
When spacecraft return to Earth, they needn’t shed all their velocity by firing retro-rockets. As an alternative, they use the environment as a brake to decelerate for a tender touchdown. Each planet within the photo voltaic system besides Mercury has sufficient of an environment to permit aerobraking maneuvers, and will permit high-speed exploration missions. A brand new paper appears on the totally different worlds and the way a spacecraft should fly to reap the benefits of this “free lunch” to decelerate on the vacation spot.
Aerocapture is an orbital switch maneuver through which a spacecraft makes a single move via a planetary environment to decelerate and obtain orbit insertion. Then again, aerobraking makes use of a propulsive burn plus repeated dips into the environment—i.e., atmospheric drag—to steadily sluggish the spacecraft and cut back the scale of the orbit to attain orbit insertion.
The new paper posted to the arXiv preprint server, by Athul Pradeepkumar Girija from the College of Aeronautics and Astronautics at Purdue College, notes that one of many vital dangers related to aerocapture is the uncertainty within the atmospheric density. Whereas aerobraking takes place within the tenuous higher environment of a planetary physique the place the density uncertainties are a lot bigger, aerocapture happens within the deeper environment the place the density uncertainties are smaller.
For instance, the atmospheric density that the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter MRO really skilled when aerobraking for its orbital insertion in 2006 was a lot totally different than what was predicted by a NASA mannequin known as GRAM (World Reference Atmospheric Mannequin) for Mars.
“At some factors within the environment, we noticed a distinction within the atmospheric density by an element of 1.3, which suggests it was 30% increased than the mannequin,” mentioned Han You, Navigation Workforce Chief for MRO, in an article on Universe Right this moment in 2006. “That is fairly a bit, however across the south pole we noticed an excellent bigger scale issue of as much as 4.5, so which means it was 350% off of the Mars GRAM mannequin.”
For both aerobraking or aerocapture, the atmospheric density on Mars and different planets can fluctuate extensively from each day, and even orbit to orbit.
“If the car enters too shallow or encounters an environment which is much less dense than the anticipated minimal, spacecraft might exit the environment with out getting captured,” Girija wrote in his new paper. “If the car enters too steep, or the density is way increased than anticipated, the car might bleed an excessive amount of pace and fail to exit the environment.”
Each situations would result in full lack of mission. Due to this fact, ample margins should be supplied for the steering system in opposition to these atmospheric uncertainties, along with supply error and aerodynamic uncertainties.
To carry out aerocapture, there are two sorts of aerodynamic management strategies to manage the speed of vitality depletion because the car flies via the environment: elevate modulation and drag modulation.
“Elevate modulation includes a ‘lifting’ aeroshell reminiscent of Apollo or Mars Science Laboratory aeroshell, which has a lift-to-drag (L/D) ratio within the vary of 0.24—0.36,” defined Girija in an e-mail to Universe Right this moment. “Management is achieved by ‘banking’ the car to fly deeper into the denser environment, or increased into the thinner environment. This management methodology requires the usage of high-rate response management thrusters and is routinely used at Earth and Mars, and has intensive heritage in Apollo and MSL (Mars Science Laboratory) missions.”
Elevate modulation provides steady management via the atmospheric flight whereas the response management steering tries to attain the specified “exit state circumstances.”
Drag modulation, however, is a less complicated management approach through which the management is achieved by steady or discrete (occasional) modulation of the drag space utilizing a deployable gadget.
“Drag modulation automobiles have L/D = 0, i.e. no lifting functionality,” Girija mentioned. “The most typical variant is a ‘discrete occasion modulation’ the place a deployed drag skirt is jettisoned in the course of the flight, with the jettison time being the one management variable.”
By jettisoning the drag skirt on the right time, Girija defined, it’s potential to focus on a fairly shut exit state situation to what’s excellent.
“Drag modulation has been proposed as a ‘cheaper’ various to elevate modulation,” Girija mentioned, “by avoiding the usage of RCS thrusters and is especially engaging for small missions. Drag modulation has no flight heritage, although a number of the primary applied sciences have been demonstrated in flight experiments such because the Adaptable Deployable Entry and Placement Expertise (ADEPT),” which had a profitable check flight in September of 2018.
One other factor to think about is the entry hall, which is the area of the environment a spacecraft enters to succeed in its desired vacation spot. The Theoretical Hall Width (TCW) quantifies the width of the hall, and should be giant sufficient to accommodate a secure touchdown, accounting for atmospheric uncertainties, and likewise present adequate security margin for mission success even in limiting situations, reminiscent of mixture of shallow entry and skinny environment.
As a normal rule of thumb, Girija mentioned, elevate modulation supplies practically twice the accessible entry hall width as drag modulation, and might thus accommodate bigger atmospheric uncertainties. The principle distinction is that whereas drag modulation provides considerably much less management, it’s extra reasonably priced for small missions (lower than $50 million) whereas lifting aeroshells sometimes price a number of a whole bunch of tens of millions of {dollars}.
Girija says that although the atmospheres of Venus, Mars, and Titan are well-characterized for engineering functions, there will be commonplace density variations of as much as 50%, plus or minus. With no in-situ knowledge, the atmospheres of Uranus and Neptune usually are not as nicely characterised, however the GRAM mannequin for them supplies a typical deviation variation of plus or minus 30%. An understanding of the anticipated uncertainties within the density profile is of nice significance to evaluate the chance it poses to a future mission.
The GRAM mannequin makes use of accessible in-situ and distant sensing measurements and supplies an “engineering mannequin for the planetary atmospheres,” Girija mentioned. “For planets reminiscent of Mars and Venus, there’s plenty of knowledge (each in situ and distant sensing) and the fashions are thought-about fairly dependable for preliminary engineering design. For Uranus and Neptune, there isn’t a in-situ knowledge accessible and the fashions are based mostly solely on distant sensing observations in the course of the Voyager flyby.”
However there’s nice variety within the bodily construction and chemical composition of the atmospheric layers of the planets in our photo voltaic system, from the “sizzling thick Venusian CO2 environment to the chilly icy H2-He atmospheres of Uranus and Neptune,” writes Girija, including that measurements such because the noble gasoline abundances and isotopic ratios in these atmospheres usually are not solely vital any aerobraking operations, but in addition to our understanding of the origin, formation, and evolution of the photo voltaic system.
For Venus’ thick environment, aerocapture utilizing its environment has been proven to be possible utilizing each elevate and drag modulation. Nevertheless, the massive heating charges at Venus make elevate modulation not as fascinating. Girija says that drag modulation with its decrease heating charge significantly makes it engaging for small satellite tv for pc orbit insertion.
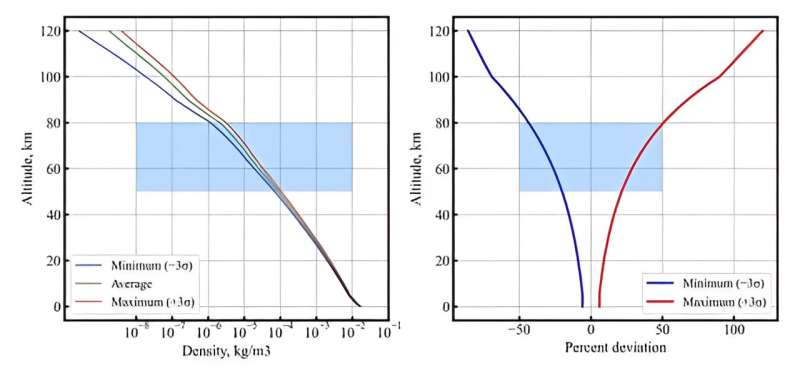
Mars has a comparatively skinny environment in comparison with the Earth, however a number of missions have efficiently used aerocapture for each orbit insertion and touchdown. Due to the quite a few mission to Mars, the Martian environment is nicely understood, but in addition has comparatively giant seasonal differences in comparison with Venus, and related uncertainties significantly within the thinner higher environment.
Nevertheless, in comparison with Venus, the low gravity and the prolonged environment present bigger TCW at Mars (by an element of two), and Girija says the bigger atmospheric uncertainties can simply be accommodated. The “candy spot” deceleration at Mars is a band of environment between 50–80 km in altitude, the place a lot of the deceleration happens for aerocapture at Mars. For any mission to the Pink Planet, the entry proposal must have ample margin for 2 limiting situations: shallow entry and skinny environment, and thick environment and steep entry.
Saturn’s largest moon Titan is the one moon in our photo voltaic system with an environment. With floor liquids and its Earth-like terrain, Titan is an attractive world to check with a future mission. Girija says that Titan’s low gravity and prolonged thick environment make it the best vacation spot for aerocapture, and these circumstances present the most important hall width of any vacation spot in our photo voltaic system. Since its small measurement makes it significantly troublesome to insert orbiters utilizing standard propulsion, aerocapture is a promising various for future missions which may carry out world mapping of Titan’s floor and its lakes and seas. We do have the in-situ knowledge from the Huygens lander, so Girija says that Titan’s density profile is pretty nicely constrained, with a number of exceptions.
“The uncertainty within the density profile will increase with altitude, reaches a most of about 40% close to 100 km above the floor after which decreases,” Girija writes. “It’s not clear that is an artifact of the assumptions used within the mannequin, or certainly an actual impact.”
The altitude band of 300–450 km is the place a lot of the deceleration happens for aerocapture at Titan, with a density variation of about 30%, which is corresponding to Venus. Girija says that though Venus’ and Titan’s environment are fairly totally different by way of their temperature (737K vs. 94K) and chemistry (CO2 vs. N2), they share a number of bodily similarities, reminiscent of each being comparatively thick, super-rotating atmospheres with the planetary physique rotating slowly and vital greenhouse warming within the decrease troposphere.
The ice giants Uranus and Neptune are the final class of planets but to be explored utilizing orbiter spacecraft. Despite the fact that their distance from Earth presents vital mission design challenges, the 2023–2032 Planetary Science Decadal Survey has recognized a Uranus Orbiter and Probe as the highest precedence for a flagship mission within the subsequent decade.
Whereas Uranus and Neptune are each equally compelling scientifically, Girija says that Uranus is much less demanding from a mission design perspective with propulsive insertion. “Aerocapture has been proven to be strongly enhancing to enabling know-how for ice large missions,” he writes. “With aerocapture, each Uranus and Neptune can be equally accessible. Latest research have proven that aerocapture allows considerably shorter flight occasions to Uranus than potential with propulsive insertion, particularly with new excessive vitality launch automobiles.”
For each Uranus and Neptune, the GRAM suite supplies a density variation of roughly 30% for the “related altitude ranges which is taken into account an optimistic estimate,” Girija writes. “Till in-situ knowledge from an atmospheric probe turns into accessible, a extra conservative world min-max estimate is beneficial to accommodate the worst-case state of affairs.”
The altitude vary of 200–400 km is the realm the place aerocapture can be best and Girija says the anticipated density variation of 30% “should be taken as an ‘optimistic’ estimate till in-situ knowledge turns into accessible. The precise uncertainty could also be a lot increased.”
Girija has written one other paper, additionally posted to the arXiv preprint server, evaluating elevate and drag modulation for ice large missions.
Total, Girija says, the aerocapture mission design “should account for the anticipated atmospheric uncertainties to guarantee the steering scheme can efficiently steer the car to the specified” location within the environment or a touchdown. Probably the most essential components of the mission design is the collection of the goal entry flight path angle.
Extra info:
Athul Pradeepkumar Girija, Comparative Examine of Planetary Atmospheric Uncertainties and Design Guidelines for Aerocapture Missions, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2310.10067
Athul Pradeepkumar Girija, Comparability of Elevate and Drag Modulation Management for Ice Big Aerocapture Missions, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2309.13812
Quotation:
Aerocapture is a ‘free lunch’ in house exploration (2023, November 28)
retrieved 28 November 2023
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

