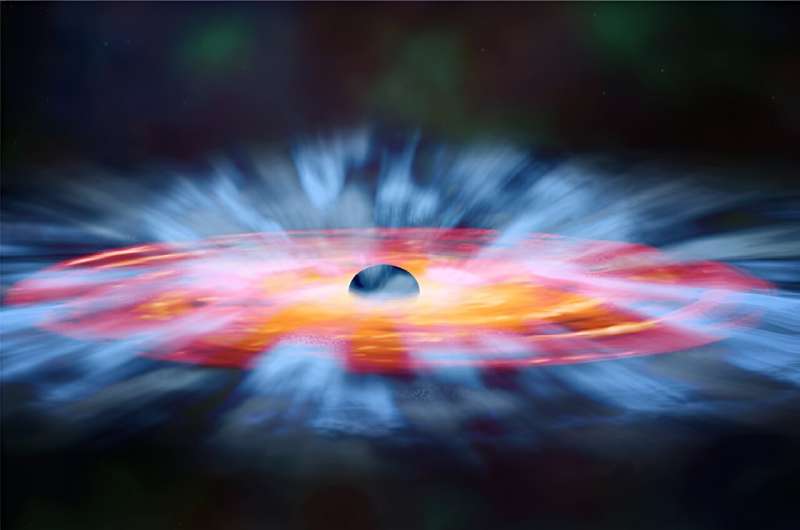

Clouds of gasoline in a distant galaxy are being pushed sooner and sooner—at greater than 10,000 miles per second—out amongst neighboring stars by blasts of radiation from the supermassive black gap on the galaxy’s heart. It is a discovery that helps illuminate the best way energetic black holes can constantly form their galaxies by spurring on or snuffing out the event of recent stars.
A group of researchers led by College of Wisconsin–Madison astronomy professor Catherine Grier and up to date graduate Robert Wheatley revealed the accelerating gasoline utilizing years of information collected from a quasar, a very brilliant and turbulent form of black gap, billions of sunshine years away within the constellation Boötes. They offered their findings at present on the 244th meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Madison.
Scientists consider black holes are located on the heart of most galaxies. Quasars are supermassive black holes surrounded by disks of matter being pulled in by the black gap’s huge gravitational energy.
“The fabric in that disk is all the time falling into the black gap, and the friction of that pulling and pulling heats up the disk and makes it very, extremely popular and really, very brilliant,” says Grier. “These quasars are actually luminous, and since there’s a wide range of temperatures from the inside to the far elements of the disk, their emission covers nearly all the electromagnetic spectrum.”

The brilliant mild makes quasars almost as outdated because the universe (as many as 13 billion mild years away) seen, and the broad vary of their radiation makes them significantly helpful for astronomers to probe the early universe.
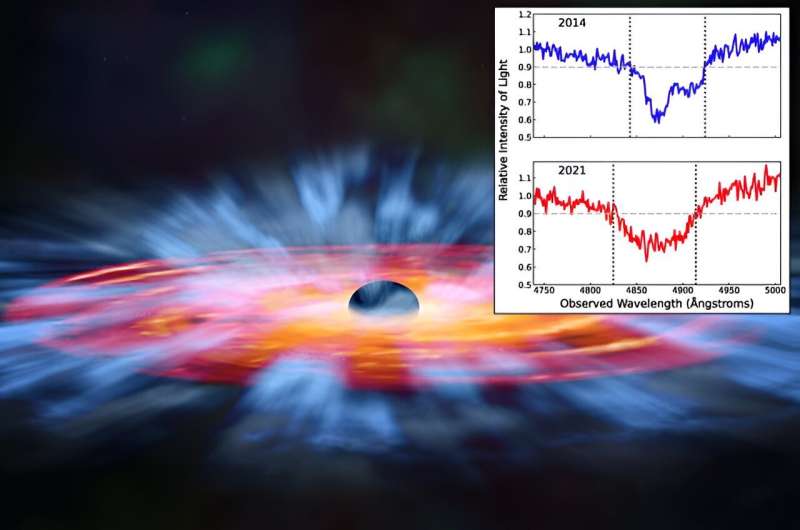
Researchers used greater than eight years of observations of a quasar referred to as SBS 1408+544, collected by a program carried out by the Sloan Digital Sky Survey now referred to as the Black Gap Mapper Reverberation Mapping Venture. They tracked winds composed of gaseous carbon by recognizing mild from the quasar that was lacking—mild that was being absorbed by the gasoline. However as a substitute of being absorbed at precisely the correct spot within the spectrum that will point out carbon, the shadow shifted farther from house with each new take a look at SBS 1408+544.
“That shift tells us the gasoline is transferring quick, and sooner on a regular basis,” says Wheatley. “The wind is accelerating as a result of it is being pushed by radiation that’s blasted off of the accretion disk.”
Scientists, together with Grier, have advised they’ve noticed accelerating winds from black gap accretion disks earlier than, however this had not but been backed by knowledge from various observations. The brand new outcomes got here from about 130 observations of SBS 1408+544 revamped almost a decade, which allowed the group to solidly establish the rise in velocity with excessive confidence.
The winds pushing gasoline out from the quasar are of curiosity to astronomers as a result of they’re a approach through which the supermassive black holes may affect the evolution of the galaxies that encompass them.
“In the event that they’re energetic sufficient, the winds might journey all the best way out into the host galaxy, the place they might have a big impression,” Wheatley says.
Relying on the circumstances, a quasar’s winds may provide strain that squeezes gasoline collectively and speeds the beginning of a star in its host galaxy. Or it may scour away that gas and hold a possible star from forming.
“Supermassive black holes are large, however they’re actually tiny in comparison with their galaxies,” says Grier. “That does not imply they can not ‘discuss’ to one another, and this can be a approach for one to speak to the opposite that we must account for after we mannequin the consequences of those sorts of black holes.”
The research of SBS 1408+544, published today in The Astrophysical Journal included collaborators at York College, Pennsylvania State College, College of Arizona and others.
Extra data:
Robert Wheatley et al, The SDSS-V Black Gap Mapper Reverberation Mapping Venture: C iv Broad Absorption Line Acceleration within the Quasar SBS 1408+544, The Astrophysical Journal (2024). DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad429e
Quotation:
Wind from black holes might affect improvement of surrounding galaxies (2024, June 11)
retrieved 12 June 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

