
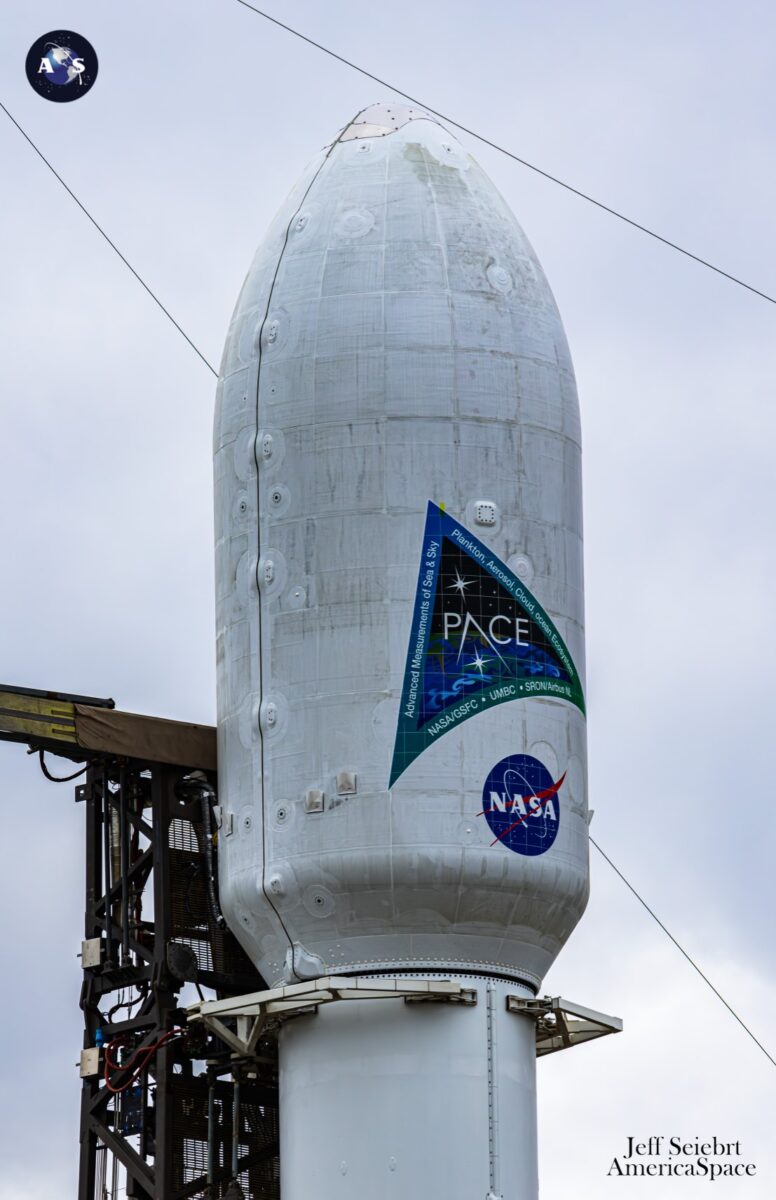
Following a pair of 24-hour postponements, due to unfavorable weather conditions on the Area Coast and higher-than-allowable ground winds preventing critical pre-launch checkouts, NASA’s $805 million Plankton, Aerosol, Cloud, Ocean Ecosystem (PACE) mission is formally underway, having taken flight at 1:33:36 a.m. EST Thursday atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 booster from storied Area Launch Complicated (SLC)-40 at Cape Canaveral Area Drive Station, Fla. The spacecraft and its three scientific devices—a first-of-its-kind optical spectrometer and a pair of multi-angle polarimeters—have been a decade within the making and can spend as much as a decade in low-Earth orbit performing important measurements of our planet’s ambiance and oceans on a worldwide scale.
“Congratulations to the PACE workforce on a profitable launch,” stated NASA Administrator Invoice Nelson. “With this new addition to NASA’s fleet of Earth-observing satellites, PACE will assist us be taught, like by no means earlier than, how particles in our ambiance and our oceans can determine key components impacting international warming. Missions like this are supporting the Biden-Harris Administration’s local weather agenda and serving to us reply pressing questions on our altering local weather.”
Launching PACE was the four-times-flown B1081 booster core, which entered service final August to ship Dragon Endurance and her Crew-7 quartet of NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli, Denmark’s Andreas Mogensen of the European Area Company (ESA), Satoshi Furukawa of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Company (JAXA) and Russian cosmonaut Konstantin Borisov to the Worldwide Area Station (ISS), the place they presently reside. Two further launches of B1081 final November and December delivered SpaceX’s CRS-29 Cargo Dragon for a month-long analysis keep on the area station and a 23-strong batch of Starlink low-orbiting web communications satellites.
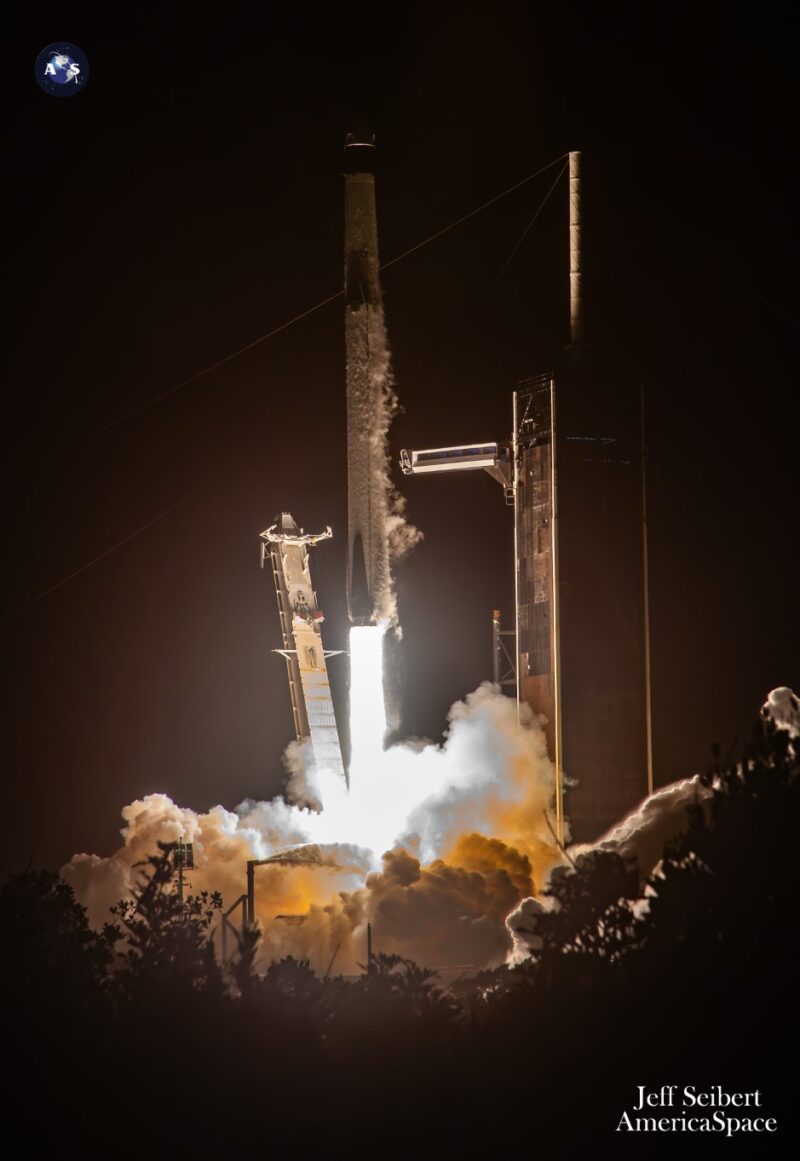

Liftoff of PACE was initially scheduled for 1:33 a.m. EST Tuesday, however with climate hovering no larger than 50-50 favorability, NASA and SpaceX groups opted late Monday to name off the primary launch try and refocus on Wednesday as a substitute. SpaceX additionally tweeted on X that prime winds on the Cape’s Touchdown Zone (LZ)-1, the place B1081 was set to make a solid-ground landing, had been additionally unfavorable.
This grim image made it not unreasonable for groups to face down effectively upfront of Tuesday’s launch try and refocus on Wednesday’s pre-dawn hours when the Likelihood of Go (PGo) was predicted to enhance to 95 p.c. Solely a “very low danger” of a Cumulus Cloud Rule violation stood in PACE’s means for Wednesday.

However yesterday additionally proved to not be an excellent day, because the long-awaited launch was once more known as off resulting from higher-than-allowable floor winds that precluded a number of important pre-flight checkouts of the automobile. Though PACE’s prime T-0 level, which has sat at 1:33 a.m. EST every day this week, shouldn’t be strictly “instantaneous”, it solely provided a roughly 90-second time frame, with SpaceX and NASA groups aiming for the center of the “launch window” so as to depart the second half obtainable to accommodate potential Collision Avoidance (COLA) concerns.
By Thursday, nonetheless, the climate had begun to show a nook and the excessive winds started to subside. “Winds will lower and veer from the north to the northeast,” famous the forty fifth Climate Squadron in an replace yesterday afternoon. “Whereas a couple of low-topped coastal showers can’t be dominated out within the night/in a single day hours, dry mid-level air will cap off any vital vertical growth.

“Excessive stress will stay in management and comparable situations will persist by way of the rest of the week,” the forty fifth concluded. “For each the first launch window early Thursday morning and backup window early Friday morning, climate appears very favorable with the one concern being the very low danger of a Cumulus Cloud Rule violation.”
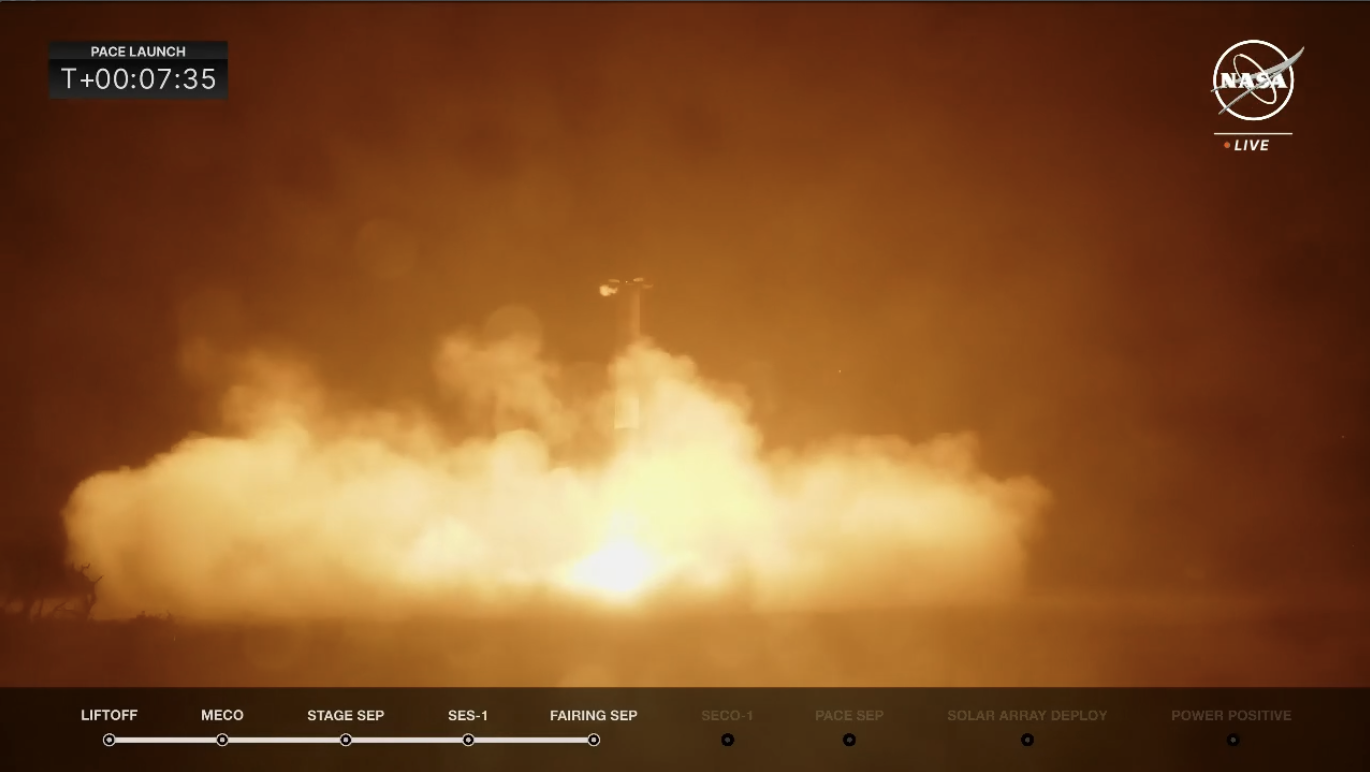
Initially monitoring a liftoff at 1:33:32 a.m. EST, the T-0 level slipped barely by 4 seconds in response to an anticipated COLA conjunction. Because the clock handed T-1 minute and the Falcon 9 flight computer systems transitioned to “Startup”, the joy started to construct as a mission that had been a decade within the making approached fruition.

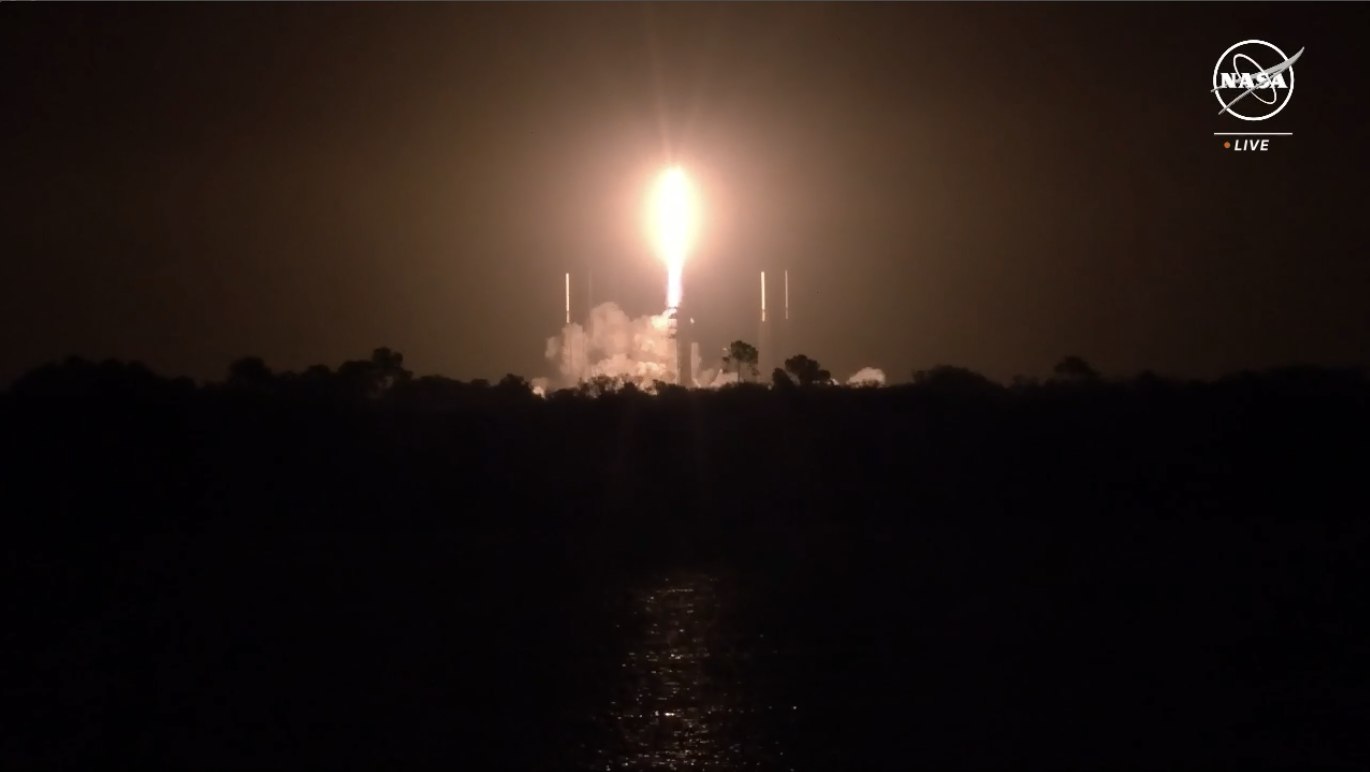
“Many on the PACE Spacecraft Staff now going outdoors to observe this launch,” reported NASA commentator Derrol Nail at T-45 seconds. “It ought to be a magnificence.”
His phrases couldn’t have been higher chosen and B1081 roared aloft completely, kicking ofF SpaceX’s inaugural mission of February. “Liftoff of the Falcon 9 and PACE,” exulted Mr. Nail. “Serving to “preserve tempo” with our ever-changing ambiance and ocean.”

B1081 powered the 230-foot-tall (70-meter) stack uphill for opening 2.5 minutes of ascent, earlier than separating and executing a picture-perfect descent to alight on strong floor on the Cape’s Touchdown Zone (LZ)-1 at T+7 minutes and 30 seconds. In the meantime, the only Merlin 1D+ Vacuum engine of the Falcon 9’s second stage burned longer than regular on this mission—igniting at T+2 minutes and 30 seconds and working for nearly eight full minutes—in what Mr. Nail described as a “direct-inject” to get PACE into its 420-mile-high (675-kilometer) polar orbit at 98 levels of inclination.
Spacecraft separation occurred at 12 minutes and 22 seconds into the flight.

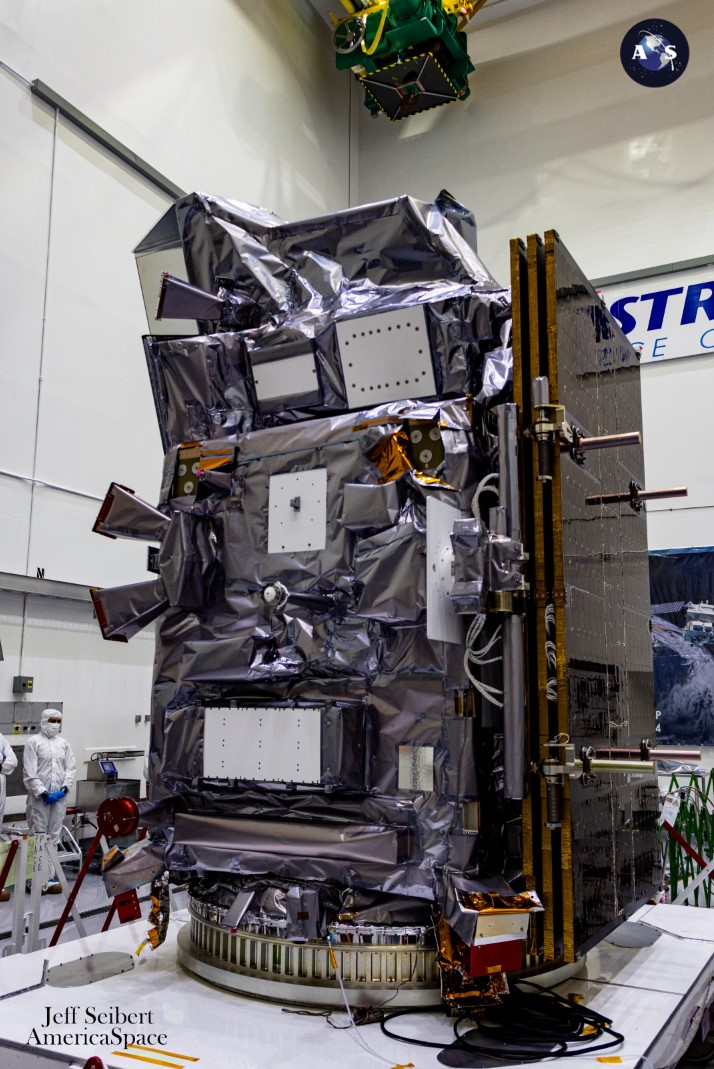
Weighing 3,750 kilos (1,700 kilograms), PACE is managed by NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle (GSFC) in Greenbelt, Md. It would present international views of microscopic algae concentrations, often called “phytoplankton”, which occupy the sunlit higher a part of the oceans and produce no less than half of Earth’s oxygen and forming the bottom of the marine meals chain.
Quantifying phytoplankton ranges, NASA noted, carries vital implications for increasing human information of the carbon cycle and monitoring climatic variability and alter over time. “Understanding extra about international phytoplankton neighborhood composition will assist us perceive how dwelling marine sources reply to a altering local weather,” stated Undertaking Scientist Jeremy Werdell of GSFC. “With PACE, we’ll be taught extra in regards to the function of marine phytoplankton within the international carbon cycle.”
In June 2016, PACE transitioned out of its preliminary design section at Key Resolution Level-A (KDP-A) and the next September NASA opted to build the spacecraft “in-house”. This resolution enabled instrument designs and capabilities to mature because the mission developed, in addition to affording improved flexibility to fulfill budgetary and schedule challenges and in recognition of the truth that all of the requisite engineering services and core competencies had been available at GSFC.
Passing Key Resolution Level-B (KDP-B) in August 2017, the “tempo” of PACE accelerated because the design of the spacecraft and its main instrument, the GSFC-furnished Ocean Shade Instrument (OCI) acquired underway. Described as a first-of-its-kind optical spectrometer by way of functionality, OCI will take hyperspectral measurements of the oceans, masking a broader swath of the electromagnetic spectrum than any of its predecessor missions.
“We’re going to take a look at every part within the vary from ultraviolet all the best way out to shortwave infrared,” stated PACE Undertaking Supervisor André Costume of GSFC. “Different missions have solely taken slices, and whereas that provides you good knowledge, it doesn’t offer you all the details about various kinds of phytoplankton life within the ocean.”
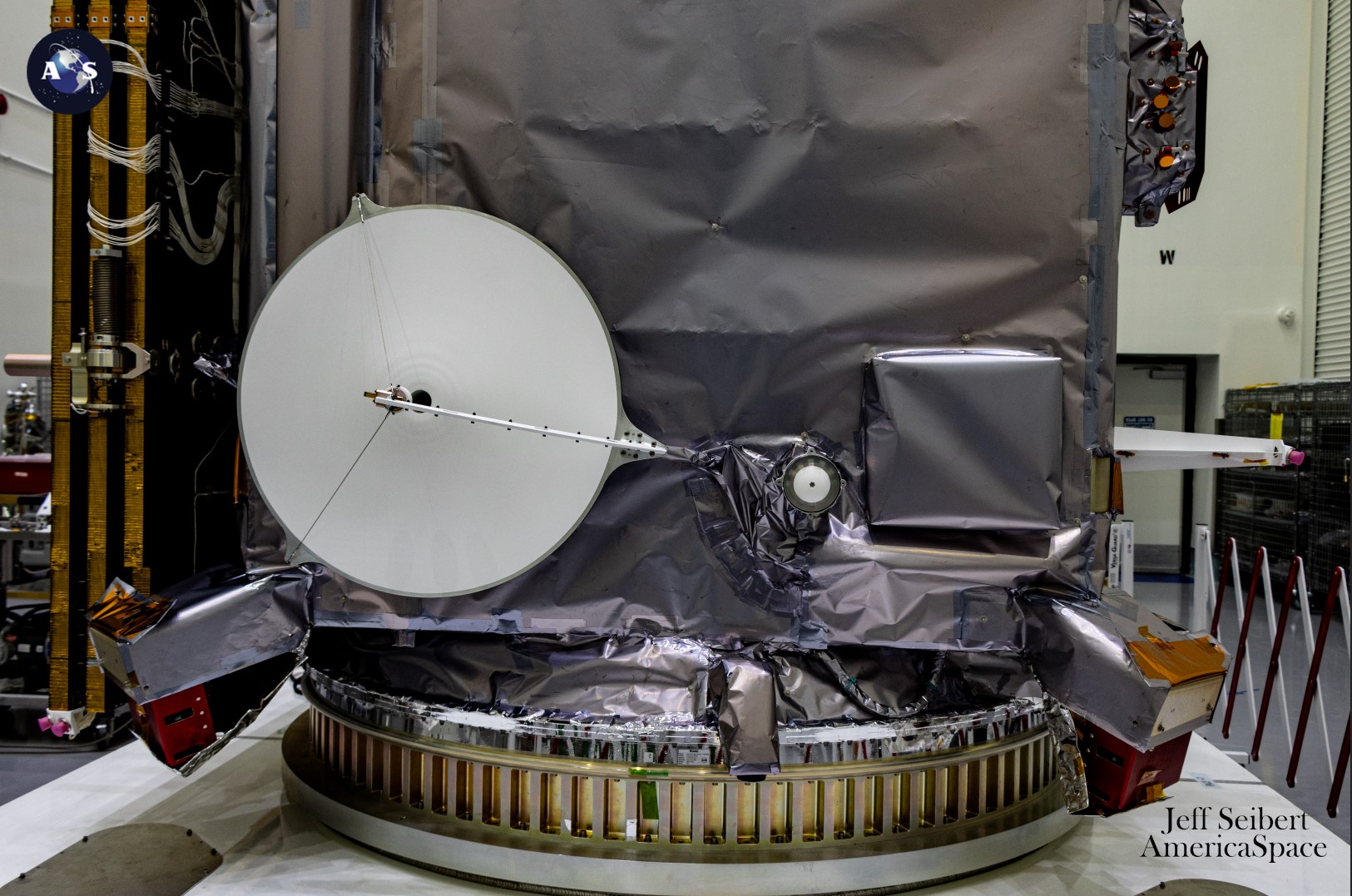
Additionally sharing payload area aboard PACE are a pair of multi-angle polarimeters: the Hyper-Angular Rainbow Polarimeter-2 (HARP-2)—a follow-on from HARP, an preliminary hyper-angular rainbow polarimeter deployed from the ISS as a CubeSat in February 2020—and the Spectropolarimeter for Planetary Exploration (SPEXone). Developed by the College of Maryland, Baltimore County (HARP-2) and the Netherlands Institute for Area Analysis (SRON) and Airbus Defence and Area Netherlands (SPEXone), these devices will precisely characterize aerosol properties and particulate sizes and compositions with unprecedented ranges of accuracy and element.

Collectively, the information output from OCI, HARP-2 and SPEXone will allow higher quantification of phytoplankton and aerosol-particle results upon marine biology, ocean chemistry and the house planet’s power finances and ecological forecasting. PACE will allow scientists to higher monitor fisheries, determine dangerous algal “blooms” and observe modifications over time in marine sources.
“Observations and scientific analysis from PACE will profoundly advance our information of the ocean’s function within the local weather cycle,” stated Karen St. Germain, director of the Earth Science Division throughout the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington. “As an open-source science mission with early adopters prepared to make use of its analysis and knowledge, PACE will speed up our understanding of the Earth system and assist NASA ship actionable science, knowledge, and sensible purposes to assist our coastal communities and industries tackle quickly evolving challenges.”

“It’s been an honor to work with the PACE workforce and witness firsthand their dedication and tenacity in overcoming challenges, together with the worldwide pandemic, to make this observatory a actuality,” stated Marjorie Haskell, PACE program govt at NASA Headquarters. “The eagerness and teamwork are matched solely by the joy of the science neighborhood for the information this new satellite tv for pc will present.”
Consideration now turns to Vandenberg Area Drive Base, Calif., the place one other Falcon 9 is gearing up for launch with a 22-strong batch of Starlink web communications satellites afterward Thursday. Postponed yesterday resulting from poor climate on the West Coast, the veteran B1071 booster is now focused to rise from Area Launch Complicated (SLC)-4E throughout a raft of T-0 factors extending from 4:56 p.m. PST by way of 8:54 p.m. PST.

