
Astronomers are at the moment having fun with a fruitful interval of discovery, investigating the numerous mysteries of the early universe. The profitable launch of the James Webb Area Telescope (JWST), a successor to NASA’s Hubble Area Telescope, has pushed the restrict of what we will see.
Observations are actually getting into the primary 500 million years after the Large Bang when the universe was lower than 5% of its present age. For people, this time would place the universe firmly within the toddler stage.
But the galaxies we’re observing are definitely not childish, with new observations revealing galaxies extra large and mature than beforehand anticipated for such early occasions, serving to to rewrite our understanding of galaxy formation and evolution.
Our worldwide analysis staff not too long ago made unprecedentedly detailed observations of one of many earliest identified galaxies—dubbed Gz9p3, and now published in Nature Astronomy.
Its title comes from the Glass collaboration (the title of our worldwide analysis staff) and the actual fact the galaxy is at a redshift of z=9.3 the place redshift is one solution to describe the space to an object—therefore G and z9p3.

Simply a few years in the past, Gz9p3 appeared as a single level of sunshine via the Hubble Area Telescope. However by utilizing the James Webb Area Telescope we might observe this object because it was 510 million years after the Large Bang, round 13 billion years in the past.
We discovered Gz9p3 was way more large and mature than anticipated for such a younger universe, already containing a number of billion stars.
By far essentially the most large object confirmed from this time, it was calculated as 10 occasions extra large than another galaxy discovered that early within the universe.
Mixed, these outcomes counsel that for the galaxy to achieve this dimension, stars should have developed a lot quicker and extra effectively than we first thought.
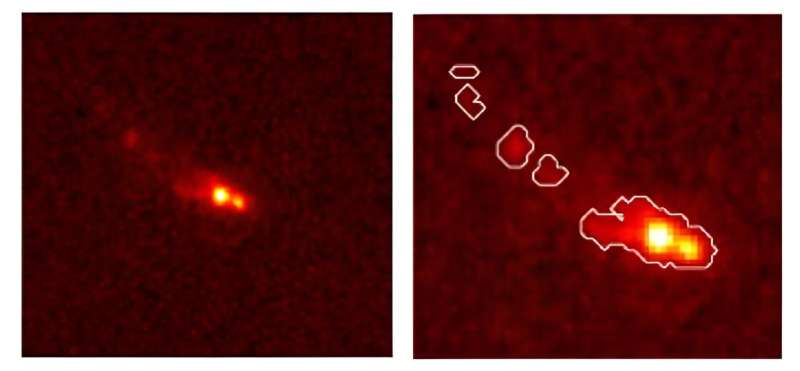
Most distant galaxy merger within the early universe
Not solely is that this Gz9p3 large, however its advanced form instantly identifies it as one of many earliest galaxy mergers ever witnessed.
The JWST imaging of the galaxy reveals a morphology sometimes related to two interacting galaxies. And the merger hasn’t completed as a result of we nonetheless see two elements.
When two large objects be part of like this, they successfully throw away among the matter within the course of. So, this discarded matter suggests what we noticed is likely one of the most distant mergers ever seen.
Subsequent, our examine regarded deeper, to explain the inhabitants of stars that make up the merging galaxies. Utilizing JWST, we had been capable of look at the spectrum of the galaxy, splitting the sunshine in the identical method a prism splits white gentle right into a rainbow.
When utilizing imaging alone, most research of those very distant objects present solely very younger stars as a result of the youthful stars are brighter and so their gentle dominates the imaging information.
For instance, a younger vivid inhabitants sparked by the galaxy merger, lower than a number of million years previous, outshines an older inhabitants already over 100 million years previous.
Utilizing the spectroscopy method, we will produce such detailed observations that the 2 populations may be distinguished.

New fashions of the early universe
Such a mature older inhabitants was not anticipated contemplating how early stars must have shaped to have aged sufficiently by this cosmic time. The spectroscopy is so detailed, we will see the delicate options of the previous stars that inform us there’s extra there than you assume.
Particular parts detected within the spectrum (together with silicon, carbon and iron) reveal this older inhabitants should exist to counterpoint the galaxy with an abundance of chemical substances.
It isn’t solely the scale of the galaxies that’s stunning but additionally the velocity with which they grew to such a chemically mature state.
These observations present proof of a fast, environment friendly build-up of stars and metals within the fast aftermath of the Large Bang, tied to ongoing galaxy mergers, demonstrating that large galaxies with a number of billion stars existed sooner than anticipated.
Remoted galaxies construct up their inhabitants of stars in situ from their finite reservoirs of fuel, nevertheless, this generally is a gradual method for galaxies to develop.
Interactions between galaxies can attract recent inflows of pristine fuel, offering gasoline for fast star formation, and mergers present an much more accelerated channel for mass accumulation and progress.
The biggest galaxies in our trendy universe all carry a historical past of mergers, together with our personal Milky Manner which has grown to its present dimension via successive mergers with smaller galaxies.
These observations of Gz9p3 present that galaxies had been capable of accumulate mass rapidly within the early universe via mergers, with star formation efficiencies greater than we anticipated.
This and different observations utilizing the JWST are inflicting astrophysicists to regulate their modeling of the early years of the universe.
Our cosmology is not essentially improper, however our understanding of how rapidly galaxies shaped most likely is, as a result of they’re extra large than we ever believed could possibly be doable.
These new outcomes are well-timed as we strategy the two-year mark for scientific observations made utilizing the JWST.
As the overall variety of galaxies noticed grows, astronomers finding out the early universe are transitioning from the invention part to a interval when we’ve got massive sufficient samples to start out constructing and refining new fashions.
There has by no means been a extra thrilling time to make sense of the mysteries of the early universe.
Extra info:
Kristan Boyett et al, An enormous interacting galaxy 510 million years after the Large Bang, Nature Astronomy (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41550-024-02218-7
Quotation:
Detailed photos present galaxy progress within the early universe was a lot quicker than first thought (2024, March 12)
retrieved 12 March 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.

