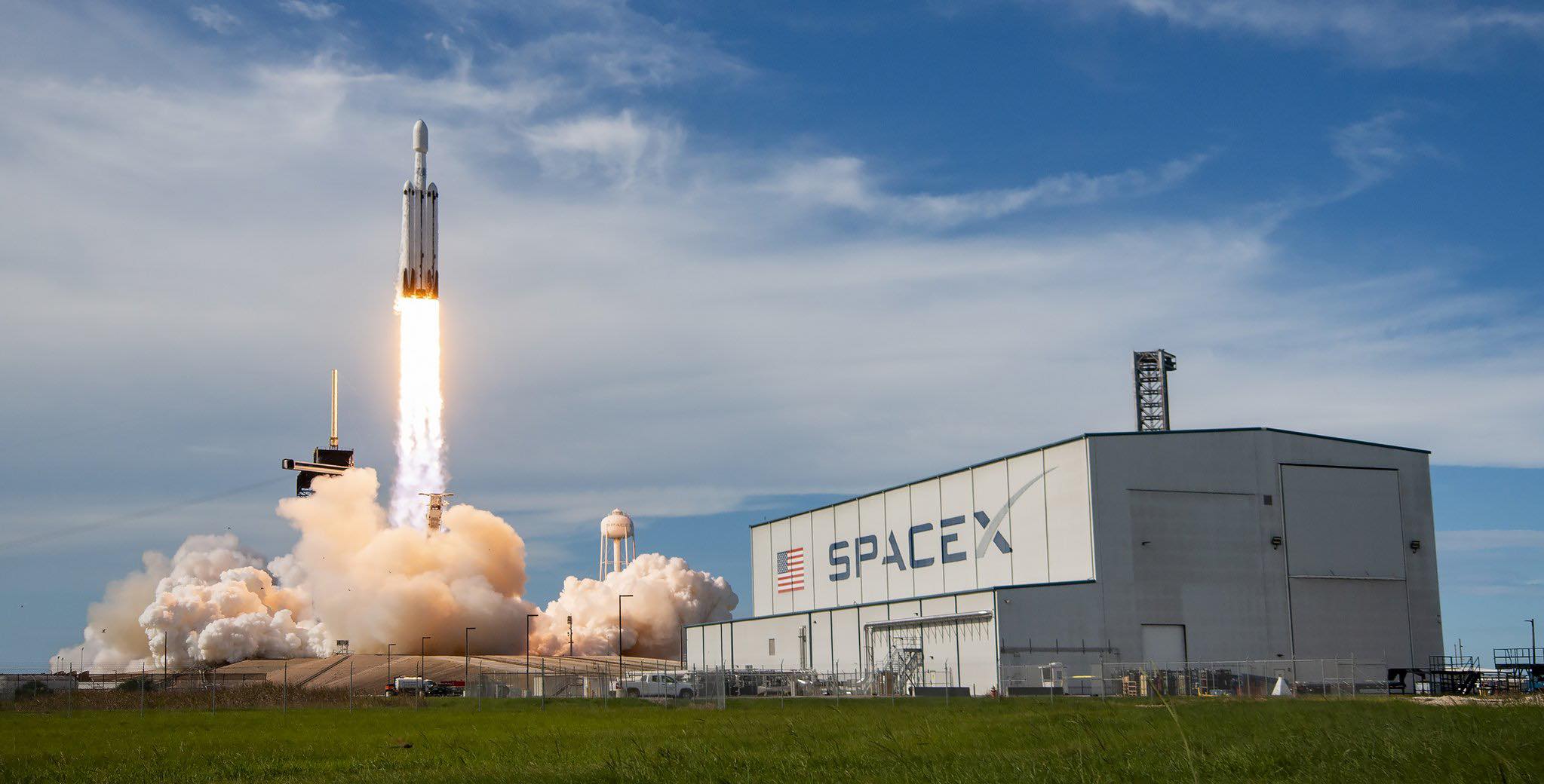

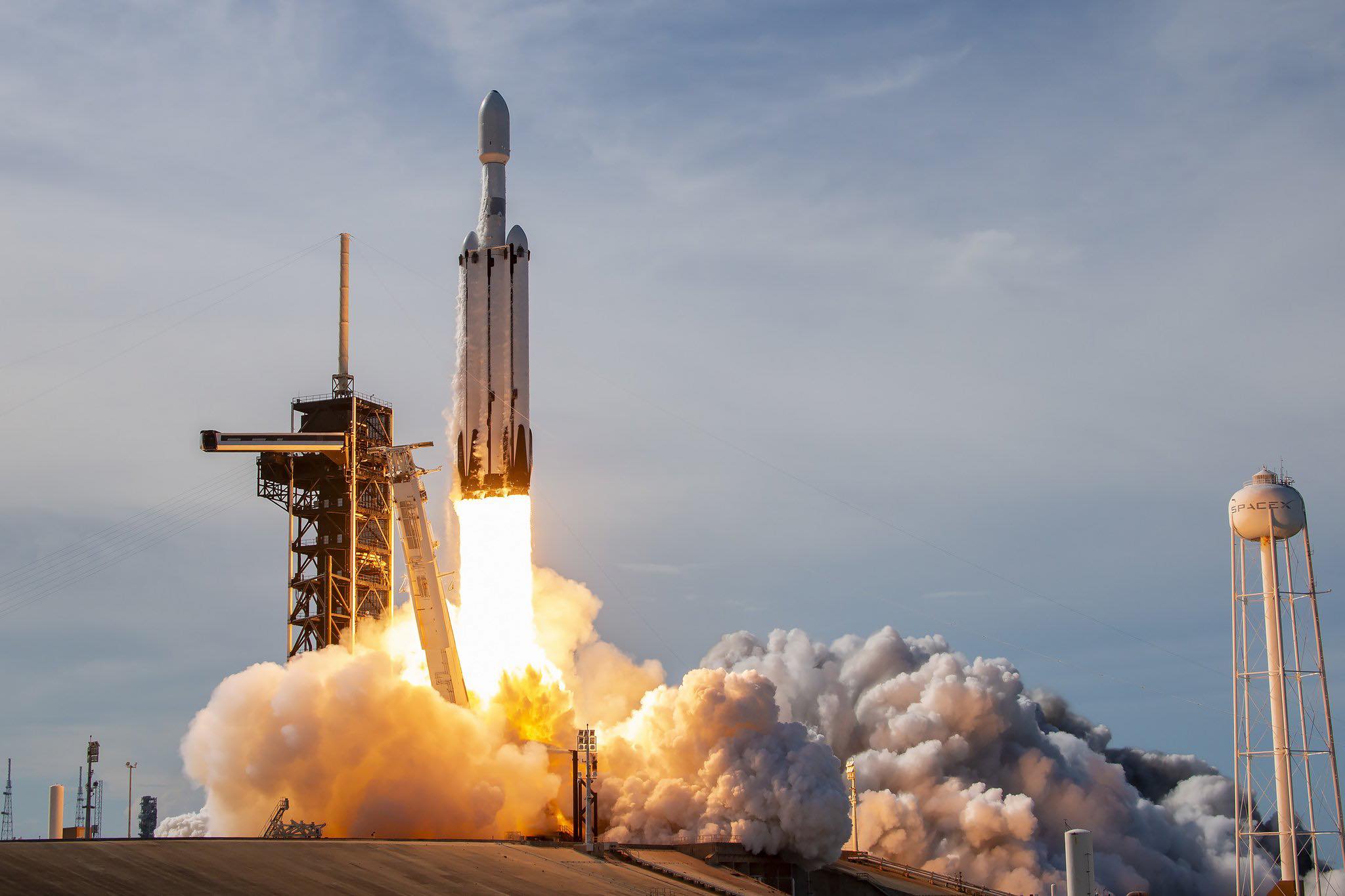
SpaceX efficiently launched its first Falcon Heavy of the 12 months on Wednesday night, the triple-barreled booster lifting the 11,000-pound (5,000-kilogram) Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite tv for pc (GOES-U) nearly to Geostationary Earth Orbit (GEO) on behalf of the Nationwide Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA). The Heavy—flying for the primary time since November 2022 with a brand-new heart core and pair of side-mounted strap-on boosters—went airborne from historic Pad 39A at Florida’s Kennedy House Heart (KSC) at 5:26 p.m. EDT, ten minutes after the opening of a two-hour “launch window”.
Tonight’s launch got here in opposition to many odds, with forecasters having predicted solely a 30-percent probability of acceptable climate for each the first launch alternative right this moment and a backup try on Thursday. Potential violations of the Cumulus Cloud Rule, the Anvil Cloud Rule and the Floor Electrical Fields Rule have been of principal concern.
“Deep tropical moisture will stay over the Florida peninsula by means of this week because the Atlantic ridge axis slowly slides southwards,” famous the forty fifth Climate Squadron at Patrick House Drive Base in a Monday replace, including that “excessive ranges of moisture and lightweight offshore low-level winds” have been anticipated to probably “set off showers/storms within the early to mid-afternoon, earlier than the night launch window opens”. These storms and their related anvil clouds have been predicted to provide a number of Lightning Launch Commit Standards (LLCC), with the most effective alternative for a “Go” situation anticipated when storm exercise pushed far sufficient inland earlier than important anvil growth.
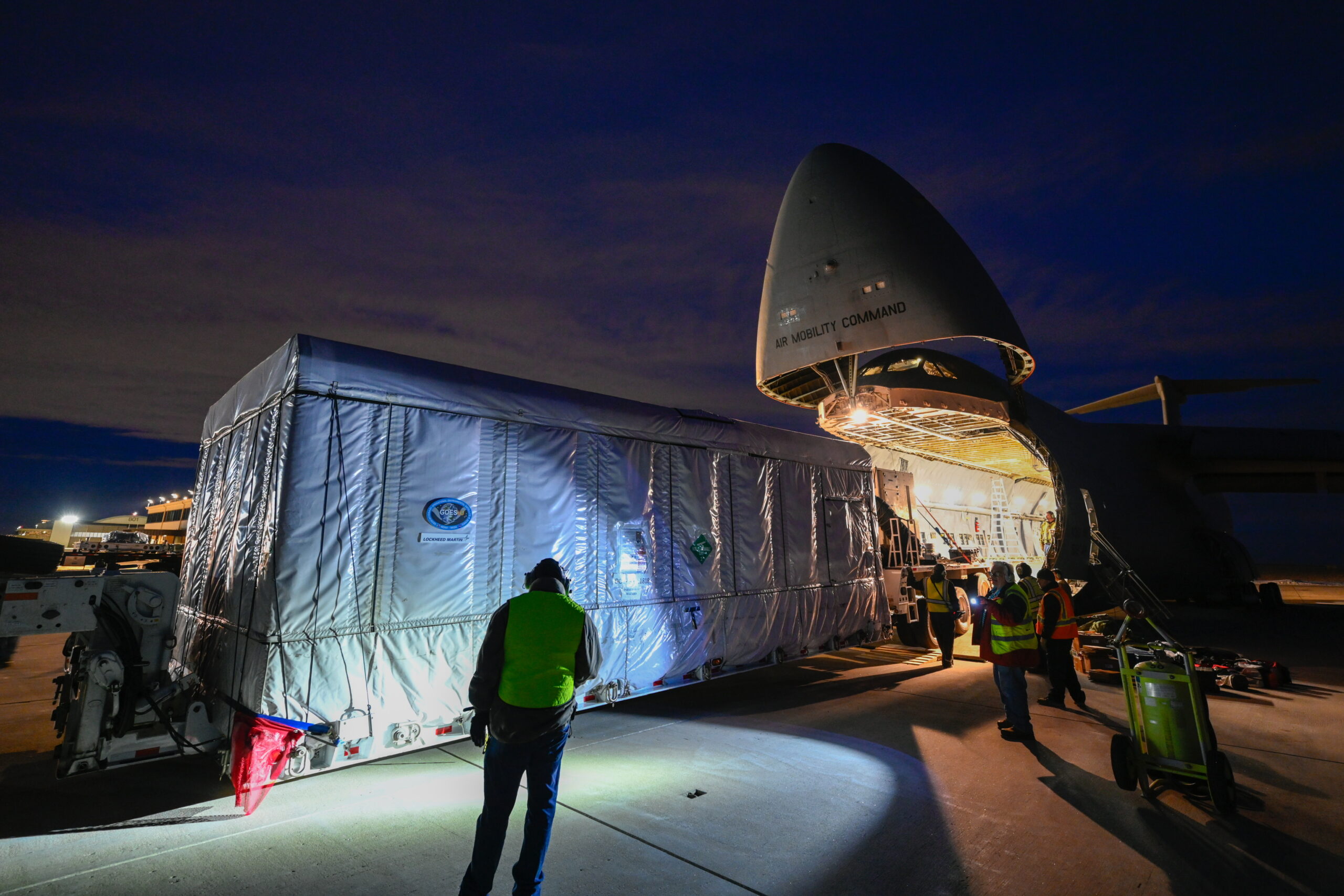

As beforehand outlined by AmericaSpace, GOES-U is the fourth and closing member of the next-generation Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite tv for pc (GOES)-R community of spacecraft, constructed by Lockheed Martin at its Littleton, Colo., facility, and operated by NOAA’s Nationwide Environmental Satellite tv for pc, Information and Data Service (NESDIS). When operational, it’ll spend roughly 15 years conducting climate forecasting, storm monitoring and meteorological analysis from geostationary orbit at an altitude of twenty-two,300 miles (35,900 kilometers).
Contracts to manufacture devices for the GOES-R community have been awarded approach again in 2006 and Lockheed Martin was chosen by NASA in December 2008 to construct an combine an preliminary pair of satellites, every carrying the choice of 1 further spacecraft, at a complete value (together with exercised choices) of $1.09 billion. That pair of satellites—GOES-R and GOES-S—have been launched atop United Launch Alliance (ULA) Atlas V boosters in November 2016 and March 2018.

The “further” choice was activated in Might 2013 to construct GOES-T—which was launched through a ULA Atlas V in March 2022—and GOES-U. In September 2021, NASA’s Launch Providers Program (LSP) chosen SpaceX to launch GOES-U, with a focused launch date of April 2024.
Based mostly upon Lockheed Martin’s A2100A “bus”, GOES-U weighs about 11,000 kilos (5,000 kilograms) and its unfurled photo voltaic arrays will afford it round 4 kilowatts {of electrical} energy. Aboard the spacecraft, in delight of place, sits L3Harris Applied sciences’ Superior Baseline Imager (ABI) to amass terrestrial imagery throughout 16 spectral bands, together with two seen, 4 near-infrared and ten infrared channels.

It will allow observations of cloud formation, atmospheric motions, convections, land-surface temperature mapping, ocean dynamics and aerosols and air high quality. The ABI’s sensitivity represents a twofold enhancement over earlier GOES incarnations.
Alongside the ABI, the Geostationary Lightning Mapper (GLM) will observe lightning emissions at near-infrared wavelengths, serving to to alert forecasters to extreme climate, creating storms and tornadoes. First utilized aboard GOES-R, this instrument can detect lightning by day and evening, with a detection price of 70-90 p.c of all strikes inside its viewing space.

A gaggle of photo voltaic and house atmosphere sensors additionally reside aboard the GOES-T bus. The Excessive Ultraviolet and X-ray Irradiance Sensors (EXIS) will look at photo voltaic irradiance upon Earth’s ambiance, while the Photo voltaic Ultraviolet Imager (SUVI) will produce full-disk photos of the Solar at excessive ultraviolet wavelengths.
Rounding out the GOES-T payload are the Magnetometer (MAG) and House Setting In-Situ Suite (SEISS). The previous will furnish generalized information on geomagnetic exercise as a part of ongoing efforts to foretell photo voltaic storms and facilitate large-scale house atmosphere modeling, while the latter contains 4 sensors to watch proton, electron and heavy ion fluxes within the magnetosphere.

The seventh and final payload aboard GOES-U is the Naval Analysis Laboratory’s Compact Coronagraph (CCOR)-1, which is able to look at the Solar’s outer corona to research large-scale plasma occasions accountable for geomagnetic photo voltaic storms. All advised, the large satellite tv for pc is roughly the dimensions of a small faculty bus.
GOES-U was delivered from Lockheed Martin’s facility in Littleton, Colo., through Buckley House Drive Base in Aurora, Colo., to Florida, aboard a C-5M Tremendous Galaxy airlifter, arriving on the House Coast final 23 January. It was then transported to Astrotech House Operations in Titusville for closing testing, fueling and encapsulation contained in the Falcon Heavy payload shroud for its impending launch.

However the mission met with a number of weeks of further delay, on account of points pertaining to the Falcon Heavy itself. Throughout routine pre-flight testing of the B1087 heart core final January at SpaceX’s Rocket Improvement Facility in McGregor, Texas, a liquid oxygen leak was detected, triggering a call to postpone the GOES-U launch from late April till Might on the soonest, earlier than the mission was finally slipped a further few weeks to No Earlier Than (NET) 25 June.
Earlier this month, closing checkouts of GOES-U and the loading of the satellite tv for pc with greater than 5,000 kilos (2,270 kilograms) of station-keeping gasoline and oxidizer have been accomplished and on 10 June it was mated to its Falcon Heavy Payload Connect Becoming (PAF). Encapsulated inside the twin payload fairing halves, GOES-U was rolled out of the Astrotech House Operations facility in Titusville and moved in a single day on 13/14 June to the Horizontal Integration Facility (HIF) at Pad 39A for mating to the Falcon Heavy.

Final Thursday, NASA, NOAA, SpaceX and GOES-U mission managers gathered for the customary Flight Readiness Evaluate (FRR), which concluded with unanimous approval to proceed with integration of the payload stack atop the Falcon Heavy. The enormous rocket was rolled out in a single day Monday/Tuesday and elevated vertical on Pad 39A.
Though this was the tenth outing by a Falcon Heavy, GOES-U marked the primary time since November 2022 that your entire booster—heart core and side-boosters—have been all embarking on their first flights. The high-energy necessities of the launch, which is able to emplace GOES-U right into a near-GEO altitude, demanded that the B1087 heart core be expended on this mission, however the B1086 and B1072 side-boosters each returned to Earth and have been recovered for future flights.
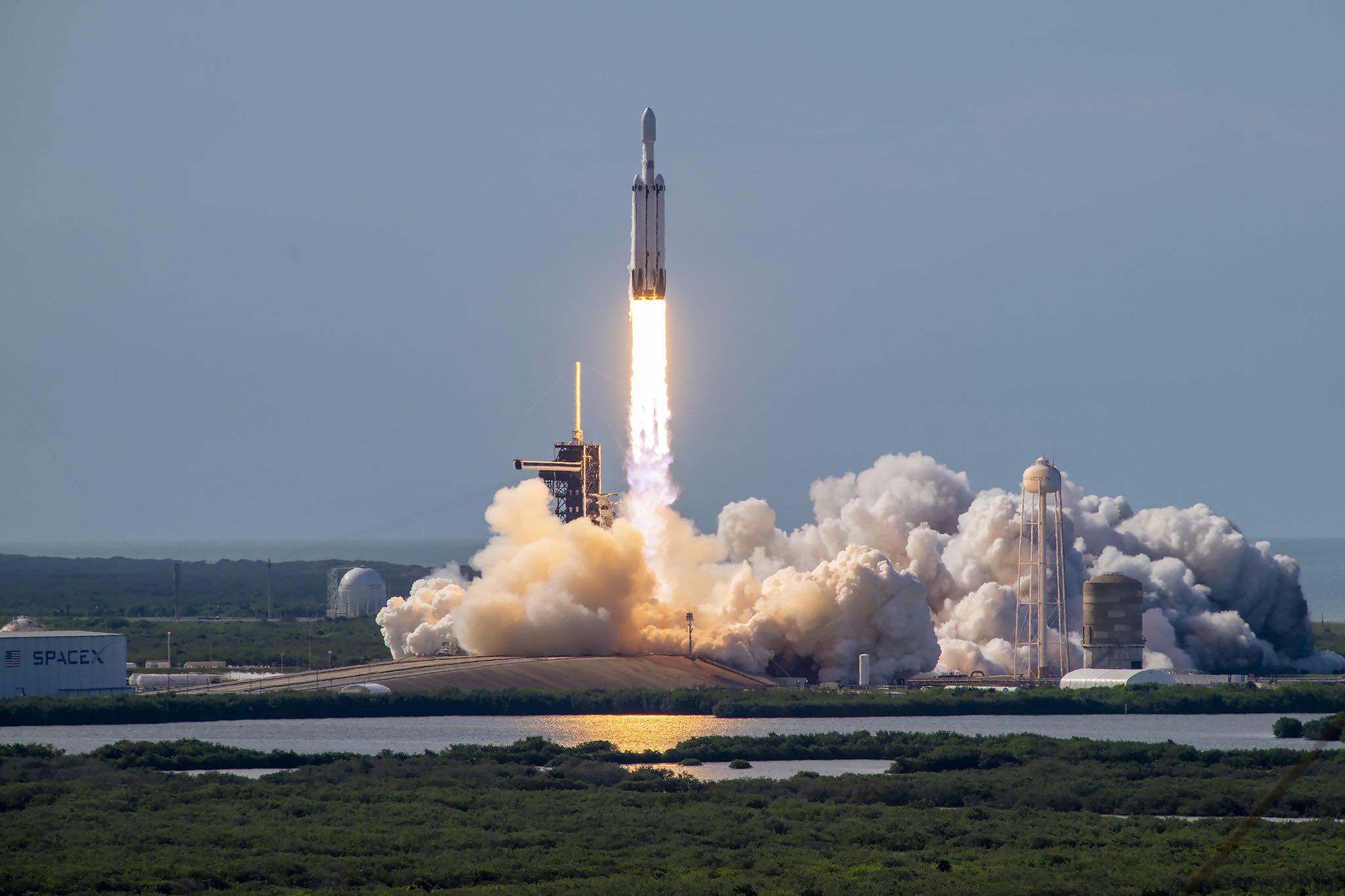

Liftoff got here at 5:26 p.m. EDT, the 27 Merlin 1D+ engines—9 every on the middle core and twin side-boosters—pushing the Falcon Heavy off Pad 39A below a mixed thrust of 5.4 million kilos (2.4 million kilograms), retaining its place because the third strongest lively operational rocket on the planet behind NASA’s House Launch System (SLS) and SpaceX’s built-in Starship/Tremendous Heavy stack. It has the capability to ship as much as 141,000 kilos (63,950 kilograms) of payload into low-Earth orbit and as a lot as 59,000 kilos (27,760 kilograms) to Geostationary Switch Orbit (GTO).
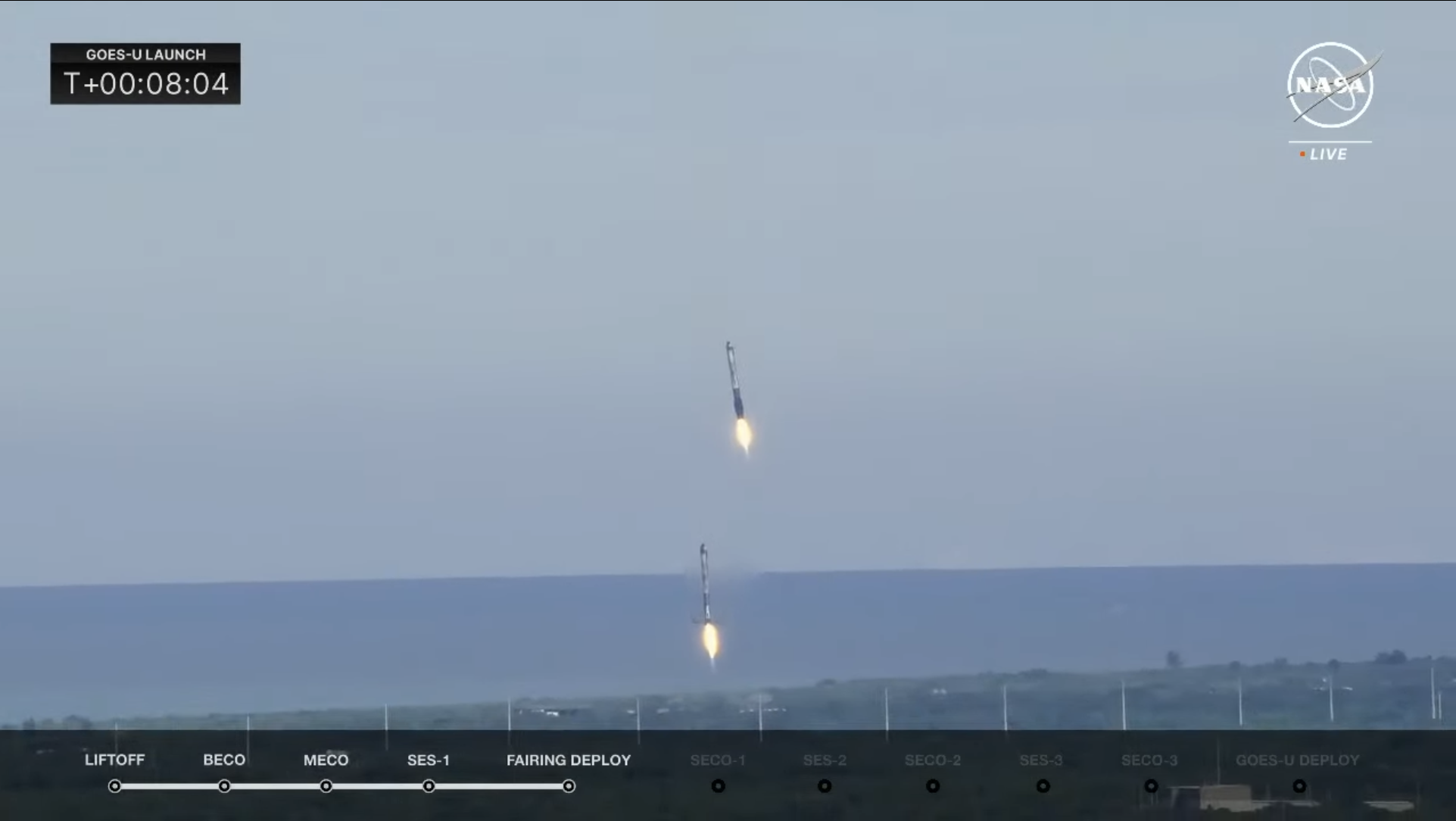
Passing the interval of peak aerodynamic turbulence, or “Max Q”, about 71 seconds into ascent, the B1086 and B1072 side-boosters shut down and separated on time about 2.5 minutes after liftoff. They commenced a swish pirouette again to Earth, alighting with synchronized precision on the twin pads at Touchdown Zones (LZ)-1 and LZ-2 at Cape Canaveral House Drive Station at T+8 minutes and 11 seconds.
Within the meantime, B1087’s personal Merlins shut down on time at simply shy of 4 minutes into ascent and the middle core was jettisoned. This set the stage for 3 “burns” by the one Merlin 1D+ Vacuum engine on the rocket stage, the primary of which kicked off at T+4 minutes and 6 seconds and lasted just a little greater than 4 minutes. Throughout this timeframe, the Falcon Heavy’s two-piece payload fairing was discarded, exposing the GOES-U spacecraft to the cruel ultra-vacuum atmosphere for the primary time.
Following the primary shutdown of the second stage, the stack drifted for about 18 minutes earlier than a second burn at 26 minutes into the mission. This brief firing lasted below 90 seconds and the stack entered one other extended interval of coasting till a closing burn was scheduled to happen at T+4 hours, 21 minutes and 18 seconds.

Lasting barely a half-minute, this closing burn assisted in lifting GOES-U to near-GEO altitude in what SpaceX described earlier this week as the best vitality efficiency ever achieved on a GOES launch. Deployment of the satellite tv for pc occurred at 4.5 hours into the flight.
Though it marked solely the primary Falcon Heavy launch of 2024, tonight’s flight was the sixty fifth general SpaceX mission of the 12 months. The opposite 64 launches have been achieved by 16 reusable Falcon 9 boosters, together with two new automobiles which got here on-line for the primary time in January and March.
These 64 launches noticed SpaceX full ten launches in a single calendar month for the primary time in January, then eleven and twelve launches in March and 13 and fourteen launches in Might alone. Two boosters have reached life-leading twenty first flights and in early March a pair of missions flew only one hour and 51 minutes aside, setting a brand new launch-to-launch turnaround report.
Up to now, as June enters its closing week, eight launches have been achieved—triggered partially by a week-long stand-down following a T-0 pad abort on 14 June, coupled with climate points which impacted two Falcon 9 flights—though not less than two extra Starlink missions are anticipated earlier than the month’s finish. One other Falcon Heavy is presently focused to fly throughout a three-week “window” in October to ship NASA’s Jupiter-bound Europa Clipper out to the neighborhood of distant Jupiter.

The 7,000-pound (3,175-kilogram) Clipper, which was delivered from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, Calif., to the House Coast, aboard an Air Drive C-17 Globemaster III airlifter final month, will spend 5.5 years voyaging out to Jupiter earlier than it conducts an in depth survey of its massive “Galilean” moon Europa, searching for indicators of latest or ongoing geological exercise, trying to find subsurface lakes and figuring out the depth and salinity of its hypothesized oceans.
Contracts value $178 million have been awarded by NASA to SpaceX in July 2021 to launch Europa Clipper, considerably decrease than might need been attainable utilizing the cargo variant of the House Launch System (SLS). Present plans envisage the mission launching as early as 10 October, the opening day of a 21-day planetary “window”.

