When NASA astronauts tried to dock Boeing’s first crewed Starliner spacecraft on the Worldwide Area Station Thursday (June 6), they needed to wait.
5 aft thrusters on the Starliner service module had been out. And that was after flight controllers discovered workarounds for 2 new helium leaks on the spacecraft on high of 1 it already had. Additionally, its cooling system was utilizing extra water than anticipated, and one other helium leak could be detected later after Starliner docked with the area station.
So what provides? Why all of the glitches?
NASA and Boeing, for his or her half, aren’t nervous. In any case, Starliner’s mission to the ISS, Boeing’s Crew Flight Take a look at, is — each in identify and nature — a check flight. The mission is simply the sixth in historical past by which NASA astronauts have flown on a brand-new spacecraft for the primary time. For Boeing, lastly reaching the ISS with astronauts after its first uncrewed check flight failed to take action in 2019 solely to have extra points delay this crewed flight marked an enormous leap ahead.
And people glitches? Thus far, NASA and Boeing have surpassed them.
Starliner docked on the ISS simply over an hour later than deliberate after some guide flying by NASA astronauts Butch Wilmore (the mission’s commander) and Sunita Williams (its pilot) helped Boeing engineers get better 4 of the 5 down thrusters. The fifth will keep deactivated for the remainder of the mission, however the glitch — which can truly be in Starliner’s software program and never the thrusters themselves — will not pose a threat for the return to Earth.
Associated: Boeing Starliner 1st astronaut flight: Dwell updates
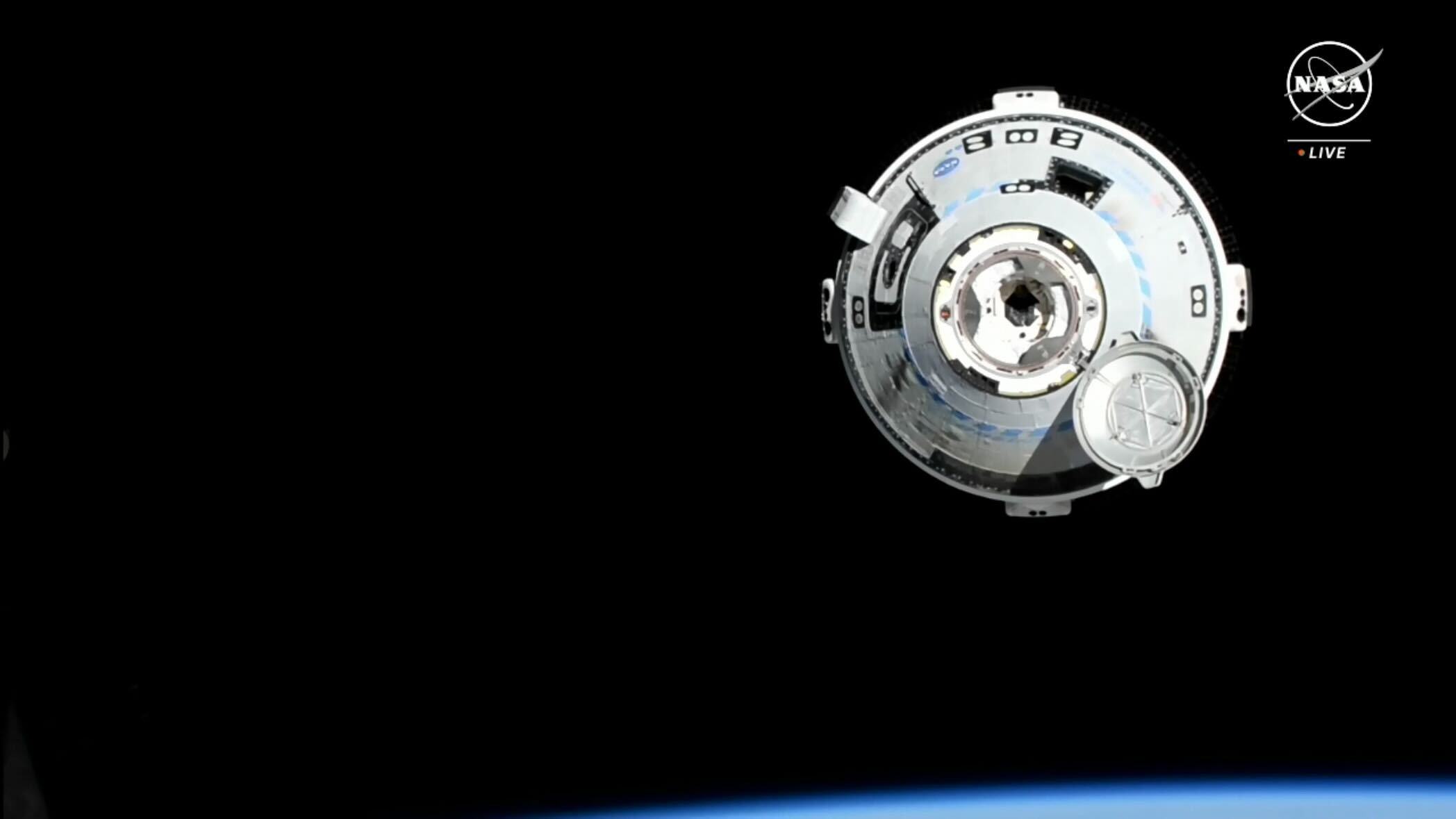
The astronauts additionally refilled the water tank of their cooling system from an onboard provide and future automobiles will carry a much bigger tank from the beginning, Boeing stated. As for these helium leaks, Starliner has an ample provide of the fuel for the remainder of the mission, however Boeing engineers nonetheless wish to perceive why they hold popping up.
“We have now two issues on this car proper now, the helium leak and determining tips on how to fine-tune these thrusters so they don’t seem to be chosen off,” Boeing Starliner program supervisor Mark Nappi instructed reporters in a press convention Thursday night. “These are fairly small, actually, points to cope with and we’ll determine them out earlier than the following mission.”
NASA’s Steve Stich, who oversees the company’s Industrial Crew Program, in contrast Boeing’s Starliner flight with the company’s personal first area shuttle mission, STS-1, which launched astronauts John Younger and Bob Crippen into orbit in 1981.
“I might say among the challenges we face are similar to the area shuttle,” Stich stated. The water cooling system glitch, for one, is strikingly much like one NASA confronted on shuttle flights all through that 30-year program, he added.
In the meantime, Wilmore and Williams have a packed week or extra whereas on the area station, the place they are going to check the whole lot from how comfy Starliner is to sleep and the way effectively it might probably accommodate crews of 4 astronauts (its nominal complement) to how the capsule serves as a secure haven in case of a station emergency.
“As a result of they’re solely scheduled to be there for a comparatively quick time, we work them rather a lot tougher than we work our ISS crews,” NASA’s Emily Nelson, chief flight director for Starliner’s Crew Flight Take a look at, instructed reporters. “There’s a whole lot of checkouts.”
Most of the these assessments are aimed toward getting ready the station and the Starliner program for Starliner 1, the primary of at the least six astronaut taxi flights for NASA by Boeing beneath its $4.2 billion Industrial Crew Program contract. That mission is predicted to launch in early 2025. Boeing is considered one of two firms with multi-billion-dollar contracts to fly NASA astronauts to and from the ISS. The opposite, SpaceX, has already flown eight missions for NASA on its Crew Dragon spacecraft.

Nelson stated ISS flight controllers can use the station’s robotic arm cameras to examine the affected thrusters on Starliner in case any points might be detected that manner. For the reason that thrusters are on Starliner’s service module, which is jettisoned forward of reentry, Boeing will not get it again to review on Earth.
Nonetheless, NASA and Boeing are assured the thruster glitch seen throughout docking will not pose a serious menace. Throughout Boeing’s second uncrewed flight check, which truly did attain the area station in 2022, a number of thrusters additionally went offline in a lot the identical manner, Stich stated.
“I feel we’re not essentially nervous about all of the thrusters,” Stich stated, including that those affected within the 2022 flight carried out high quality after being recovered. “These thrusters did effectively after we introduced them again.”
For his or her half, Wilmore and Williams are wanting to get to work placing Starliner by way of its paces.
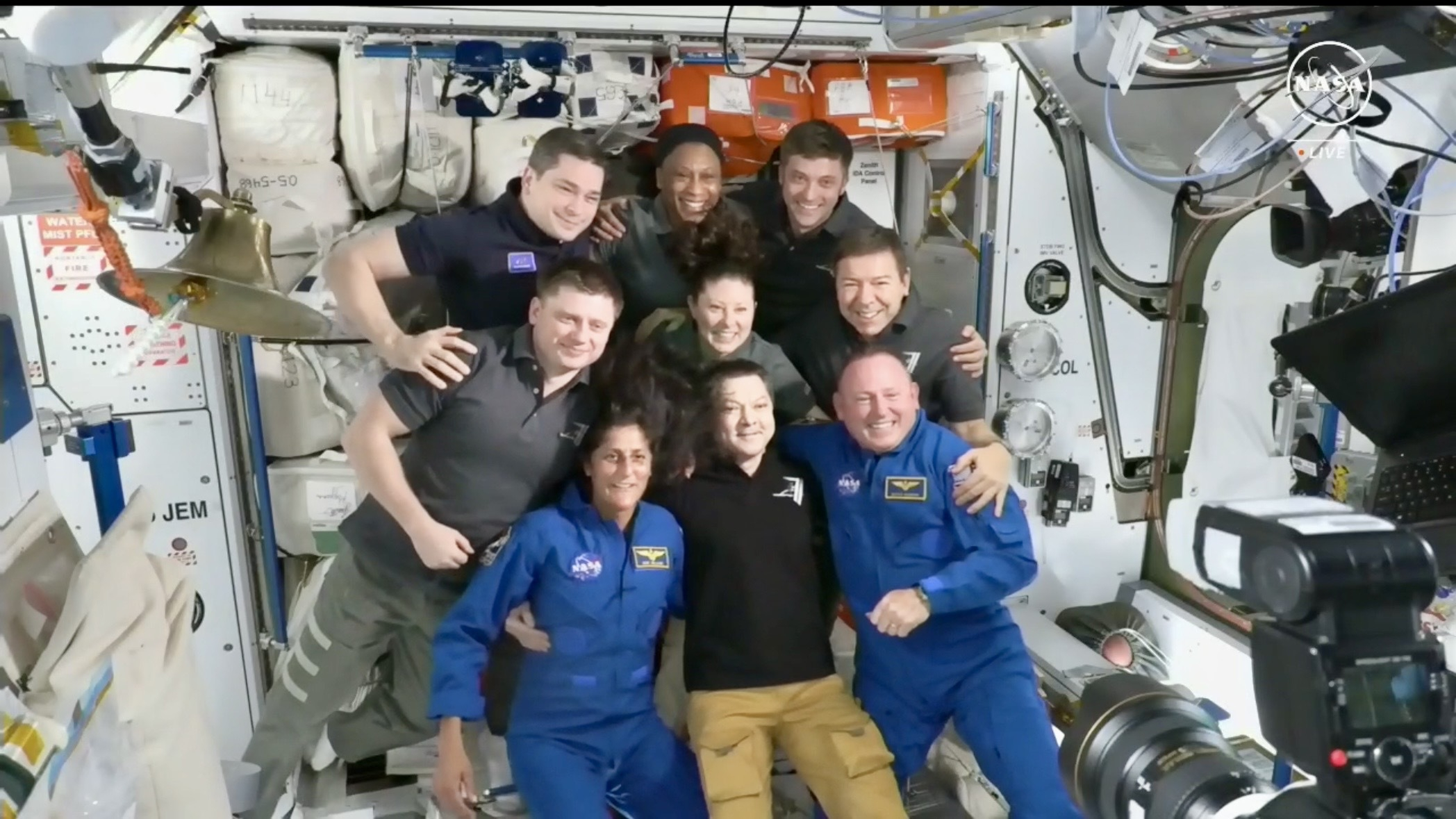
The astronauts acquired a heat welcome as they floated into the ISS from Starliner, full with the ringing of a ship’s bell, some weightless dancing and hugs throughout from the station’s seven-person Expedition 71 crew representing america and Russia. They’ve till at the least June 14, if not a bit longer, to finish their work, and solely have at some point off throughout that point, NASA has stated.
“We’re able to go to work for the worldwide companions right here,” Wilmore stated. “No matter it’s you bought us to do. We’re prepared.”

