MONTREAL, CANADA — From simulators to house snacks, Artemis 2 astronauts are attempting to follow all aspects of moon dwelling earlier than they head towards the lunar floor in 2025.
Artemis 2 astronaut Jeremy Hansen emphasised right here at Canadian Area Company (CSA) headquarters that each element issues when preparing for the large mission, as it’s the first moon tour since 1972 that can have people on board.
The fixed follow, he advised reporters in a gaggle, helps “hold our expertise sharp, to problem ourselves … we’re continually in an operational surroundings the place you are making selections.”
CSA’s Hansen and his three NASA astronaut crewmates are virtually dwelling in mockups of their Orion spacecraft to learn to safely maneuver themselves in tight quarters. And amongst their duties to sort out is one thing mundane, but important: studying tips on how to keep slot in a tiny house whereas floating on a regular basis.
Associated: Astronauts will not stroll on the moon till 2026 after NASA delays subsequent 2 Artemis missions
Whereas Orion has 60% more room than the Apollo moon capsules of the Nineteen Sixties and Nineteen Seventies, it has to hold 4 astronauts as an alternative of three. Definitely, computer systems are wearable today as an alternative of the “single-room” machines of two generations in the past — and, NASA is aware of tips on how to pack effectively.
Nonetheless, getting something on board might be a problem.
“We’re very mass-constrained and space-constrained, and that does decide how a lot room now we have to convey issues,” Hansen mentioned, noting his restricted private gadgets will embrace a single pendant for his spouse and three youngsters. Orion only has 316 cubic feet (8.9 cubic meters) of house in it, which is one thing akin to a tiny bed room you’d discover in city areas like New York Metropolis or Singapore. Add in computer systems and tools, and that small house shrinks swiftly.
By these requirements, the six-bedroom-house-sized Worldwide Area Station appears extremely roomy. To that finish, Orion has no house for any of the massive train machines the ISS at the moment holds: a treadmill with straps to carry working astronauts down, a piston-driven weight machine to counteract “weightlessness,” and an train bicycle. Taken collectively, the train tools alone would require nearly triple the space of an Orion spacecraft, so new pondering is required.
Enter a conveyable answer: The flywheel.
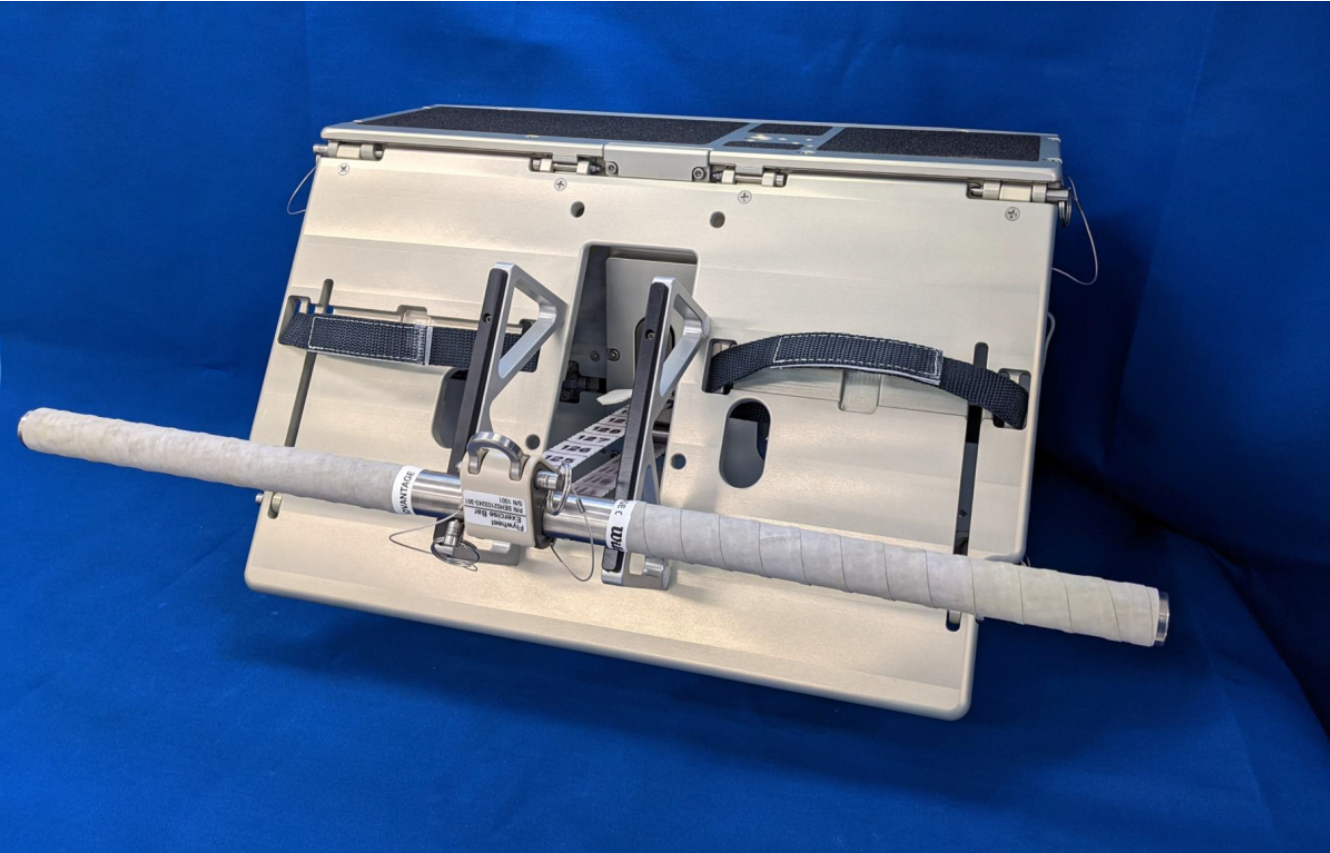
Variations of the flywheel have been floating round since at least 2016, when the machine for astronauts was known as ROCKY after the fictional boxer portrayed by Sylvester Stallone in quite a few movies. (That is Resistive Overload Mixed with Kinetic Yo-Yo, should you’re on the lookout for some band title inspiration.)
As we speak’s flywheel model is nested beneath the aspect hatch on Orion meant for getting into and exiting.
In true small house pondering, the machine acts as a step when the astronauts come inside throughout launch day. The crew will spend half-hour day by day doing squats and deadlifts utilizing cables on the machine that act like a yo-yo; easy changes additionally permit the flywheel to behave as a rowing machine.
The flywheel is tiny, smaller than a carry-on suitcase airways usually permit within the passenger cabin. It additionally has a mass of solely about three sacks of potatoes: 30 kilos, or 14 kilograms. However with small measurement comes a giant limitation: the elastic energy maxes out at solely 400 kilos (181 kilograms), which is fascinating contemplating related cables didn’t work so properly for ISS missions.
NASA used to have a weight-lifting machine on the ISS known as the Interim Resistive Exercise Device that additionally used cables that maxed out round 300 kilos (136 kg). Worse, stories from places like Wired point out workout routines like squats have been solely half as efficient in microgravity. The newer Superior Resistive Train System does away with energy workout routines “maxing out” by as an alternative utilizing pistons, serving to astronauts keep fitter for 180 days or extra in orbit. ARED is a key consider permitting astronauts to return house with extra bone mass than earlier than, peer-reviewed research shows.
Fortuitously, nevertheless, Orion is rated for shorter missions. The Artemis 2 astronauts ought to solely use the capsule for 10 days, and time in house will go up solely to a month on future missions. The worry of “deconditioning” in a floating surroundings is subsequently much less on this case, though medical professionals might finally think about different options.
“Because the missions get longer, that is one of many issues we have to take a look at: what’s the minimal quantity of train that you’ll want to carry out to keep up a sure stage of health?” mentioned Natalie Hirsch, CSA’s venture supervisor of operational house drugs, throughout a media gaggle and demonstration of flywheel.
Hirsch famous astronaut well being will not be the one factor to consider. As any lab supervisor is aware of, vibrations can induce sudden results in experiments or in tools. Orion engineers have by no means examined train tools in house, on condition that Artemis 1 flew uncrewed across the moon in 2022 and the spacecraft simply had a quick Earth-orbiting mission with out astronauts in 2014.
Astronaut train information on Artemis 2, Hirsch mentioned, will assist fortify the spacecraft design towards dangerous vibrations forward of extra formidable moon-landing missions later within the decade.

