On September 24, 2023, NASA’s OSIRIS-REx spacecraft dropped a capsule to Earth containing pristine carbonaceous regolith collected from the near-Earth asteroid Bennu. These samples had been obtained after the probe took a formidable, seven-year roundtrip journey by way of the photo voltaic system and again.
Since these area rock items arrived (roughly 120 grams of pattern, to be exact) scientists have extremely anticipated an evaluation of the specimens that may inform us what molecules lie inside Bennu. They have been hoping to seek out clues in regards to the historical past of our photo voltaic system, seeing as Bennu ought to’ve been current when our cosmic neighborhood was coming collectively, and prebiotic molecules that may present insights into the origin of life on Earth. It is attainable, many consultants speculated, that these samples may host the seeds of different important components, similar to water, that might have contributed to Earth’s habitability in the event that they ended up on our planet, too.
“The pattern we returned is the most important reservoir of unaltered asteroid materials on Earth proper now,” Dante Lauretta, co-lead writer of the paper and principal investigator for OSIRIS-REx on the College of Arizona, Tucson, stated in a statement.
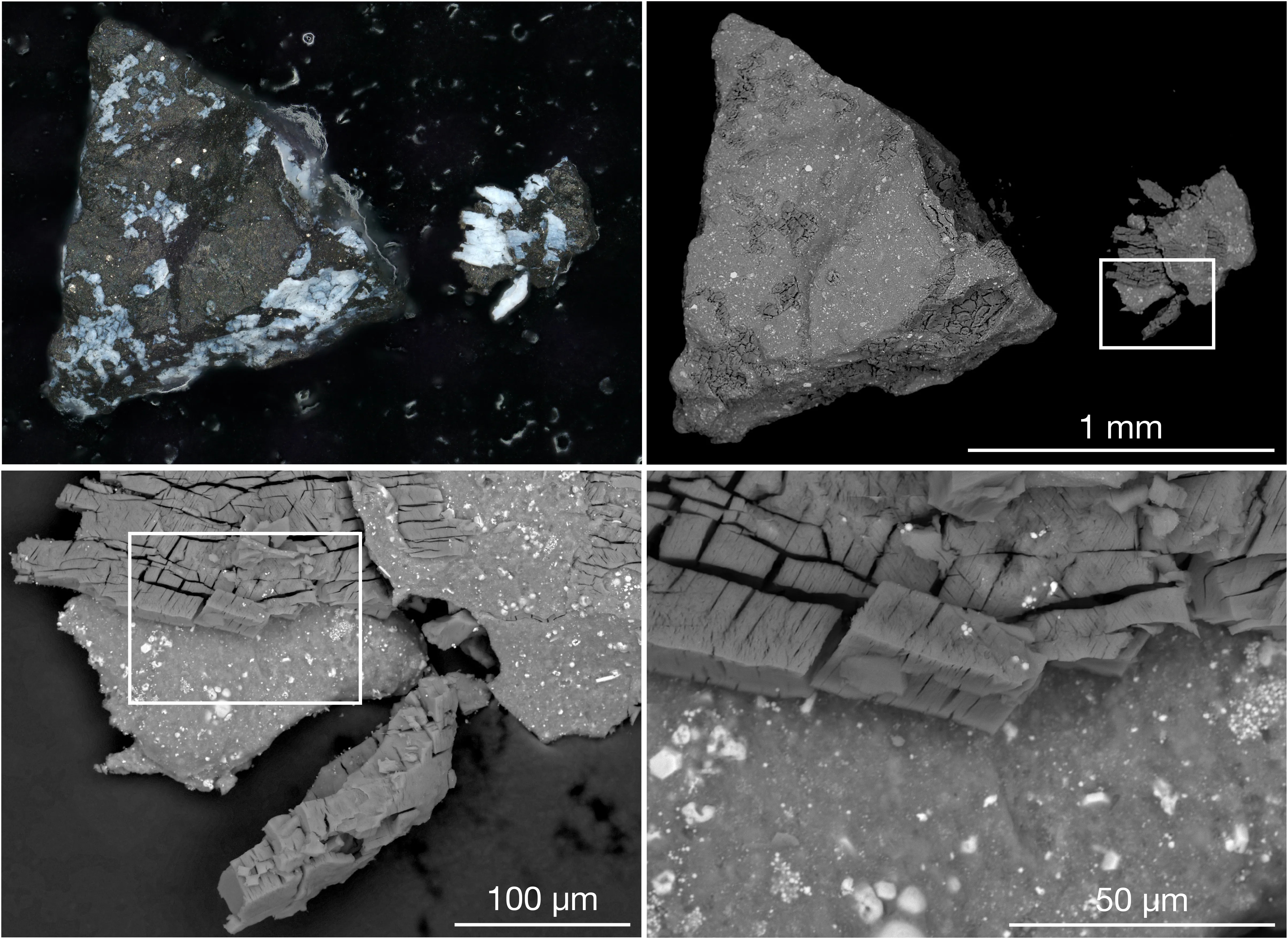
Whereas preliminary research did certainly point out the OSIRIS-REx samples exhibited evidence of carbon and water, maybe much more outstanding is the crew’s latest, and sudden, discovery of magnesium-sodium phosphate. That is an ionic compound composed of the magnesium cation (Mg2+) and phosphate anion (PO43-).
Associated: NASA’s OSIRIS-REx lands samples of asteroid Bennu to Earth after historic 4-billion-mile journey
On Earth, magnesium-sodium phosphate will be present in sure minerals and geological formations, in addition to inside residing organisms the place it’s current in varied biochemical processes and is a part of bone and enamel. In response to a NASA press launch, nonetheless, its presence on Bennu shocked the analysis crew as a result of it wasn’t seen within the OSIRIS-REx probe’s distant sensing information previous to pattern assortment. The crew says its presence “hints that the asteroid may have splintered off from a long-gone, tiny, primitive ocean world.”
“The presence and state of phosphates, together with different parts and compounds on Bennu, recommend a watery previous for the asteroid,” stated Lauretta. “Bennu probably may have as soon as been a part of a wetter world. Though, this speculation requires additional investigation.”
The OSIRIS-REx spacecraft obtained a pattern of Bennu’s regolith on October 20, 2020 utilizing its Contact-and-Go Pattern Acquisition Mechanism (TAGSAM), which includes a specialised sampler head located on an articulated arm. Bennu is a small B-type asteroid, that are comparatively unusual carbonaceous asteroids. “[Bennu] was chosen because the mission goal partially as a result of telescopic observations indicated a primitive, carbonaceous composition and water-bearing minerals,” acknowledged the crew of their paper.
The pattern was collected from a website nicknamed Nightingale, which is located in Hokioi Crater, an impression function in Bennu’s northern hemisphere that is about 20 meters (66 toes) in diameter.
Additional evaluation on the samples revealed the prevailing part of the regolith pattern is magnesium-bearing phyllosilicates, primarily serpentine and smectite — sorts of rock usually discovered at mid-ocean ridges on Earth. A comparability of those serpentinites with their terrestrial counterparts supplies attainable insights into Bennu’s geological previous. “Providing clues in regards to the aqueous setting wherein they originated,” wrote the crew.

Whereas Bennu’s floor might have been altered by water over time, it nonetheless preserves a few of the historic traits scientists consider had been current through the early photo voltaic system’s days. Bennu’s floor supplies nonetheless comprise some authentic options from the cloud of fuel and mud from which our photo voltaic system’s planets shaped — generally known as the protoplanetary disk.
The crew’s examine additionally confirmed the asteroid is wealthy in carbon, nitrogen and a few natural compounds — all of which, along with the magnesium phosphate, are important elements for all times as we all know it on Earth.
“These findings underscore the significance of accumulating and finding out materials from asteroids like Bennu — particularly low-density materials that might usually expend upon coming into Earth’s ambiance,” stated Lauretta. “This materials holds the important thing to unraveling the intricate processes of photo voltaic system formation and the prebiotic chemistry that might have contributed to life rising on Earth.”
Along with the essential scientific discoveries made throughout this mission, it underscores the importance of pattern return in unraveling the geological and geochemical intricacies of asteroids like Bennu, and their implications for the formation and evolution of the photo voltaic system.
“The info now we have offered listed here are solely the tip of the iceberg: there’s possible extra in regards to the pattern that we have no idea than we do know,” concluded the scientists.

