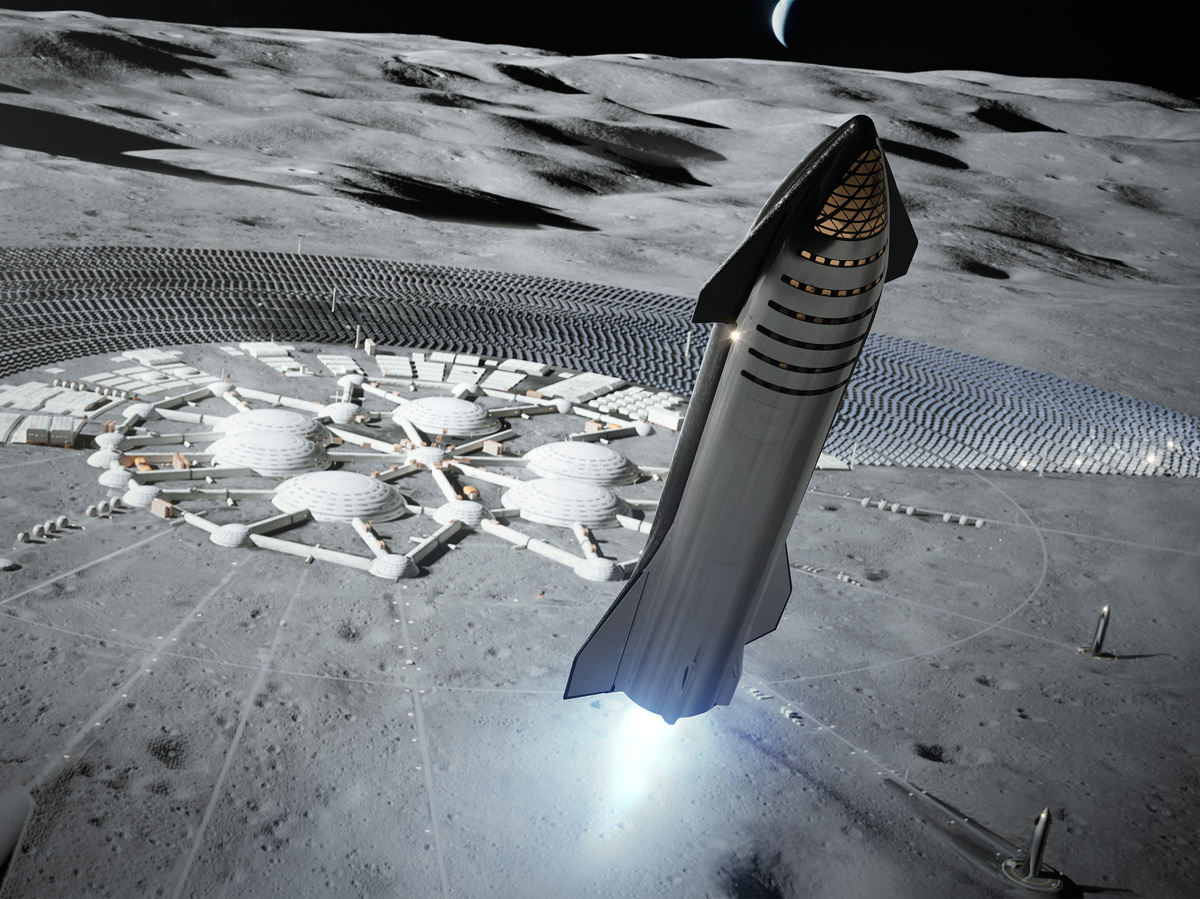
NASA is paying SpaceX billions to develop Starship right into a lunar touchdown craft, however first it has to show itself on Earth.
SpaceX
That is the plan on paper. What really occurs may look fairly completely different.
SpaceX performed two check fires of the brand new Tremendous Heavy booster in August. The primary, performed on Aug. 6, ended prematurely after 4 engines didn’t perform correctly. The second, performed on Aug. 22, was profitable, though two engines didn’t run for the total length of the six-second check.
As well as, the flight can be testing the rocket’s “scorching stage” separation system for the primary time. And it stays to be seen whether or not the thermal safety system on Starship can stand as much as the brutal warmth of reentering the Earth’s environment.

McDowell says he thinks any state of affairs by which Starship separates from its booster and retains flying ought to most likely be thought of successful, no matter what occurs to the spacecraft after that. However given the issue of getting the 33 first-stage Raptor engines to fireplace correctly, he is unsure it will get that far.
“I feel the ignition reliability of the Raptor engines is the largest query in my thoughts proper now,” he says.
Even when it ends in failure, Quilty believes that it will not have a direct impact on SpaceX’s enterprise. The corporate is presently dominating the marketplace for launching business satellites, thanks partially to previous improvements, like a primary stage that may land vertically on a barge. “They’re doing completely nice with out Starship,” he says.
However McDowell provides that given the massive ambitions of SpaceX, this monster rocket should work ultimately.
“They want Starship to work ultimately,” he says. “The massive query for me is: ‘How a lot ultimately can they get away with? What number of failures can they tolerate?'”

