Very quickly, a robotic surgeon could start its orbit round our planet — and although it will not fairly be a metallic, humanoid machine sporting a white coat and holding a scalpel, its mission is fascinating nonetheless.
On Tuesday (Jan. 30), scientists might be sending a slew of revolutionary experiments to the Worldwide Area Station by way of Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft. It is scheduled to launch no sooner than 12:07 p.m. ET (1707 GMT) and, if all goes to plan, arrive on the ISS a number of days in a while Feb. 1.
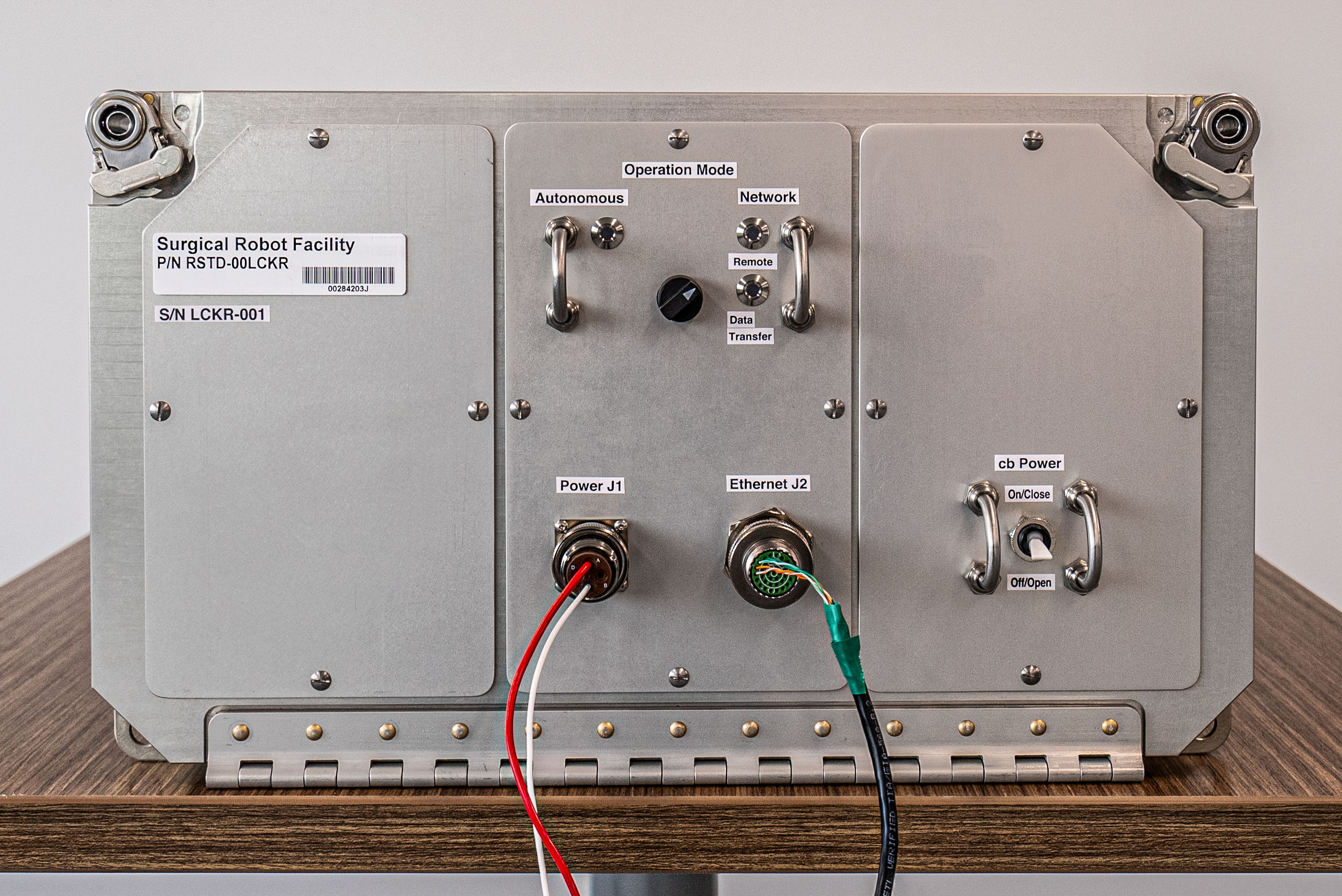
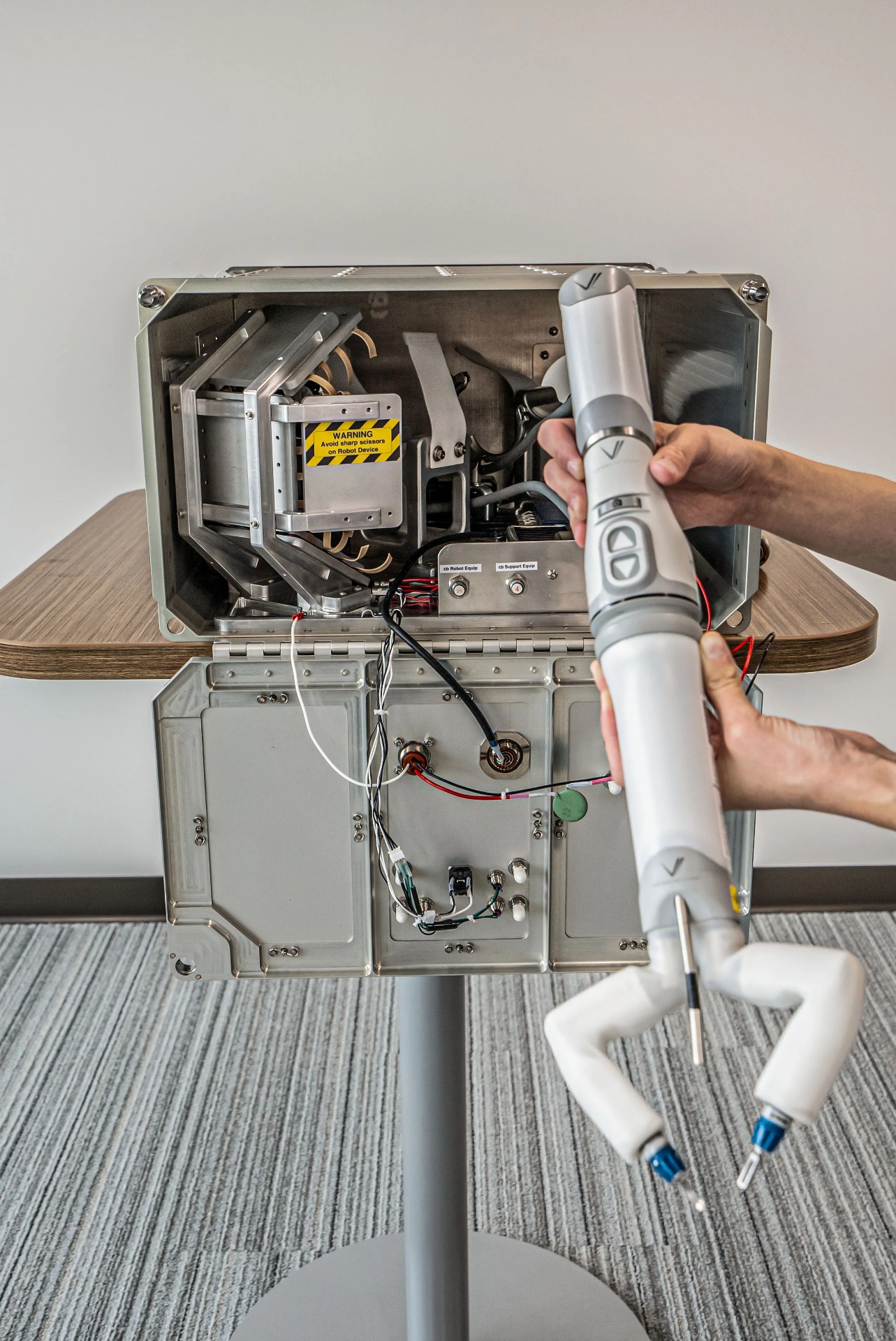
Certainly one of many experiments onboard is a two-pound (0.9-kilogram) robotic system, about so long as your forearm, with two controllable arms that respectively maintain a grasper and a pair of scissors. Developed by an organization named Digital Incision, this physician robotic of kinds is constructed to sometime be capable to talk with human docs on the bottom whereas inserting itself into an astronaut affected person to conduct medical procedures with excessive accuracy.
“The extra superior a part of our experiment will management the system from right here in Lincoln, Nebraska, and dissect simulated surgical tissue on orbit,” Shane Farritor, co-founder of Digital Incision, stated throughout a presentation about Cygnus on Friday.
For now, because it’s in preliminary phases, it will be examined on rubber bands — however the workforce has excessive hopes for the long run as missions to the moon, Mars and past begin rolling down the area exploration pipeline. Distant area drugs has develop into a scorching subject throughout the previous couple of years as area companies and personal area corporations lay plans for a wide range of future crewed area missions.
Associated: Worldwide Area Station will host a surgical robotic in 2024
NASA’s Artemis Program, as an example, hopes to have boots on the moon in 2026 — plus, that is purported to pave the best way for a day on which humanity can say they’ve reached the Pink Planet. And collectively, these missions are anticipated to pave the best way for a far future wherein humanity embarks on deeper area journey, maybe to Venus or, if we’re actually dreaming, past the photo voltaic system. So to verify astronauts stay secure in area — an setting they’re actually not made to outlive in — scientists need to make certain space-based medical remedy sees development in tandem with the rockets that’ll take these astronauts wherever they are going.
A fast instance that involves thoughts is how, in 2021, NASA flight surgeon Josef Schmid was “holoported” to the ISS by way of HoloLens know-how. It is type of like digital actuality meets FaceTime meets augmented actuality, if that is smart.

Nonetheless, because the workforce explains, not solely may this robotic surgical procedure mission profit folks exploring the void of area, but additionally these residing proper right here on Earth. “When you’ve got a specialist who’s an excellent surgeon, that specialist may dial into totally different places and assist with telesurgery or distant surgical procedure,” Farritor stated. “Solely about 10% of working rooms at the moment are robotic, however we do not see any cause that should not be 100%.”

This could be a very essential benefit for hospitals in rural areas the place fewer specialists can be found, and the place working rooms are restricted. In reality, as Farritor defined, not solely is Digital Incision funded by NASA but additionally by the army. “Each teams need to do surgical procedure in loopy locations,” he stated, “and our small robots form of lend themselves to mobility like that.”
What else goes up?
The little robotic physician might be removed from alone on the Cygnus spacecraft because it heads to the ISS; throughout the identical presentation wherein Farritor mentioned Digital Incision, different specialists talked about what they’re going to be sending up come Monday.
For one, it’s going to have a robotic buddy becoming a member of it within the orbital laboratory — a robotic arm. This arm has already been examined inside the station’s constraints earlier than, however with this new mission the workforce hopes to check it in totally unpressurized situations.
“Unplugging, replugging, shifting objects, that is the form of stuff that we did with the primary investigation,” stated Might Murphy, the director of packages at firm NanoRacks. “We’re form of stepping up the complexity … we’ll change off which instruments we’re utilizing, we’ll be capable to use screwdriver analogs and issues like that; that can allow us to do much more work.”
“We will take a look at even past simply taking away one thing that the crew must spend time engaged on,” she continued. “Now, we even have the capability to do extra work in harsher environments we do not essentially need to expose the crew to.”
The European Area Company, in the meantime, might be sending a 3D-printer that may create small metallic components. The objective right here is to see how the construction of 3D-printed metallic fares in area when in comparison with Earth-based 3D-printed metallic. 3D-printed semiconductors, key parts of most digital units, might be examined as effectively for the same cause.
“After we discuss having autos in area for longer durations of time with out with the ability to convey provides up and down, we want to have the ability to print a few of these smaller components in area, to assist the integrity of the automobile over time,” stated Meghan Everett, NASA’s ISS program deputy scientist.
Per Everett, this might additionally assist scientists be taught whether or not some kinds of supplies that are not 3D-printable on Earth may be 3D-printed in area. “Some preliminary information means that we are able to really produce higher merchandise in area in comparison with Earth which might straight translate to higher electronics in vitality producing capabilities,” she stated.
One other experiment getting launched on Monday seems to be on the results of microgravity on bone loss. Referred to as MABL-A, it would take a look at the position of what’re often called mesenchymal cells (related to bone marrow) and the way that may change when uncovered to the area setting. This might provide perception into astronaut bone loss — a well-documented, main situation for area explorers — in addition to into the dynamics of human growing old. “We may also take a look at the genes which are concerned in bone formation and the way gravity affected them,” stated Abba Zubair, a professor of Laboratory Drugs and Pathology at Mayo Clinic.
Lisa Carnell, division director for NASA’s Organic and Bodily Sciences Division, spoke concerning the Apex-10 mission headed up, which is able to see how plant microbes work together in area. This might assist decode the best way to improve plant productiveness on Earth, too.
Computer systems and retinas
Two of the opposite key experiments mentioned through the presentation embrace an area pc and a man-made eye — effectively, a man-made retina, to be actual. We’ll begin with the latter.
Nicole Wagner, CEO of an organization named LambdaVision, has a staggering objective: To revive imaginative and prescient to the tens of millions of sufferers which are blinded by finish stage retinal degenerative illnesses like macular degeneration and retinitis pigmentosa.
To do that, she and her workforce are attempting to develop a protein-based synthetic retina that is constructed by way of a course of often called “electrostatic layer-by-layer deposition.” Briefly, this consists of depositing a number of layers of a particular form of protein onto a scaffold. “Consider the scaffold virtually like a tightly woven piece of gauze,” Wagner stated.
Nonetheless, as she explains, this course of on Earth may be impeded by the results of gravity. And any imperfections within the layers can just about destroy the factitious retina’s efficiency. So … what about in microgravity? Up to now, LambdaVision has flown greater than eight missions to the ISS, she says, and the experiments have proven that microgravity does certainly generate extra homogenous layers and subsequently higher skinny movies for the retina.
“On this mission,” she stated, “we’re sending a powdered type of bacteriorhodopsin to the ISS that can then be resuspended into an answer, and we might be utilizing particular devices, on this case spectrometers, to take a look at the protein high quality and purity on the Worldwide Area Station, in addition to to validate this course of used to get the protein into resolution.”
May you think about if docs would be capable to fee a number of synthetic retinas to be developed in area sometime, then delivered to the bottom for implantation right into a affected person. And that this complete course of may give somebody their sight again?
As for the area pc, Mark Fernandez, principal investigator for the Spaceborne Laptop-2 challenge, posed a hypothetical. “Astronauts go on a spacewalk, and after their work day, the gloves are examined for wear-and-tear,’ he stated. “This have to be carried out by each astronaut, after each spacewalk, earlier than the gloves can be utilized once more.”
Usually, Fernandez explains, the workforce takes a bunch of high-resolution pictures of the doubtless contaminated gloves, then sends these pictures out for evaluation.

This evaluation, he says, usually takes one thing like 5 days to complete and return. So, hoping to resolve the issue, the workforce developed an AI mannequin in collaboration with NASA and Microsoft that may do the evaluation straight on the station and flag areas of concern. Every takes about 45 seconds to finish. “We’re gonna go on from 5 days to just some minutes,” he stated, including that the workforce additionally did DNA evaluation usually performed on the area station in about 12 minutes. Usually, he emphasised, that’d take months.
However, the workforce needs to verify Spaceborne Laptop-2’s servers will perform correctly whereas on the ISS, therefore the Cygnus payload. This can mark the company’s third ISS mission.
“The ISS Nationwide Lab has so many advantages that it is attributing to our nation,” Carnell stated. “It creates a universe of latest potentialities for the following technology of scientists and engineers.”

