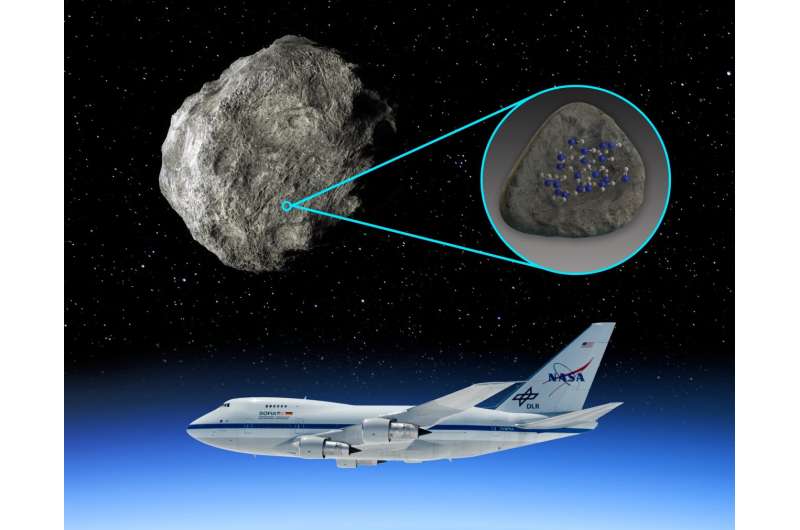
Utilizing knowledge from the retired Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA)—a joint mission of NASA and the German House Company at DLR—Southwest Analysis Institute scientists have found, for the primary time, water molecules on the floor of an asteroid. Scientists checked out 4 silicate-rich asteroids utilizing the FORCAST instrument to isolate the mid-infrared spectral signatures indicative of molecular water on two of them.
“Asteroids are leftovers from the planetary formation course of, so their compositions differ relying on the place they fashioned within the photo voltaic nebula,” stated SwRI’s Dr. Anicia Arredondo, lead creator of a paper in The Planetary Science Journal concerning the discovery. “Of specific curiosity is the distribution of water on asteroids, as a result of that may make clear how water was delivered to Earth.”
Anhydrous, or dry, silicate asteroids kind near the solar whereas icy supplies coalesce farther out. Understanding the placement of asteroids and their compositions tells us how supplies within the photo voltaic nebula had been distributed and have developed since formation. The distribution of water in our photo voltaic system will present perception into the distribution of water in different photo voltaic techniques and, as a result of water is important for all life on Earth, will drive the place to search for potential life, each in our photo voltaic system and past.
“We detected a characteristic that’s unambiguously attributed to molecular water on the asteroids Iris and Massalia,” Arredondo stated. “We based mostly our analysis on the success of the staff that discovered molecular water on the sunlit floor of the moon. We thought we may use SOFIA to seek out this spectral signature on different our bodies.”
SOFIA detected water molecules in one of many largest craters within the moon’s southern hemisphere. Earlier observations of each the moon and asteroids had detected some type of hydrogen however couldn’t distinguish between water and its shut chemical relative, hydroxyl. Scientists detected roughly equal to a 12-ounce bottle of water trapped in a cubic meter of soil unfold throughout the lunar floor, chemically certain in minerals.
“Primarily based on the band energy of the spectral options, the abundance of water on the asteroid is in line with that of the sunlit moon,” Arredondo stated. “Equally, on asteroids, water can be certain to minerals in addition to adsorbed to silicate and trapped or dissolved in silicate affect glass.”
The info from two fainter asteroids, Parthenope and Melpomene, had been too noisy to attract a definitive conclusion. The FORCAST instrument is outwardly not delicate sufficient to detect the water spectral characteristic if current. Nonetheless, with these findings, the staff is enlisting NASA’s James Webb House Telescope, the premier infrared house telescope, to make use of its exact optics and superior signal-to-noise ratio to analyze extra targets.
“Now we have performed preliminary measurements for one more two asteroids with Webb throughout cycle two,” Arredondo stated. “Now we have one other proposal in for the subsequent cycle to have a look at one other 30 targets. These research will enhance our understanding of the distribution of water within the photo voltaic system.”
Extra info:
Anicia Arredondo et al, Detection of Molecular H2O on Nominally Anhydrous Asteroids, The Planetary Science Journal (2024). DOI: 10.3847/PSJ/ad18b8
Quotation:
Scientists establish water molecules on asteroids for the primary time (2024, February 12)
retrieved 13 February 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.

