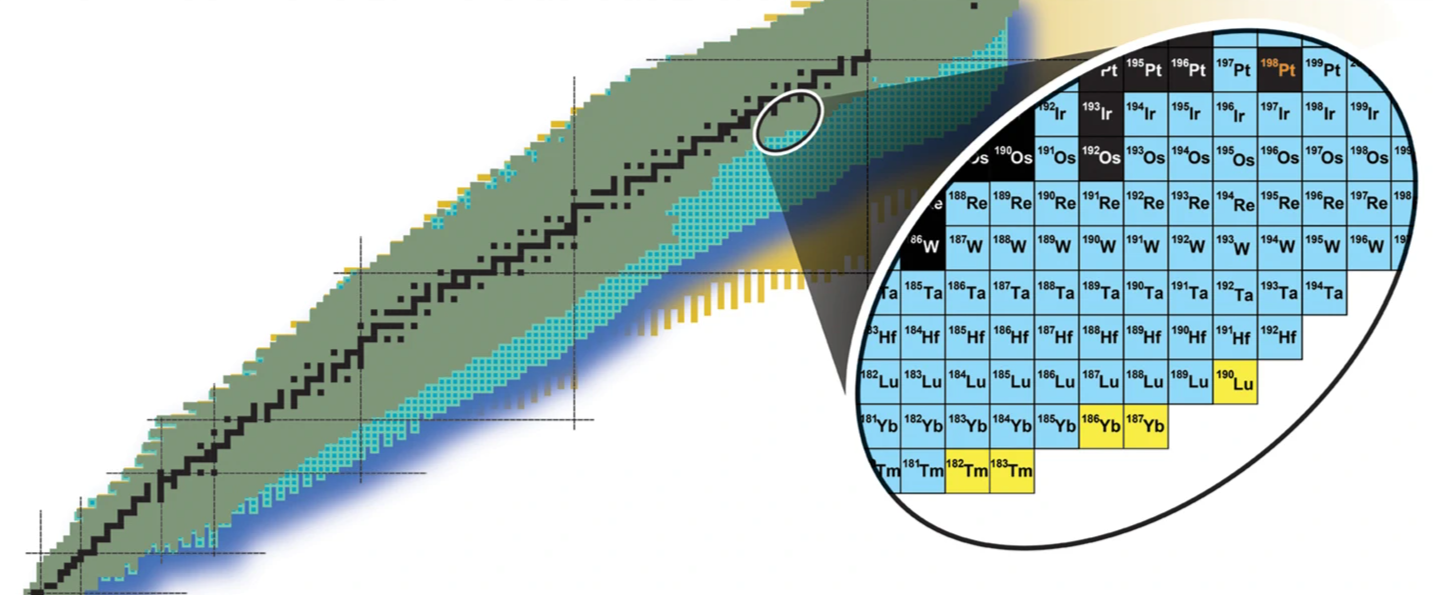
Researchers have synthesized 5 new isotopes that might assist carry the celebs all the way down to Earth — and coax scientists a step nearer to understanding how collisions between ultra-dense, lifeless stars may create heavy components like gold and silver.
The isotopes are Thulium-182, thulium-183, ytterbium-186, ytterbium-187 and lutetium-190; that is the primary time they have been ever been synthesized on Earth. Their creation befell on the Facility for Uncommon Isotope Beams (FRIB) at Michigan State College (MSU) and represents a step in the direction of constructing atoms on Earth which can be sometimes solely created within the ultra-turbulent surroundings round merging lifeless stars often called neutron stars.
“That is the thrilling half,” Alexandra Gade, FRIB scientific director and a professor in MSU’s Division of Physics and Astronomy, said in a statement. “We’re assured we will get even nearer to these nuclei which can be vital for astrophysics.”
Associated: What occurs when neutron stars collide? Astronomers could lastly know
What’s an isotope?
Every chemical component of the periodic desk is outlined by the variety of protons in its atomic nuclei. For instance, hydrogen all the time has one proton, helium all the time has two, and iron has 26. Hydrogen cannot have two protons, and iron cannot have 25; in the event that they did, they would not be hydrogen or iron anymore.
Nonetheless, protons are joined in atomic nuclei by neutrons, and the variety of these particles can differ with out altering the character of a component. Nuclei with various numbers of neutrons are known as isotopes of a component. So, isotopes of iron embody iron-54 with 26 protons and 28 neutrons, iron-56 with 26 protons and 30 neutrons, and iron-57 with 26 protons and 31 neutrons.
The 5 newly synthesized isotopes are thrilling, although, as a result of they are not generally occurring on our planet. Actually, they’ve by no means even been discovered on our planet earlier than.
“That is in all probability the primary time these isotopes have existed on the floor of the Earth,” Bradley Sherrill, College Distinguished Professor in MSU’s School of Pure Science and head of the Superior Uncommon Isotope Separator Division at FRIB, mentioned within the assertion. “I like to attract the analogy of taking a journey. We have been trying ahead to going someplace we have by no means been earlier than, and this is step one. We have left residence, and we’re beginning to discover.”
Superheavy isotopes and superheavy components
Stars typically may be regarded as nuclear furnaces that forge the weather of the universe, starting with the fusion of hydrogen to helium, which is then fused to forge nitrogen, oxygen and carbon.
Essentially the most large stars in our universe can forge components within the periodic desk all the best way as much as iron, however scientists consider even these highly effective stellar furnaces aren’t ample sufficient to create components heavier than that. However, what if two stars be a part of their furnaces? And reasonably violently at that?
The factor is, when dying, large stars are left with their cores of iron that may not fuse into heavier components, the vitality that has supported these stars towards the inward push of their very own gravitational influences additionally ceases. This causes the cores to break down because the outer layers are blasted away by highly effective supernova explosions.
This collapse may be halted, nevertheless, when the electrons and protons in these cores have been reworked right into a sea of neutrons, that are prevented from cramming collectively by a facet of quantum physics known as “degeneracy.” This degeneracy stress may be overcome if a stellar core has sufficient mass, leading to a whole collapse and making a black gap. However typically there is not sufficient mass. These stay as lifeless, superdense neutron stars.
Moreover, the top of this course of does not mark the top of nuclear fusion for neutron stars in the event that they occur to exist in a binary system with one other large star that additionally finally collapsed to start a neutron star. As these ultradense stars with lots between one and two instances that of the solar crammed into the width of round 12 miles (20 kilometers) orbit round one another, they emit ripples in spacetime known as gravitational waves.
These gravitational waves carry away angular momentum from the system, inflicting the neutron stars to attract collectively and emit extra gravitational waves at larger intensities. This continues till the 2 finally smash collectively.
Unsurprisingly, given their excessive nature, the collisions of binary neutron stars create a really violent surroundings. The occasion sprays out neutron-rich matter, as an illustration, and that matter is believed to be vital to the synthesis of gold and different heavy components.
That is as a result of these free neutrons may be grabbed by different atomic nuclei within the surroundings in what is known as the speedy seize course of or “r-process.” These grasping atomic nuclei then develop heavier, creating superheavy isotopes which can be unstable. These unstable isotopes are anticipated to finally decay into secure components, like gold, which can be lighter than superheavy components however nonetheless heavier than iron.
“It is not sure, however individuals assume that the entire gold on Earth was made in neutron star collisions,” Sherrill mentioned.
So, how can we study whether or not this course of happens with certainty?
If scientists may recreate the superheavy components concerned within the r-process, they may higher perceive the creation of gold and different heavy components. Alas, the creation of Thulium-182, thulium-183, ytterbium-186, ytterbium-187 and lutetium-190. These isotopes, fashioned by firing a beam of platinum ions at a goal of carbon at FRIB, won’t be current within the wreckage of neutron star collisions, however their existence on Earth is certainly a step towards creating these briefly lived transitional superheavy components on our planet to see in the event that they end in components like gold.
Down the road, a greater understanding of those newly solid isotopes may even have vital implications for nuclear physics.
“It is not a giant shock that these isotopes exist, however now that we now have them, we now have colleagues who can be very all for what we will measure subsequent,” Gade concluded. “I am already beginning to consider what we will do subsequent by way of measuring their half-lives, their lots, and different properties.”
The group’s analysis was revealed on Thursday (Feb. 15) within the journal Physical Review Letters.

