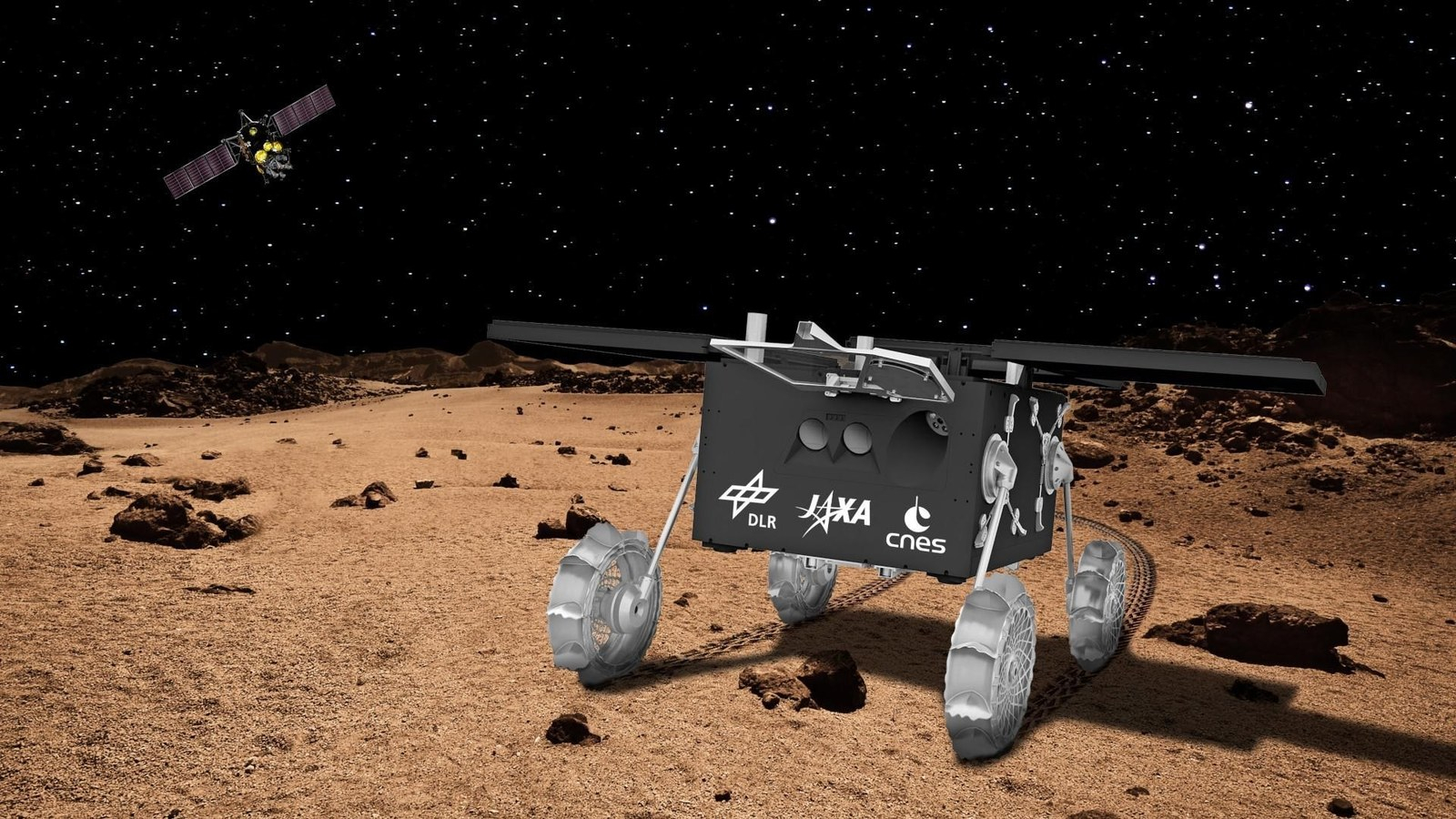
A small rover in-built Europe has arrived in Japan in preparation for its voyage to Mars.
The autonomous 55-pound (25-kilogram) rover is named IDEFIX and is a part of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Company’s (JAXA) Martian Moon Exploration (MMX) probe that goals to gather samples of the Mars’ moon, Phobos.
The little, four-wheeled rover just lately arrived in Japan, in keeping with a Feb. 26 submit on X (previously often called Twitter) written by the MMX mission account.
Associated: New Japanese spacecraft goals to discover the mysterious moons of Mars
IDEFIX, named for the small white canine within the Asterix comics, was collectively constructed by the German Aerospace Middle (recognized by the German acronym DLR) and the French area company Centre Nationwide d’Etudes Spatiales (CNES).
After a protracted journey from Europe, the MMX rover IDEFIX (developed by @DLR_EN/@CNES) has arrived in Japan! We share within the workforce’s gleeful “Yatta!/Tadaa!” because the rover is unpacked 📦🤩 An official handover will happen after post-transport checks 🇯🇵🇫🇷🇩🇪 Welcome to Japan, IDEFIX! pic.twitter.com/y2CXed8ya8February 26, 2024
The primary MMX spacecraft goals to seize 0.35 ounces (10 grams) of Phobos’ materials in 2029. It would then ship the dear cargo in direction of Earth; arrival is predicted to happen in 2031. IDEFIX will play an element on this total goal by touchdown on Phobos first and gathering key data in preparation for the touchdown of the primary spacecraft. The rover may even analyze the Martian moon’s floor composition and texture at chosen areas, according to DLR — if it could land and function efficiently in a close to zero-gravity atmosphere all by itself, that’s.
“The largest problem for IDEFIX is that it has to hold out many operations — significantly the uprighting after touchdown on Phobos — totally autonomously so as to survive,” Stéphane Mary, CNES Undertaking Supervisor for IDEFIX, stated in a DLR statement. “It would not survive if it waited for instructions from Earth to reach.”
A key aim of MMX is to find out whether or not Phobos and its fellow Martian satellite tv for pc Deimos are captured asteroids or a coalescence of fragments that have been blown into orbit after an enormous impression struck Mars.
MMX was initially scheduled to launch in September of this 12 months, but doubts over the readiness of the brand new Japanese H3 rocket meant JAXA took the choice to delay the mission till the following Mars launch window in 2026.
H3 has since reached Earth orbit for the primary time, bouncing again from the failure of its debut launch in 2023. The mission will launch on an H3 rocket from Tanegashima House Middle in 2026, hopefully arriving in Mars orbit in 2027 to start mapping and analyzing Deimos and Phobos. IDEFIX and the primary MMX spacecraft will then be capable to land on Phobos in 2029.

