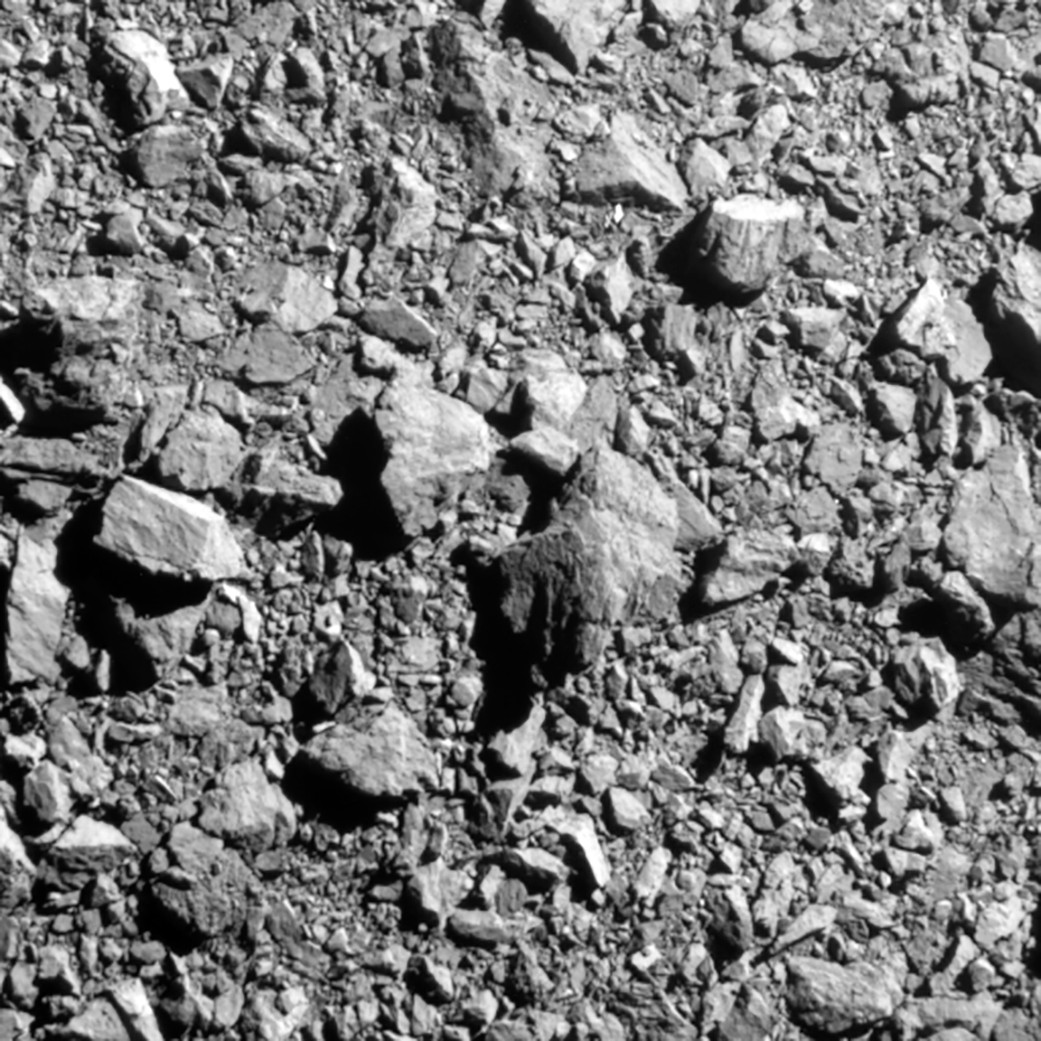
The previous couple of years noticed a spate of up-close encounters and smash-ups with numerous asteroids. Apparently, the rubble pile composition of asteroids has been stunning in a number of instances.
Asteroid probes from a number of nations have discovered not strong objects, however numerous items of gravel and boulders loosely sure collectively by the article’s personal small gravity subject.
Of late, it was the NASA OSIRIS-REx mission that left chew marks on asteroid Bennu, snagging and bagging bits and items of that rubble pile, then parachuting these collectibles into Utah final September. Equally, Japan’s two Hayabusa missions hauled again to Earth specimens of the rubble piles, asteroid Itokawa (2010) and asteroid Ryugu (2020).
This revelation is drifting by way of the planetary protection group. How can we cope with incoming area rocks which are double bother: Unhealthy for Earth, but in addition robust to cope with on account of their make-up?
Associated: Rubble-pile asteroids are ‘big area cushions’ that dwell endlessly
Go-to method
The smashing success of NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Check, or DART, noticed humankind ace its first mission to purposely transfer a celestial object. After ten months of journey, DART’s kinetic, spot-on thumping of asteroid Dimorphos occurred in September 2022, altering the asteroid’s orbit interval round its tiny celestial companion, asteroid Didymos.
“Pre-impact projections estimated a spread of attainable deflections, and the post-impact observations revealed a major deflection of the goal asteroid on the high-end of the pre-impact fashions,” reviews NASA, citing the DART final result as “a promising consequence for making use of the method sooner or later if wanted.”
The kinetic influence technique showcased by DART has been the “go-to strategy of alternative” if making an attempt to deflect an asteroid headed towards Earth, mentioned John Brophy, an Engineering Fellow at Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
“They hit it very near the middle of mass. It was an excellent shot,” Brophy instructed House.com.
Then again, asteroid rubble piles seemingly give rise to that Forrest Gump axiom that life is sort of a field of goodies: “You by no means know what you are gonna get.”
“In the event you hit it arduous sufficient to deflect it, in a single influence, you’re very more likely to disrupt it. And disrupt it means blast it aside,” Brophy mentioned. What takes place subsequent is “a chaotic course of with unsure outcomes,” he mentioned.

Managed course of
Having kinetic impactors repeatedly strike a goal in a kinder and gentler trend is one thought, however that method additionally presents challenges.
Brophy was a examine lead for a brand new planetary protection thought often known as ion beam deflection. “You direct the ion beam to influence the asteroid, alongside its velocity vector. With ion beam deflection you unfold that energy out over months or possibly even a yr or two,” he mentioned.
Utilizing this ion beam idea has a number of advantages, Brophy added. For one, it’s a very managed course of. It additionally works on rubble piles and does not care what the energy of the article is or its make-up or how the area rock is rotating.
Ion beam deflection “is a doubtlessly enticing method that may assist mitigate the problems of deflecting rubble piles,” Brophy mentioned. Then in fact, he famous, there’s use of a nuclear machine for deflection functions, however that is seen by many as a method of final resort.
Learn extra: 8 methods to cease an asteroid: Nuclear weapons, paint and Bruce Willis
Massive canine
Ed Lu is govt director of the Asteroid Institute, which is a program of the B612 Basis. As a NASA Astronaut, he flew three area missions, logging 206 days in Earth orbit, to assist assemble and dwell aboard the Worldwide House Station.
Lu can be a co-inventor of the Gravity Tractor, a controllable technique of deflecting asteroids, utilizing solely a spacecraft’s gravitational subject to convey the required impulse. Testing out the idea in area in experimental mode is below examine, he mentioned.
From a planetary protection standpoint, Lu has lengthy been saying that deflection just isn’t the tough problem. “It has by no means been the arduous half. It has all the time been discovering, monitoring, and getting a whole catalog and know when one thing goes to hit,” he instructed House.com.
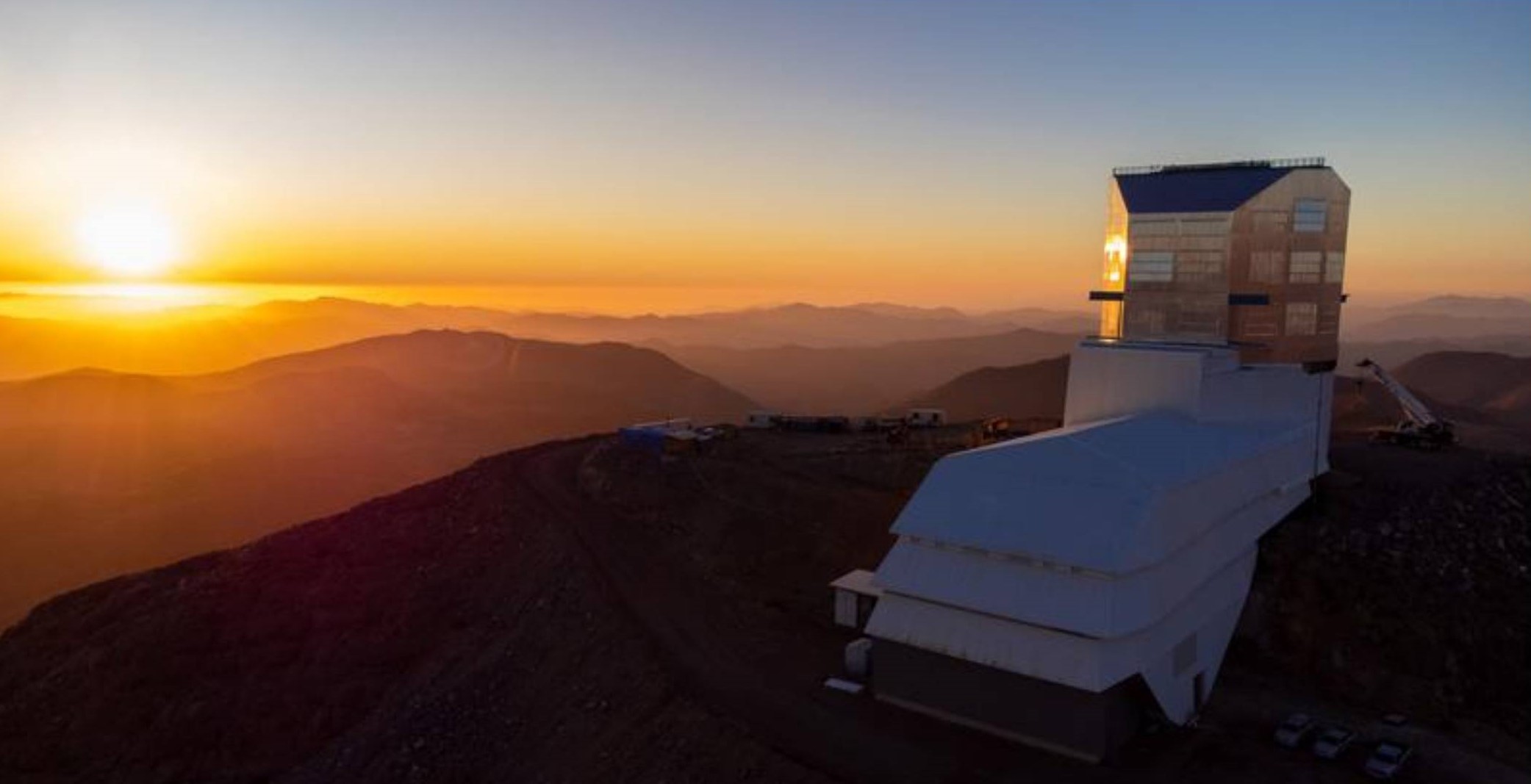
The large asteroid information, Lu mentioned, is the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, presently below building on Cerro Pachón in Chile. It’s anticipated to excel at recognizing new asteroids as the ability will monitor massive areas of the sky each evening and may detect very dim shifting objects.
“It’s the actually the large canine and may make most of these discoveries over the following few years. The primary a number of years of its operation are essentially the most prolific. That is when the whole lot is simple pickings,” Lu mentioned.

Governance points
A current public ballot mentioned keeping track of Earth-bruising trajectories of asteroids ought to be NASA’s prime precedence.
“Monitoring asteroids that might doubtlessly hit the Earth ranks on the prime of the general public’s precedence checklist for NASA. Monitoring the planet’s local weather system additionally ranks extremely as a precedence for NASA. However comparatively few Individuals say it ought to be a prime precedence to ship human astronauts to the moon or Mars,” reported a July 20 Pew Analysis Heart “truth tank” discovering.
Technologically coping with rubble piles is one factor, however extra work additionally seems wanted to hash out the political and sociological features of heading off asteroids which have cross-hairs on Earth.
Nikola Schmidt works as a senior researcher and is head of the Heart for Governance of Rising Applied sciences on the Institute of Worldwide Relations in Prague. He’s writer of a current take a look at 30 years of planetary protection governance.
“The issue is that we have no idea what’s below the floor of the rubble piles,” Schmidt instructed House.com. “There could possibly be hollows inside or areas between greater rocks could be absolutely crammed by regolith. That is one thing we have no idea and may trigger considerably totally different results. So sure, the construction is an issue and about 70-80% of the asteroid inhabitants is believed to include rubble piles,” he mentioned.
Safety regimes
In Schmidt’s paper showing within the January problem of the journal Acta Astronautica, he observes that in the present day, we aren’t in a state of affairs through which the Earth can be easily defended.
“This isn’t to say that the United Nnations our bodies, skilled entities and the entire planetary protection scientific group should not speaking and sharing data.” They’re, Schmidt rapidly provides, however the truth that states wish to hold decision-making in their very own palms runs counter to being ready on a planetary stage and avoiding pointless worldwide discussions within the occasion of of an imminent menace.
“That is why states have developed worldwide cooperation within the type of multilateral safety regimes,” Schmidt mentioned. “They lay down procedures for decision-making that won’t be modified on account of elections specifically states and may present safety assurance to all for unequal contribution, which is essential for the safety of small states and legitimacy of motion for highly effective states — every can contribute what they will, however all get pleasure from identical safety from the cooperation.”
Cosmopolitan accountability
Schmidt instructed House.com that he has been arguing for years that planetary protection is about cosmopolitan accountability, “which is constituted by the continued manufacturing of latest scientific data about asteroids and their orbits. The data adjustments our notion of the world round us that traverses the borders of nation-states and their energy to do something about it. Due to this fact, states should discover a strategy to cooperate or they fail to meet their principal purpose of existence — present safety to the residents.”
Cosmopolitan can be not the sort of language to be offered to the general public, Schmidt concludes, “however planetary protection is rearticulating social contract as the rest within the constantly reworking society.”

