A survey of over 1,500 supernovas carried out by the Darkish Power Digicam has positioned robust constraints on the accelerating enlargement of the universe.
The outcomes recommend that the mysterious power that drives this cosmic acceleration, darkish power, might change over time, various in density, which calls the usual mannequin of cosmology into query.
Associated: Darkish power stays a thriller as Einstein’s principle of gravity passes one other check
The outcomes have been delivered by the most important pattern of supernovas ever harvested by a single instrument as a part of the Darkish Power Survey. Supernovas have been integral to the invention within the late Nineteen Nineties that not solely is the universe increasing, however it’s also doing so at an accelerating fee.
That was an enormous shock to physicists, who had anticipated that after the preliminary speedy inflation of the cosmos throughout the Large Bang. Cosmic enlargement ought to have slowed down, however it’s rushing up.
Darkish power was urged as a placeholder for no matter unknown side of the universe is inflicting that mysterious and troubling cosmic acceleration, however scientists cannot say for sure what it’s. That downside is compounded by the truth that darkish power is now thought to account for 65% to 70% of the whole power and matter within the cosmos.
The Darkish Power Survey carried out by the Darkish Power Digicam mounted on the Víctor M. Blanco 4-meter Telescope at Cerro Tololo Inter-American Observatory in Northern Chile reveals that observations of supernovas stay integral to fixing the thriller that such investigations triggered 25 years in the past.
The brand new Darkish Power Survey outcomes have been introduced on the 243rd assembly of the American Astronomical Society on Jan. 8, 2024, with the group behind them including they’re per the usual mannequin of cosmology, the so-called “Lambda chilly darkish matter” mannequin (ΛCDM), that encompasses a universe with accelerating enlargement.
These place the tightest constraints on the historical past of enlargement all through the 13.8 billion-year historical past of the cosmos, however in addition they depart respiratory room for extra complicated fashions of the universe.
Investigating darkish power with normal candles
To collect this knowledge, the 570-megapixel Darkish Power Digicam constructed by Fermilab noticed the sky over Earth for 758 nights, observing 2 million distant galaxies. Inside these, the highly effective digicam noticed 1000’s of supernovas.
Of this pattern, machine studying was in a position to decide that 1,499 have been a particular kind of stellar explosion referred to as a Sort Ia supernova. These happen when useless stars referred to as white dwarfs, which have lengthy exhausted hydrogen to drive nuclear fusion and convert to helium of their cores, exist in a binary system with one other star.
The white dwarfs drag materials from their companion or “donor” star, and as this matter piles up on the useless star, it might push the white dwarf past the so-called Chandrasekhar restrict. That is the mass restrict {that a} star must go supernova.
These Sort Ia supernovas are so uniform that scientists confer with them as “normal candles,” and their gentle can be utilized to measure huge distances throughout the cosmos.
Moreover, as a result of the wavelength of sunshine from distant objects is stretched towards the pink finish of the electromagnetic spectrum, a course of referred to as “redshift,” as they transfer away from Earth, the uniform gentle output of ordinary candles at various distances can be utilized to measure the enlargement of the universe.
Evaluating the redshift of nearer Sort Ia supernovas to the redshift of extra distant, and thus earlier, white dwarf explosions can, subsequently, give a touch on the energy of this enlargement and thus the density of darkish matter on the corresponding intervals in cosmic historical past.
The brand new Darkish Power Survey outcomes triple the identified variety of supernovas at a redshift of round 0.2, which corresponds to a distance of about 2.5 billion light-years away. It quintuples the identified variety of normal candles with a redshift of round 0.5, which correlates to a distance of round 6 billion light-years away.
“It is a actually large scale-up from 25 years in the past when solely 52 supernovae have been used to deduce darkish power,” Darkish Power Survey working group member and College of Queensland professor Tamara Davis said in a statement.
Darkish power wasn’t all the time so dense
With such a bigger pattern measurement of Sort Ia supernovas throughout such a width of cosmic distances, the group may hint out a report of cosmic enlargement when combining the distances of those explosions with the velocity at which they’re receding from Earth.
This acted as a sign of whether or not darkish power density had remained secure, which appeared to not be the case.
“Because the universe expands, the matter density goes down,” Darkish Power Survey director and spokesperson Wealthy Kron mentioned in the identical assertion. “But when the darkish power density is a continuing, which means the whole proportion of darkish power should be growing as the quantity will increase.”
This is likely to be a problem to the ΛCDM mannequin of the universe, a mathematical mannequin that describes how the universe evolves with only a few key options just like the density of matter, the kind of matter, and the habits of darkish power.
That’s as a result of ΛCDM assumes the density of darkish power is fixed and does not dilute because the universe expands, one thing these supernova survey outcomes recommend might not be true.
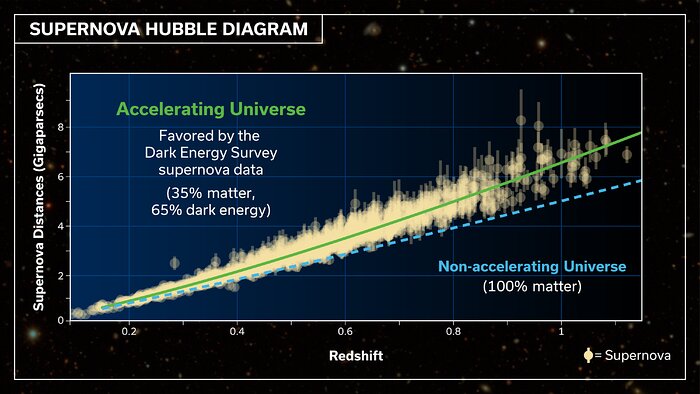
“There are tantalizing hints that darkish power modifications with time. We discover that the best mannequin of darkish power — ΛCDM — shouldn’t be the very best match,” Davis added. “It is not to this point off that we have dominated it out, however within the quest to know what’s accelerating the enlargement of the universe, that is an intriguing new piece of the puzzle. A extra complicated rationalization is likely to be wanted.”
Solutions to this conundrum might have to attend till the subsequent era of supernova surveys will get began and picks up from the Darkish Power Survey.
“This consequence clearly reveals the worth of astronomical survey tasks that proceed to yield wonderful science nicely after knowledge assortment has ended,” Nationwide Science Basis Astronomical Sciences Division program director Nigel Sharp mentioned in the identical assertion.
“We’d like as many numerous approaches as we are able to get with a view to perceive what darkish power is and what it isn’t. This is a vital path to that understanding.”
The Darkish Power Survey outcomes have been submitted to the Astrophysical Journal.

