The photographs we get lately from superior telescopes, such because the James Webb House Telescope, undoubtedly depart us in awe and surprise of galaxies that exist light-years away from Earth. However what if these footage may very well be improved much more?Researchers from the College of Shanghai for Science and Expertise and the Chinese language Academy of Sciences hope they’re capable of assist with simply that by means of their growth of a skinny, ultrablack film coating for aerospace-grade magnesium alloys.
Give it some thought this fashion — if you wish to see the stars and search for planets on a transparent evening, you want it to be as darkish as doable. So, to perform this, you could drive away from metropolis lights and right into a extra rural location the place you will discover your self in full darkness, apart from the moonlight, maybe. The identical idea is true for astronomers working with precision optics. However, they get somewhat extra creative. To realize the darkest of darkness, they do not simply search out areas with out metropolis lights. In addition they incorporate black paint of their stargazing processes, coating their units with such pigment to scale back stray mild as a lot as doable and supply the most effective image and efficiency they will. The identical principle applies when constructing a telescope that operates in area as properly.
With this in thoughts, the workforce’s new black coating can take in a whopping 99.3% of sunshine in even the harshest of situations.
“Present black coatings like vertically aligned carbon nanotubes or black silicon are restricted by fragility,” Yunzhen Cao, research co-author and professor on the Shanghai Institute of Ceramics, Chinese language Academy of Sciences mentioned in a statement. “It’s also tough for a lot of different coating strategies to use coatings inside a tube or on different sophisticated buildings. That is essential for his or her utility in optical units as they typically have important curvature or intricate shapes.”
The analysis workforce used atomic layer deposition (ALD) to deal with these considerations, which is a producing approach that takes place in a vacuum chamber and exposes a goal to particular forms of fuel. The ultrablack coating is created with alternating layers of aluminum-doped titanium carbide (TiAlC) and silicon nitride (SiO2) which, when mixed, act as a barrier to just about all mild.
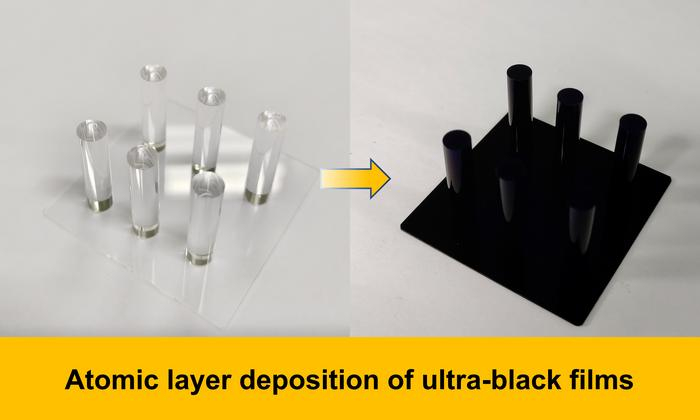
“One massive benefit of the ALD technique lies in its wonderful step-coverage means, which suggests we will acquire uniform movie protection on very complicated surfaces, similar to cylinders, pillars, and trenches,” Cao mentioned. “TiAlC acted as an absorbing layer, and SiO2 was employed to create an anti-reflection construction and consequently, almost all the incident mild is trapped within the multilayer movie, attaining environment friendly mild absorption.”
From the testing, the workforce concluded that 99.3% of sunshine wavelengths from throughout a variety of the electromagnetic spectrum have been absorbed on common, spanning from violet mild at 400 nanometers to as much as close to infrared mild at 1,000 nanometers. Researchers hope that this coating will enhance the following technology of area telescopes and optical {hardware} considerably, and permit them to carry out even higher than earlier than in even the harshest of situations.
“What’s extra, the movie reveals very good stability in opposed environments, and is hard sufficient to resist friction, warmth, damp situations, and excessive temperature adjustments,” Cao mentioned.
The study was revealed on March 12 within the Journal of Vacuum Science and Expertise A.

