Frank Herbert’s Dune is epic sci-fi storytelling with an environmental message at its coronary heart. The novels and films are set on the desert planet of Arrakis, which varied characters dream of remodeling right into a greener world – very similar to some envision for Mars as we speak.
We investigated Arrakis utilizing a climate model, a pc program just like these used to present climate forecasts. We discovered the world that Herbert had created, nicely earlier than local weather fashions even existed, was remarkably correct – and could be liveable, if not hospitable.
Nevertheless, Arrakis wasn’t all the time a desert. In Dune lore, 91% of the planet was as soon as lined by oceans, till some historical disaster led to its desertification. What water remained was additional eliminated by sand trout, an invasive species delivered to Arrakis. These proliferated and carried liquid into cavities deep underground, resulting in the planet turning into increasingly arid.
Associated: ‘Dune: Half Two’ tries to seek out its pulse in a plodding sci-fi spectacle (evaluation)

To see what a big ocean would imply for the planet’s local weather and habitability, now we have now used the identical local weather mannequin – placing in an ocean whereas altering no different components.
When most of Arrakis is flooded, we calculate that the worldwide common temperature could be decreased by 4°C. That is principally as a result of oceans add moisture to the environment, which ends up in extra snow and sure forms of cloud, each of which replicate the solar’s vitality again into house. But it surely’s additionally as a result of oceans on Earth and (we assume) on Arrakis emit “halogens” that cool the planet by depleting ozone, a potent greenhouse gasoline which Arrakis would have considerably extra of than Earth.
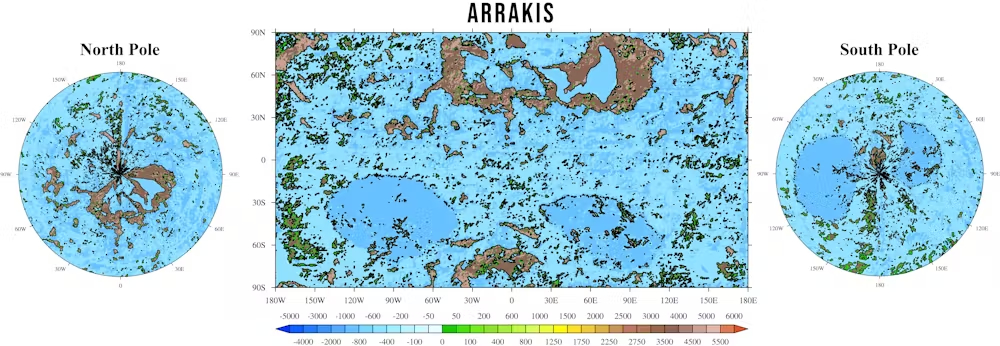
Unsurprisingly, the ocean world is a whopping 86 instances wetter, as a lot water evaporates from the oceans. This implies vegetation can develop as water is now not a finite useful resource, as it’s on desert Arrakis.
A wetter world could be extra secure
Oceans additionally scale back temperature extremes, as water heats and cools extra slowly than land. (That is one cause Britain, surrounded by oceans, has comparatively delicate winters and summers, whereas locations far inland are typically hotter in summer and very cold in winter). The local weather of an ocean planet is subsequently extra secure than a desert world.
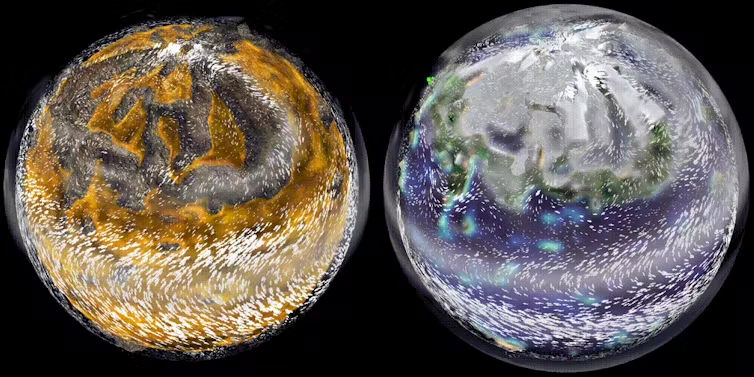
In desert Arrakis, temperatures would attain 70°C or extra, whereas in its ocean state, we put the very best recorded temperatures at about 45°C. Meaning the ocean Arrakis could be habitable even in summer time. Forests and arable crops might develop outdoors of the (nonetheless chilly and snowy) poles.
There’s one draw back, nonetheless. Tropical areas could be buffeted by massive cyclones because the enormous, heat oceans would comprise a lot of the vitality and moisture required to drive hurricanes.
The seek for liveable planets
All this isn’t a completely summary train, as scientists trying to find liveable “exoplanets” in distant galaxies are in search of these kinds of issues too. In the meanwhile, we are able to solely detect such planets utilizing enormous telescopes in house to seek for these which can be just like Earth in measurement, temperature, out there vitality, capability to host water, and different components.
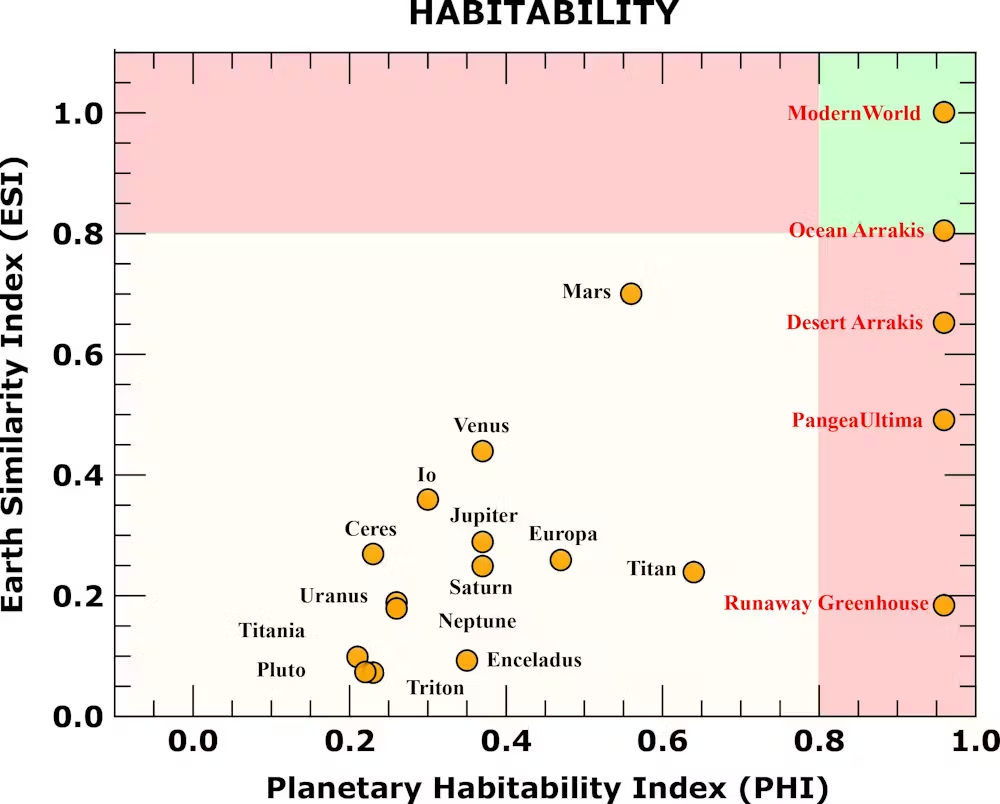
We all know that desert worlds are in all probability extra widespread than Earth-like planets in the universe. Planets with doubtlessly life-sustaining oceans will often be discovered within the so-called “Goldilocks zone”: far sufficient from the Solar to keep away from being too sizzling (so additional away than boiling sizzling Venus), however shut sufficient to keep away from every part being frozen (so nearer than Jupiter’s icy moon Ganymede).
Analysis has discovered this liveable zone is especially small for planets with large oceans. Their water is vulnerable to both utterly freezing, subsequently making the planet even colder, or of evaporating as a part of a runaway greenhouse impact by which a layer of water vapour prevents warmth from escaping and the planet will get hotter and warmer.
The liveable zone is subsequently a lot bigger for desert planets, since on the periphery they are going to have much less snow and ice cowl and can take in extra of their solar’s warmth, whereas on the inside edge there’s much less water vapour and so much less danger of a runaway greenhouse impact.
It’s additionally necessary to notice that, although distance from their native star may give a normal common temperature for a planet, such a median may be deceptive. As an illustration, each desert and ocean Arrakis have a liveable common temperature, however the day-to-day temperature extremes on the ocean planet are far more hospitable.
At present, even probably the most highly effective telescopes can’t sense temperatures at this element. Additionally they can’t see intimately how the continents are organized on distant planets. This once more might imply the averages are deceptive. As an illustration, whereas the ocean Arrakis we modelled could be very liveable, many of the land is within the polar areas that are underneath snow year-round – so the precise quantity of inhabitable land is way much less.
Such issues might be necessary in our personal far-future, when the Earth is projected to type a supercontinent centred on the equator. That continent would make the planet far too sizzling for mammals and different life to outlive, doubtlessly resulting in mass extinction.

If the probably habitable planets within the universe are deserts, they could be very excessive environments that require vital technological options and assets to allow life – desert worlds will in all probability not have an oxygen-rich environment, as an example.
However that received’t cease people from attempting. As an illustration, Elon Musk and SpaceX have grand ambitions to create a colony on our closest desert world, Mars. However the many challenges they are going to face solely emphasises how necessary our personal Earth is because the cradle of civilisation – particularly as ocean-rich worlds is probably not as plentiful as we’d hope. If people ultimately colonise different worlds, they’re prone to need to take care of most of the similar issues because the characters in Dune.

