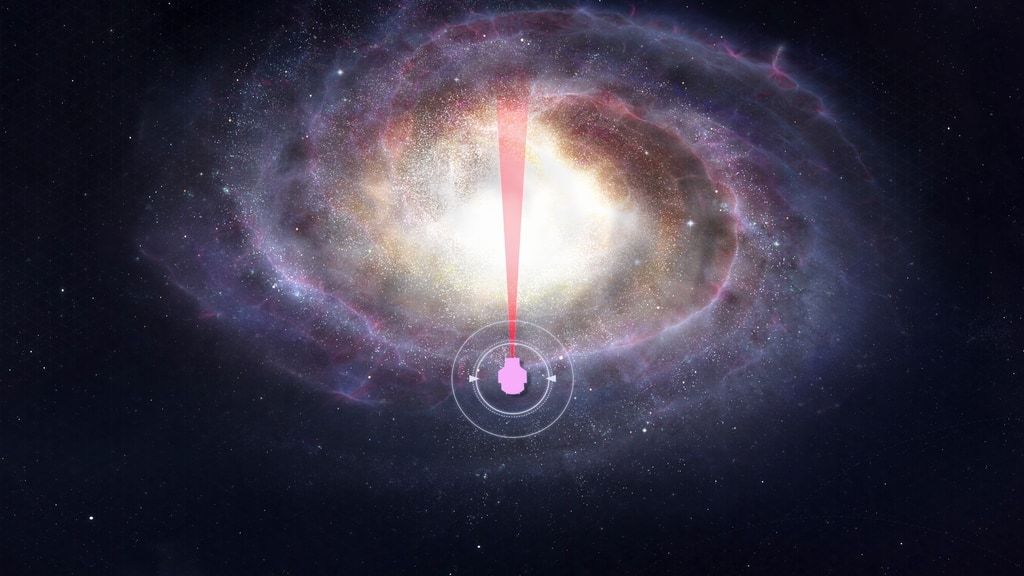
A simulated picture of NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope’s future observations towards the middle of our galaxy, spanning lower than 1 % of the whole space of Roman’s Galactic Bulge Time-Area Survey. The simulated stars had been drawn from the Besançon Galactic Mannequin.
The view out of your yard would possibly paint the universe as an unchanging realm, the place solely twinkling stars and close by objects, like satellites and meteors, stray from the obvious fidelity. However stargazing via NASA’s upcoming Nancy Grace Roman Space Telescope will supply a entrance row seat to a blinding show of cosmic fireworks glowing throughout the sky.
Roman will view extraordinarily faint infrared gentle, which has longer wavelengths than our eyes can see. Two of the mission’s core observing packages will monitor particular patches of the sky. Stitching the outcomes collectively like stop-motion animation will create films that reveal altering objects and fleeting occasions that might in any other case be hidden from our view.
Watch this video to study time-domain astronomy and the way time shall be a key ingredient in NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope’s galactic bulge survey. Credit score: NASA’s Goddard House Flight Heart
One of these science, referred to as time-domain astronomy, is tough for telescopes which have smaller views of area. Roman’s giant area of view will assist us see big swaths of the universe. As a substitute of all the time particular issues and occasions astronomers have already recognized, Roman will be capable to repeatedly observe giant areas of the sky to catch phenomena scientists can’t predict. Then astronomers can discover issues nobody knew had been there!
One in all Roman’s important surveys, the Galactic Bulge Time-Domain Survey, will monitor tons of of tens of millions of stars towards the middle of our Milky Approach galaxy. Astronomers will see lots of the stars seem to flash or flicker over time.
This animation illustrates the idea of gravitational microlensing. When one star within the sky seems to go almost in entrance of one other, the sunshine rays of the background supply star are bent because of the warped space-time across the foreground star. The nearer star is then a digital magnifying glass, amplifying the brightness of the background supply star, so we consult with the foreground star because the lens star. If the lens star harbors a planetary system, then these planets may also act as lenses, each producing a brief change within the brightness of the supply. Thus, we uncover the presence of every exoplanet, and measure its mass and the way far it’s from its star. Credit score: NASA’s Goddard House Flight Heart Conceptual Picture Lab
That may occur when one thing like a star or planet strikes in entrance of a background star from our viewpoint. As a result of something with mass warps the fabric of space-time, gentle from the distant star bends across the nearer object because it passes by. That makes the nearer object act as a pure magnifying glass, creating a brief spike within the brightness of the background star’s gentle. That sign lets astronomers know there’s an intervening object, even when they will’t see it immediately.
This artist’s idea exhibits the area of the Milky Approach NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope’s Galactic Bulge Time-Area Survey will cowl – comparatively uncharted territory relating to planet-finding. That’s essential as a result of the way in which planets kind and evolve could also be completely different relying on the place within the galaxy they’re positioned. Our photo voltaic system is located close to the outskirts of the Milky Approach, about midway out on one of many galaxy’s spiral arms. A latest Kepler Space Telescope study confirmed that stars on the fringes of the Milky Approach possess fewer of the commonest planet varieties which have been detected to date. Roman will search in the wrong way, towards the middle of the galaxy, and will discover variations in that galactic neighborhood, too.
Utilizing this methodology, referred to as microlensing, Roman will possible set a brand new document for the farthest-known exoplanet. That might supply a glimpse of a distinct galactic neighborhood that may very well be house to worlds fairly not like the more than 5,500 which can be presently identified. Roman’s microlensing observations may even discover starless planets, black holes, neutron stars, and extra!
This animation exhibits a planet crossing in entrance of, or transiting, its host star and the corresponding gentle curve astronomers would see. Utilizing this system, scientists anticipate NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope may discover 100,000 new worlds. Credit score: NASA’s Goddard House Flight Heart/Chris Smith (USRA/GESTAR)
Stars Roman sees may seem to flicker when a planet crosses in entrance of, or transits, its host star because it orbits. Roman could find 100,000 planets this manner! Small icy objects that hang-out the outskirts of our personal photo voltaic system, often known as Kuiper belt objects, could often go in entrance of faraway stars Roman sees, too. Astronomers will be capable to see how a lot water the Kuiper belt objects have as a result of the ice absorbs particular wavelengths of infrared gentle, offering a “fingerprint” of its presence. It will give us a window into our photo voltaic system’s early days.
This animation visualizes a kind Ia supernova.
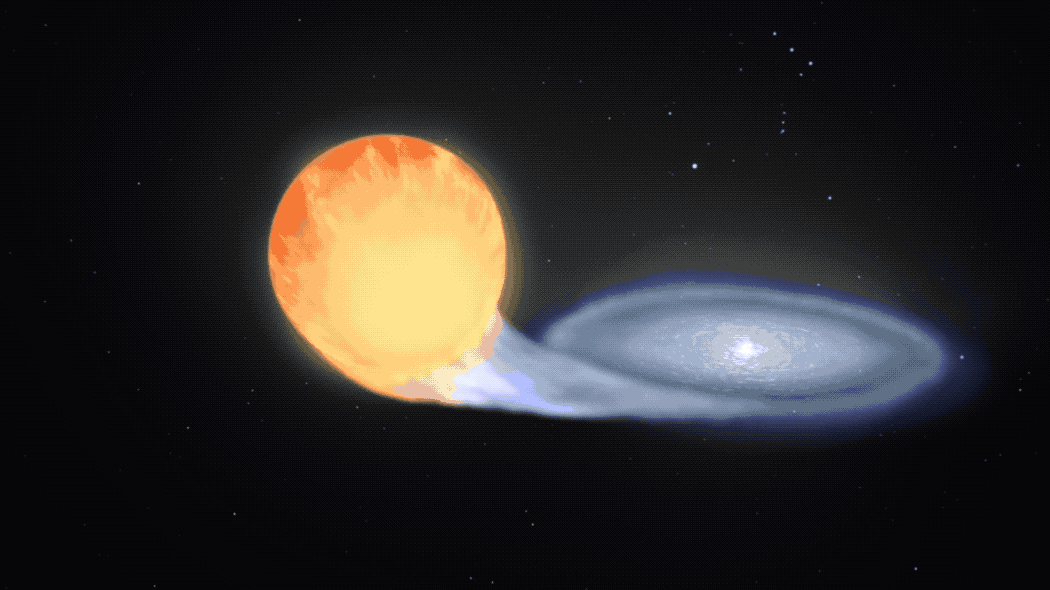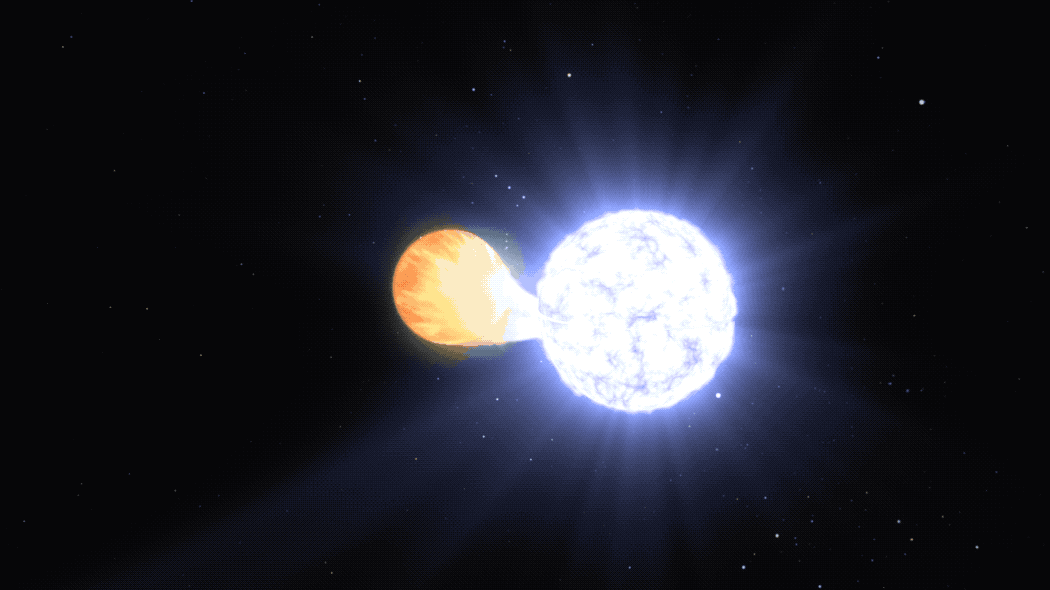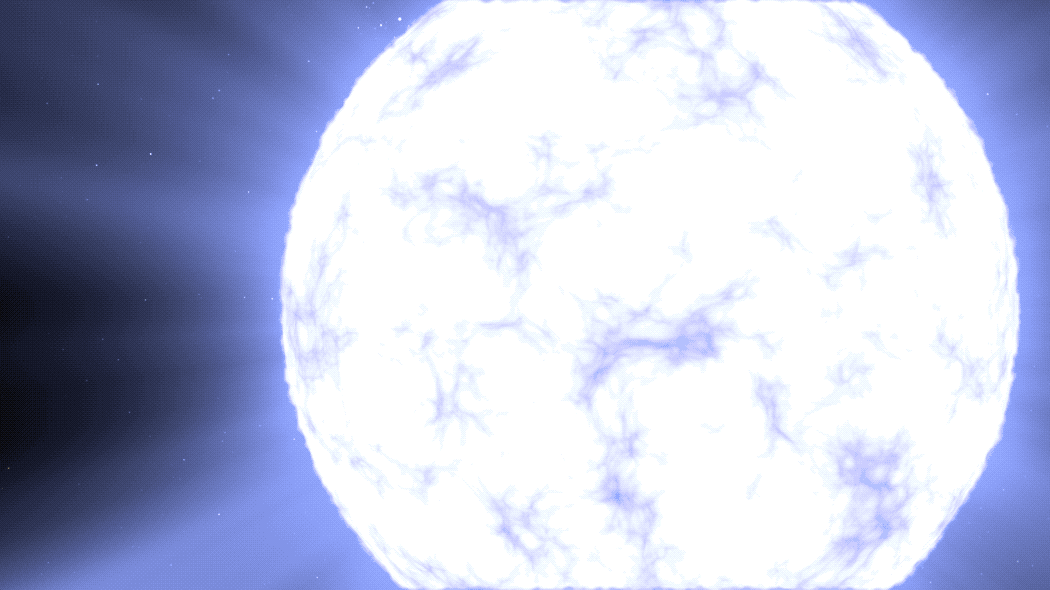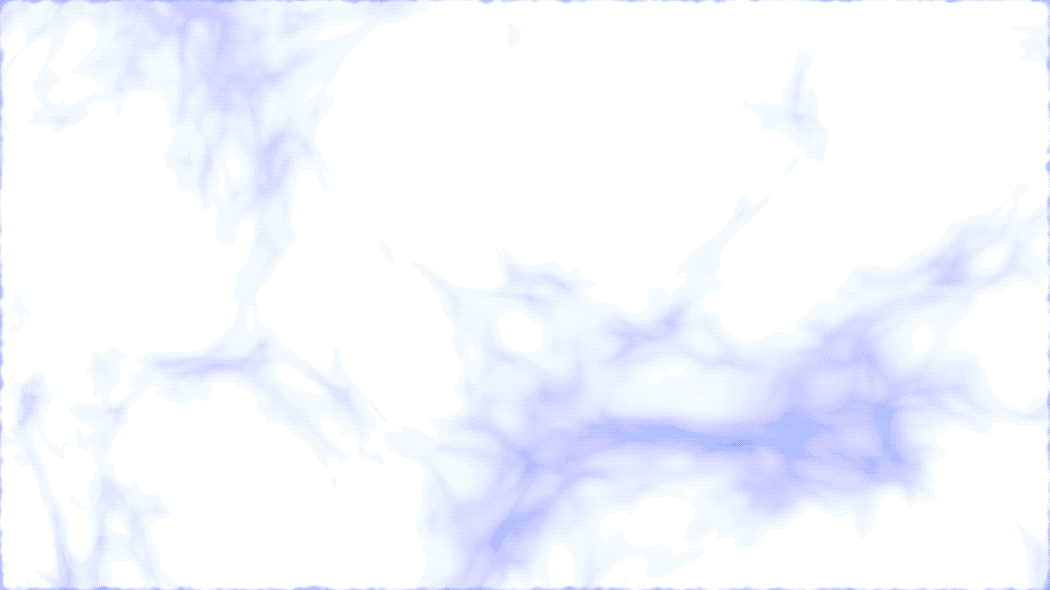
Roman’s High Latitude Time-Domain Survey will look past our galaxy to hunt for type Ia supernovas. These exploding stars originate from some binary star techniques that include not less than one white dwarf – the small, scorching core remnant of a Solar-like star. In some instances, the dwarf could siphon materials from its companion. This triggers a runaway response that in the end detonates the thief as soon as it reaches a selected level the place it has gained a lot mass that it turns into unstable.
NASA’s upcoming Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope will see hundreds of exploding stars referred to as supernovae throughout huge stretches of time and area. Utilizing these observations, astronomers intention to shine a lightweight on a number of cosmic mysteries, offering a window onto the universe’s distant previous. Credit score: NASA’s Goddard House Flight Heart
Since these uncommon explosions every peak at the same, identified intrinsic brightness, astronomers can use them to find out how distant they’re by merely measuring how vibrant they seem. Astronomers will use Roman to review the sunshine of those supernovas to learn how rapidly they look like transferring away from us.
By evaluating how briskly they’re receding at completely different distances, scientists can hint cosmic enlargement over time. It will assist us perceive whether or not and the way dark energy – the unexplained stress thought to hurry up the universe’s enlargement – has modified all through the historical past of the universe.
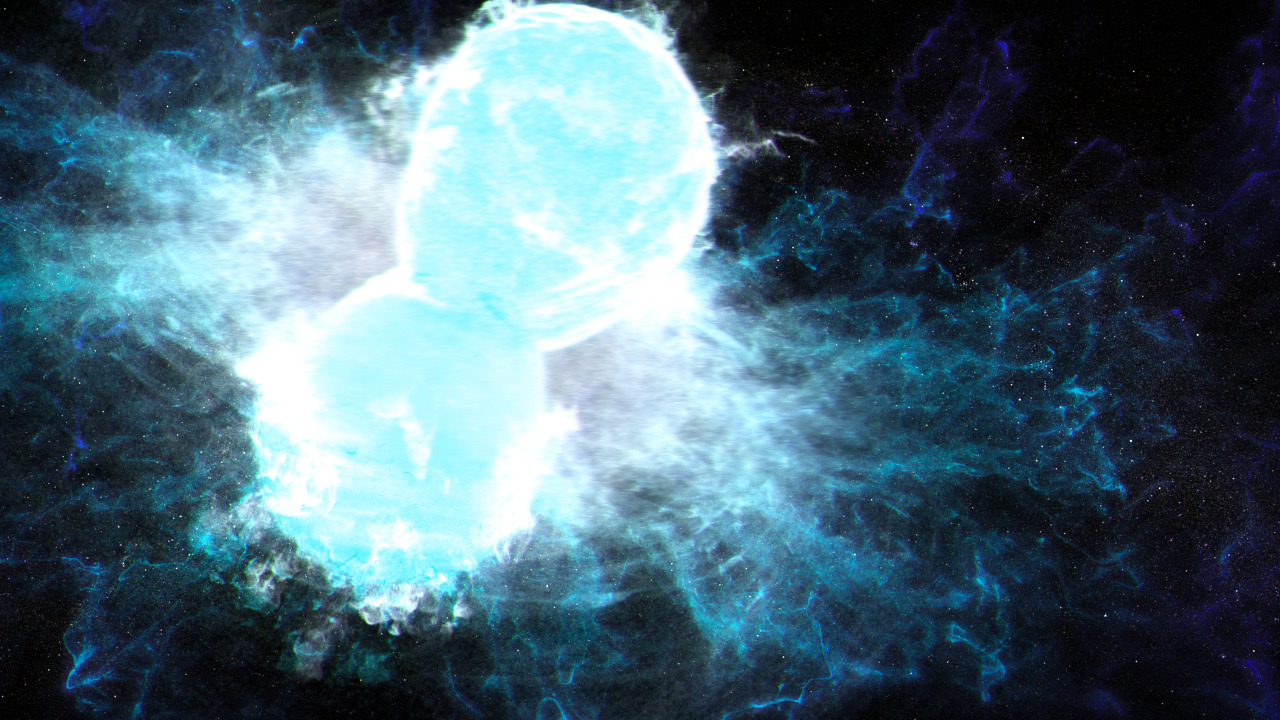
NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope will survey the identical areas of the sky each few days. Researchers will mine this information to determine kilonovas – explosions that occur when two neutron stars or a neutron star and a black gap collide and merge. When these collisions occur, a fraction of the ensuing particles is ejected as jets, which transfer close to the pace of sunshine. The remaining particles produces scorching, glowing, neutron-rich clouds that forge heavy parts, like gold and platinum. Roman’s in depth information will assist astronomers higher determine how usually these occasions happen, how a lot power they provide off, and the way close to or far they’re.
And since this survey will repeatedly observe the identical giant vista of area, scientists may even see sporadic occasions like neutron stars colliding and stars being swept into black holes. Roman may even discover new varieties of objects and occasions that astronomers have by no means seen earlier than!
Be taught extra in regards to the thrilling science Roman will examine on X and Facebook.
Make certain to comply with us on Tumblr to your common dose of area!