
A ground-breaking new discovery by College of Leeds scientists may rework the best way astronomers perceive among the greatest and most typical stars within the universe. The paper, “Gaia uncovers distinction in B and Be star binarity at small scales: proof for mass switch inflicting the Be phenomenon,” is revealed within the journal Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Analysis by Ph.D. scholar Jonathan Dodd and Professor René Oudmaijer, from the College’s Faculty of Physics and Astronomy, factors to intriguing new proof that huge Be stars—till now primarily thought to exist in double stars—may in truth be “triples.”
The exceptional discovery may revolutionize our understanding of the objects—a subset of B stars—that are thought of an necessary “check mattress” for growing theories on how stars evolve extra usually.
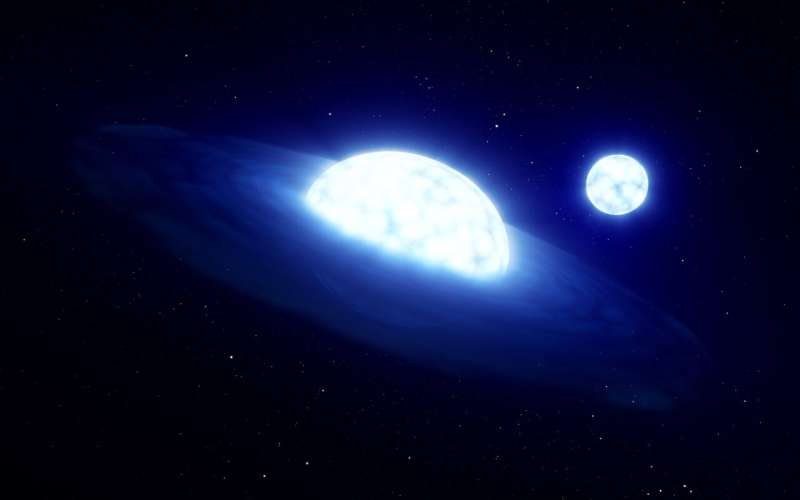
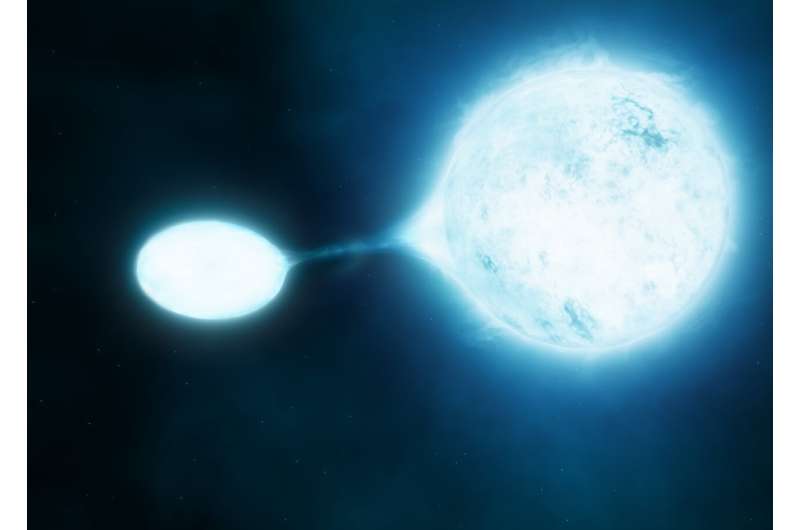
These Be stars are surrounded by a attribute disk made from gasoline—much like the rings of Saturn in our personal photo voltaic system. And though Be stars have been identified for about 150 years—having first been recognized by famend Italian astronomer Angelo Secchi in 1866—till now, nobody has identified how they had been shaped.
Consensus amongst astronomers thus far has stated the disks are shaped by the fast rotation of the Be stars, and that itself may be attributable to the celebs interacting with one other star in a binary system.
Triple methods
Mr. Dodd, corresponding creator of the analysis, stated, “The most effective level of reference for that’s in the event you’ve watched Star Wars, there are planets the place they’ve two suns.”
However now, by analyzing knowledge from the European Space Agency’s Gaia satellite, the scientists say they’ve discovered proof these stars truly exist in triple methods—with three our bodies interacting as an alternative of simply two.
Mr. Dodd added, “We noticed the best way the celebs transfer throughout the evening sky, over longer durations like 10 years, and shorter durations of round six months. If a star strikes in a straight line, we all know there’s only one star, but when there’s a couple of, we’ll see a slight wobble or, in the perfect case, a spiral.
“We utilized this throughout the 2 teams of stars that we’re —the B stars and the Be stars—and what we discovered, confusingly, is that initially it appears just like the Be stars have a decrease charge of companions than the B stars. That is attention-grabbing as a result of we might count on them to have a better charge.”
Nonetheless, Principal Investigator Prof Oudmaijer stated, “The truth that we don’t see them may be as a result of they’re now too faint to be detected.”
Mass switch
The researchers then checked out a special set of information, searching for companion stars which can be additional away, and located that at these bigger separations, the speed of companion stars may be very related between the B and Be stars.
From this, they had been in a position to infer that in lots of circumstances a 3rd star is coming into play, forcing the companion nearer to the Be star—shut sufficient that mass may be transferred from one to the opposite and kind the attribute Be star disk. This might additionally clarify why we don’t see these companions anymore; they’ve turn out to be too small and faint to be detected after the “vampire” Be star has sucked in a lot of their mass.
The invention may have big impacts on different areas of astronomy—together with our understanding of black holes, neutron stars and gravitational wave sources.
Prof Oudmaijer stated, “There is a revolution occurring in physics for the time being round gravitational waves. Now we have solely been observing these gravitational waves for a couple of years now, and these have been discovered to be as a consequence of merging black holes.
“We all know that these enigmatic objects—black holes and neutron stars—exist, however we do not know a lot concerning the stars that will turn out to be them. Our findings present a clue to understanding these gravitational wave sources.”
He added, “During the last decade or so, astronomers have discovered that binarity is an extremely necessary aspect in stellar evolution. We at the moment are transferring extra in the direction of the thought it’s much more advanced than that and that triple stars have to be thought of.”
“Certainly,” Oudmaijer stated, “triples have turn out to be the brand new binaries.”
Extra info:
Jonathan M Dodd et al, Gaia uncovers distinction in B and Be star binarity at small scales: proof for mass switch inflicting the Be phenomenon, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2023). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad3105. On arXiv: arxiv.org/pdf/2310.05653.pdf
Quotation:
‘Triple star’ discovery may revolutionize understanding of stellar evolution (2023, November 20)
retrieved 21 November 2023
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

