
‘Hidden’ stars together with a brand new sort of aged large nicknamed ‘outdated smoker’ have been noticed for the primary time by astronomers. The thriller objects exist on the coronary heart of our Milky Approach galaxy and may sit quietly for many years—fading nearly to invisibility—earlier than out of the blue puffing out clouds of smoke, in keeping with new analysis revealed within the Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
A global crew of scientists led by Professor Philip Lucas, of the College of Hertfordshire, made their ground-breaking discovery after monitoring nearly a billion stars in infrared gentle throughout a 10-year survey of the night time sky.
The papers, “Probably the most variable VVV sources: eruptive protostars, dipping giants within the Nuclear Disk and others,” “Spectroscopic affirmation of high-amplitude eruptive YSOs and dipping giants from the VVV survey” and “On the incidence of episodic accretion in Class I YSOs from VVV,” have all been revealed within the Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
In addition they detected dozens of rarely-seen new child stars, referred to as protostars, which bear excessive outbursts over a interval of months, years or many years, as a part of the formation of a brand new photo voltaic system.
Most of those newly-spotted stars are hidden from view in seen gentle by massive quantities of mud and gasoline within the Milky Approach—however infrared gentle can get via, permitting scientists to see them for the primary time.
Astronomers from the UK, Chile, South Korea, Brazil, Germany and Italy carried out their analysis with the assistance of the Seen and Infrared Survey Telescope (VISTA)—a British-built telescope excessive within the Chilean Andes at Cerro Paranal Observatory, which is a part of the European Southern Observatory (ESO).
The crew saved a watchful eye on a whole bunch of hundreds of thousands of stars and analyzed 222 that confirmed the biggest adjustments in brightness.

Professor Lucas stated, “About two-thirds of the celebrities had been simple to categorise as well-understood occasions of assorted varieties.
“The remaining had been a bit harder so we used ESO’s Very Massive Telescope to get spectra of a lot of them individually. A spectrum exhibits us how a lot gentle we are able to see at a ramification of various wavelengths, giving a a lot clearer thought of what we’re .”
The work was carried out as a part of a long-term survey known as “VISTA Variables within the Through Lactea,” or VVV.
Dr. Zhen Guo, previously of the College of Hertfordshire and now primarily based on the College of Valparaiso in Chile, led the work on the spectra.
He stated, “Our most important goal was to search out rarely-seen new child stars, additionally known as protostars, whereas they’re present process a fantastic outburst that may final for months, years, and even many years.
“These outbursts occur within the slowly spinning disk of matter that’s forming a brand new photo voltaic system. They assist the new child star within the center to develop, however make it tougher for planets to type.
“We do not but perceive why the disks change into unstable like this.”
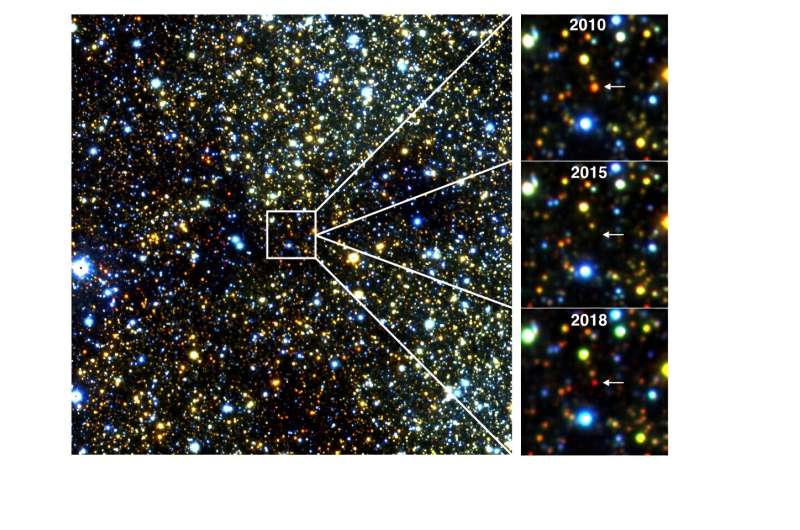
The crew found 32 erupting protostars that elevated in brightness at the least 40-fold, and in some instances over 300-fold.
Many of the eruptions are nonetheless ongoing, permitting astronomers for the primary time to investigate a big batch of those mysterious occasions all through their evolution—from the preliminary quiescent state, via the height of brightness, and into the declining stage.
Nonetheless, the examine additionally threw up one thing utterly surprising.
There have been 21 purple stars close to the middle of the Milky Approach that confirmed ambiguous adjustments in brightness in the course of the 10-year survey.
Professor Lucas stated, “We weren’t certain if these stars had been protostars beginning an eruption, or recovering from a dip in brightness brought on by a disk or shell of mud in entrance of the star—or in the event that they had been older large stars throwing off matter within the late phases of their life.”
Evaluation of the spectra for seven of those stars, in contrast with knowledge from earlier surveys, concluded that they had been in reality a brand new sort of purple large star.
Professor Dante Minniti at Andrés Bello College, Chile, founding father of the VVV survey, stated, “These aged stars sit quietly for years or many years after which puff out clouds of smoke in a completely surprising manner. They give the impression of being very dim and purple for a number of years, to the purpose that typically we won’t see them in any respect.”
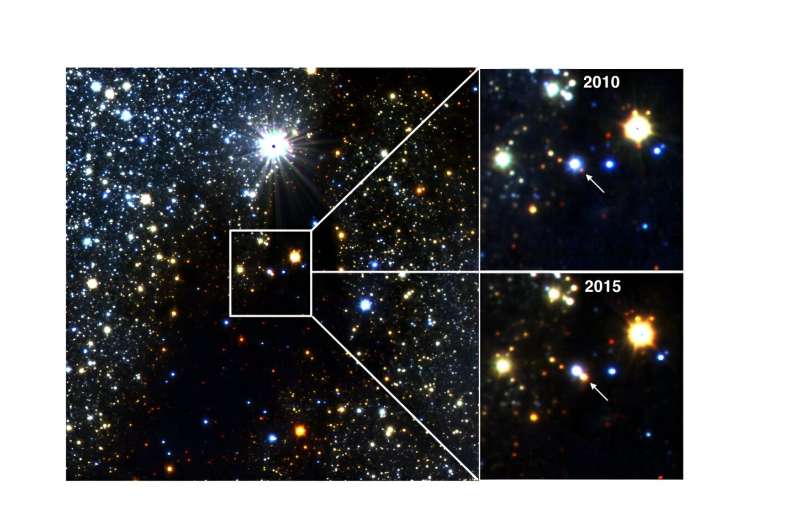
An extra clue about this new discovery lies within the location of those dwindling large stars. They’re closely concentrated within the innermost a part of the Milky Approach, referred to as the Nuclear Disk, a area the place stars are usually richer in heavy components than anyplace else.
This could make it simpler for mud particles to condense out of gasoline within the comparatively cool outer layers of purple large stars. Nonetheless, how this results in the ejection of puffs of dense smoke that the crew noticed stays a thriller.
The researchers stated their discoveries might change what we learn about the best way that components are distributed throughout area, as Professor Lucas explains.
“Matter ejected from outdated stars performs a key position within the life cycle of the weather, serving to to type the subsequent era of stars and planets,” he stated.
“This was thought to happen primarily in a well-studied sort of star known as a Mira variable.
“Nonetheless, the invention of a brand new sort of star that throws off matter might have wider significance for the unfold of heavy components within the Nuclear Disk and metal-rich areas of different galaxies.”
Extra info:
Phil Lucas et al, Probably the most variable VVV sources: eruptive protostars, dipping giants within the Nuclear Disc and others, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad3929
Zhen Guo et al, Spectroscopic affirmation of high-amplitude eruptive YSOs and dipping giants from the VVV survey, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad3700
Carlos Contreras Peña et al, On the incidence of episodic accretion in Class I YSOs from VVV, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad3780
Zhen Guo et al, Multi-wavelength detection of an ongoing FUOr-type outburst on a low-mass YSO, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnrasl/slad201
Quotation:
‘Previous people who smoke’ and ‘squalling newborns’ amongst hidden stars noticed for first time (2024, January 25)
retrieved 25 January 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

