
After what has appeared much less like “Groundhog Day” and extra “Groundhog Week”, SpaceX’s CRS-29 Cargo Dragon efficiently undocked from the Worldwide House Station (ISS) late Thursday afternoon, carrying greater than 3,500 kilos (1,600 kilograms) of scientific experiment outcomes, payloads and unneeded {hardware} again residence to Earth. The cargo ship—which launched in November atop a Falcon 9 booster from historic Pad 39A at Florida’s Kennedy House Middle (KSC)—undocked from the forward-facing port of the Concord node at 5:05 p.m. EST, after greater than a month hooked up to the sprawling orbital outpost.
Unfavorable climate situations conspired to a raft of postponed departure dates for CRS-29, which was initially focused to undock from the ISS on 14 December, earlier than repeatedly being pushed again day-to-day, finally till the twenty first. Of explicit be aware was a chilly entrance that pushed via Atlantic waters within the Cargo Dragon’s principal splashdown zone off the Florida Coast final week.
CRS-29, flying as a part of the second-round Business Resupply Providers (CRS2) program between NASA and SpaceX, is the twenty ninth Cargo Dragon to efficiently attain the house station since Might 2012 and the ninth below the 2016-awarded CRS2 contract. And the cargo ship flying this mission, codenumbered “C211”, was making its second outing, having beforehand supported the month-long CRS-26 final winter.
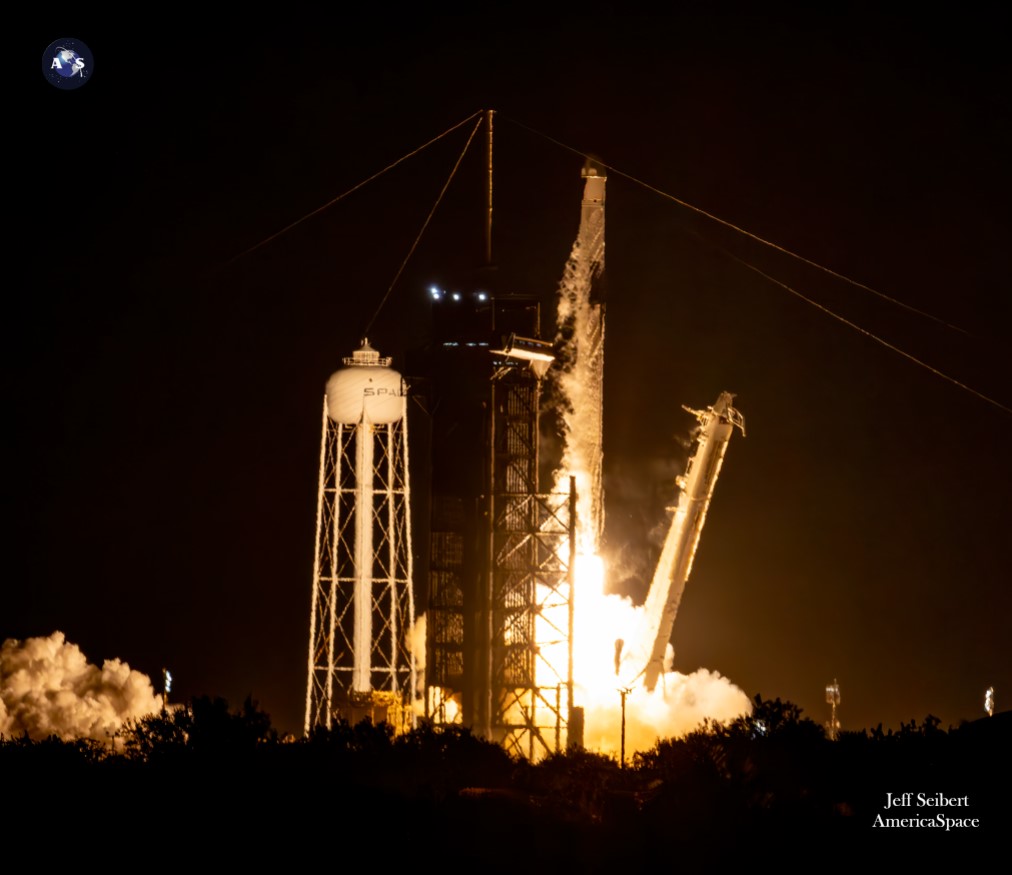

Delayed by payload-related issues, a have to reconfigure Pad 39A following October’s Falcon Heavy launch with the Psyche deep-space mission and substitute of a leaky Draco thruster on the Cargo Dragon itself, the mission rose into the Florida darkness at 8:28 p.m. EST on 9 November. After a 32-hour and 22-orbit rendezvous and method profile, CRS-29 docked autonomously on the ISS at 5:07 a.m. EST on the eleventh, because the station orbited 262 miles (422 kilometers) over Central Brazil.
Monitoring the cargo ship’s method from the multi-windowed cupola had been Expedition 70 astronauts Jasmin Moghbeli and Loral O’Hara. Inside hours of docking, they and the opposite two members of the U.S. Operational Section (USOS) crew—Commander Andreas Mogensen of the European House Company (ESA) and Japan’s Satoshi Furukawa—set briskly to work conducting pressurization and leak checks, earlier than opening hatches and starting the method of unloading greater than 6,500 kilos (3,000 kilograms) of latest science, experiments, payloads and provides.

Dominating the payload haul was NASA’s Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE), which is managed by the Goddard House Flight Middle (GSFC) in Greenbelt, Md., for the Science Mission Directorate (SMD) on the company’s Washington, D.C., headquarters. This $42 million experiment was carried inside CRS-29’s unpressurized “trunk” for ascent and robotically extracted by Mission Management utilizing the station’s 57.7-foot-long (17.6-meter) Canadarm2 robotic arm on 15 November.
The experiment was put in on Web site 3 of ExPRESS Logistics Provider (ELC)-1 on the furthest-port aspect of the station’s Built-in Truss Construction (ITS). Present plans name for it to spend two years inspecting atmospheric gravity waves to raised perceive vitality stream via our planet’s higher ambiance and house.

“Atmospheric gravity waves are one mechanism for transporting vitality and momentum inside the local weather system and so they play a task in defining the local weather and its evolution,” stated AWE co-investigator Jeff Forbes of the College of Colorado at Boulder. “This is a vital step ahead in understanding waves within the ambiance and their contributions to near-Earth house climate.”
AWE will make use of a single instrument, the 128-pound (58-kilogram) Superior Mesospheric Temperature Mapper (AMTM) to seize wide-field-of-view (90-degree) infrared nighttime photos at a charge of 1 picture each second. This can enable the AMTM to provide high-quality temperature maps of atmospheric gravity waves at altitudes between 30 miles (50 kilometers) and 300 miles (500 kilometers)—the “ionosphere-thermosphere-mesosphere area”—earlier than they enter the near-Earth house setting.

“Banking, navigation, climate forecasting and plenty of different purposes offered by satellites, in addition to human house missions, will be affected by house climate,” stated AWE Principal Investigator Michael Taylor of Utah State College. “AWE will present scientists with much-needed data to raised perceive the physics and traits of atmospheric gravity waves in Earth’s higher mesosphere and ionosphere, the area the place house climate begins.”
AWE was chosen for growth in February 2019 and confirmed for implementation by NASA in January 2021. Unique plans referred to as for it to fly in August 2022, but it surely slipped on the manifest and wrapped up its electromagnetic, vibration, thermal vacuum and calibration testing earlier this year. The instrument obtained its flight-safety certification in September, forward of cargo to KSC.
A day earlier than the AWE set up, one other payload was additionally transferred from CRS-29’s trunk to the outside of the ISS. In a extremely choreographed process between NASA and the Japan Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA), on 14 November NASA’s refrigerator-sized Built-in Laser Communications Relay Demonstration Low-Earth-Orbit Consumer Modem and Amplifier Terminal (ILLUMA-T) was eliminated and relocated to its present perch on the Uncovered Facility (EF) of Japan’s Kibo lab.
After being extracted from the trunk by Canadarm2, ILLUMA-T was “handed-off” to Kibo’s personal robotic arm—the Japanese Experiment Module Distant Manipulator System (JEMRMS)—for set up onto the EF. In assist of this operation, Furukawa routed cables and arrange laptop computer computer systems inside Kibo for ILLUMA-T operations.
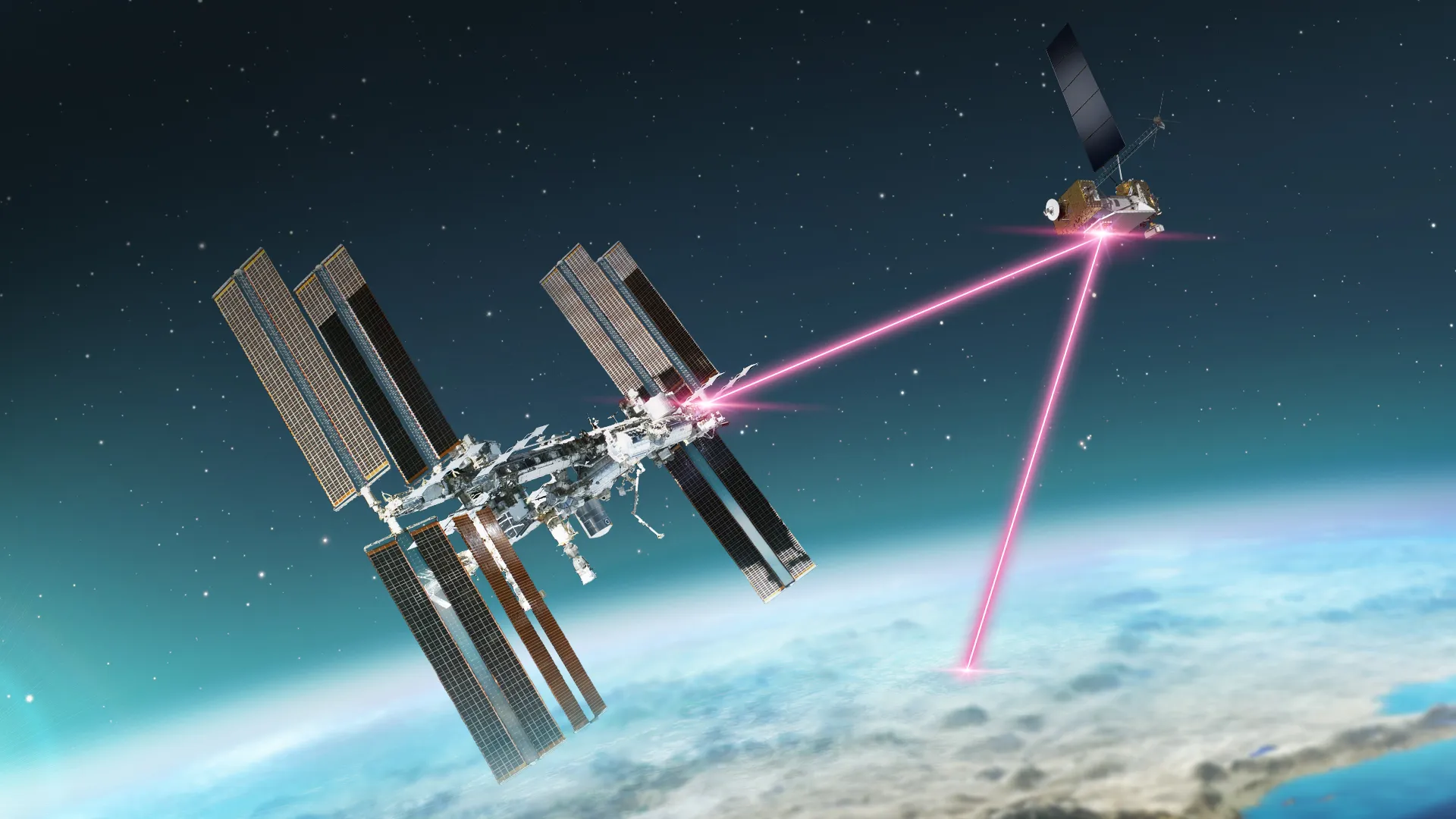

ILLUMA-T will check high-data-rate laser communications between the ISS and floor stations by way of the geosynchronous-orbiting Laser Communications Relay Demonstration (LCRD), which launched atop a United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V in December 2021 on the House Check Program (STP)-3 mission. Collectively, ILLUMA-T and LCRD will full NASA’s first-ever two-way, end-to-end laser communications relay system.
The ILLUMA-T terminal will ship high-resolution image and video knowledge at a charge of 1.2 gigabits per second to the LCRD system. This knowledge might be transmitted to optical floor stations in Haleakala, Hawaii, and Desk Mountain, Calif.

Elsewhere, the Expedition 70 crew labored to take away time-critical experiment supplies from CRS-29, together with science freezers for set up aboard the U.S. Future lab. The method of unloading cargo from the ship went into reverse in late November, because the astronauts set to work loading unneeded gear and scientific outcomes aboard for CRS-29’s return to Earth, then timetabled for mid-December.
Earlier this month, Mogensen disassembled elements from a U.S. house swimsuit, preparatory to their return residence for refurbishment. O’Hara photographed a few of the specifically delivered {hardware} and on 11 December Furukawa and Moghbeli labored to switch frozen analysis specimens from ISS freezers again aboard CRS-29.
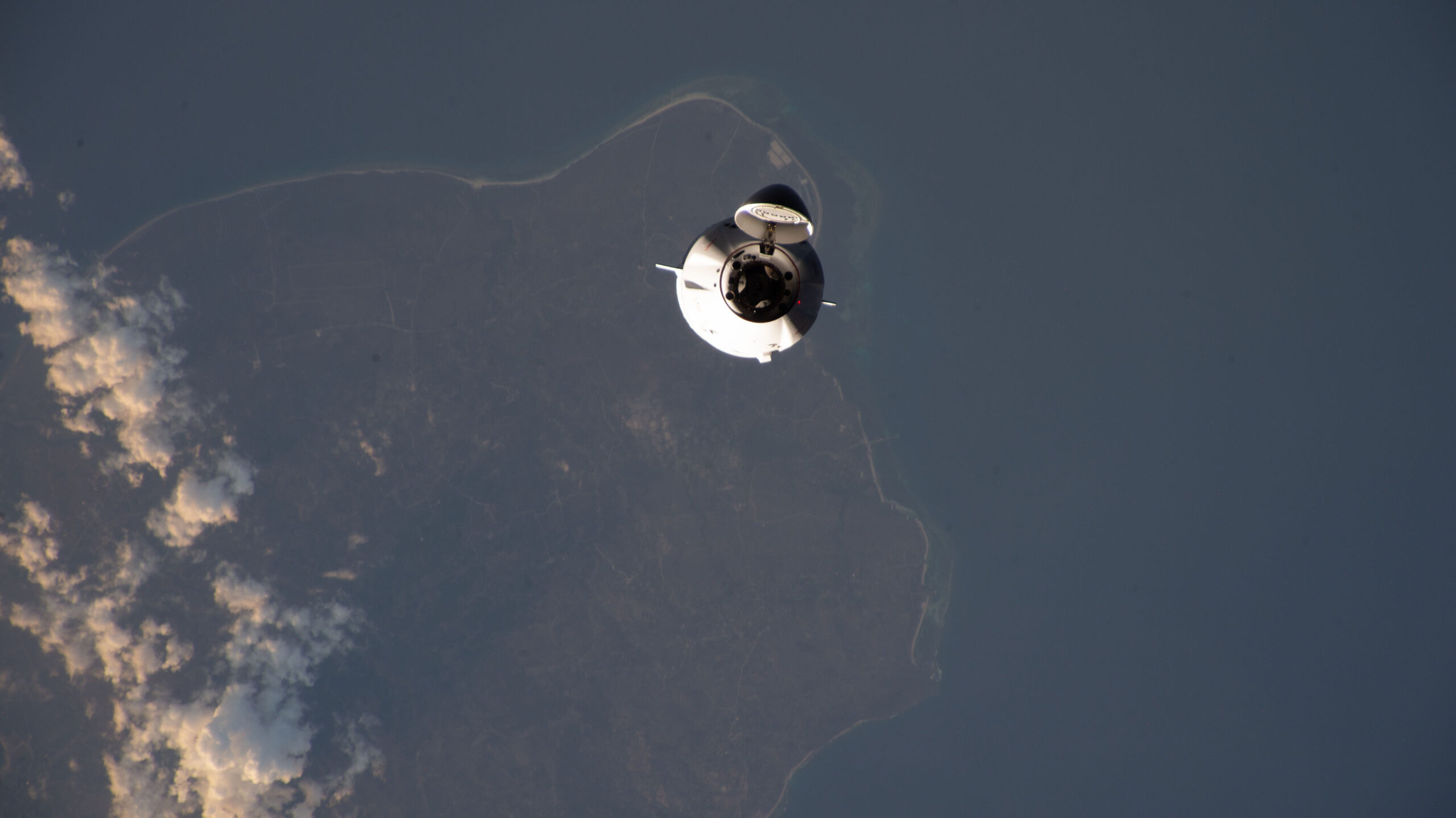

However the cargo ship’s departure, initially slated for 14 December, discovered itself delayed nearly a full week, as a chilly entrance handed via Florida and particularly impacted the first splashdown zone. Lastly, CRS-29 undocked at 5:05 p.m. EST Thursday, after a docked interval of greater than 40 days, one of many longest of any Cargo Dragon, concentrating on splashdown on Friday.

