Utilizing the Keck II telescope, astronomers have detected an object that could be a brown dwarf or a low-mass star, exhibiting a really excessive radial velocity. The thing, designated CWISE J124909.08+362116.0 is situated some 400 mild years away. The discovering was reported July 11 on the pre-print server arXiv.
Brown dwarfs (BDs) are intermediate objects between planets and stars, occupying the mass vary between 13 and 80 Jupiter plenty (0.012 and 0.076 photo voltaic plenty). They kind like stars however aren’t sufficiently large to maintain hydrogen fusion of their cores.
Now, a crew of astronomers led by Adam Burgasser of the College of California San Diego reviews the detection of a brand new object on the brown dwarf/star mass boundary.
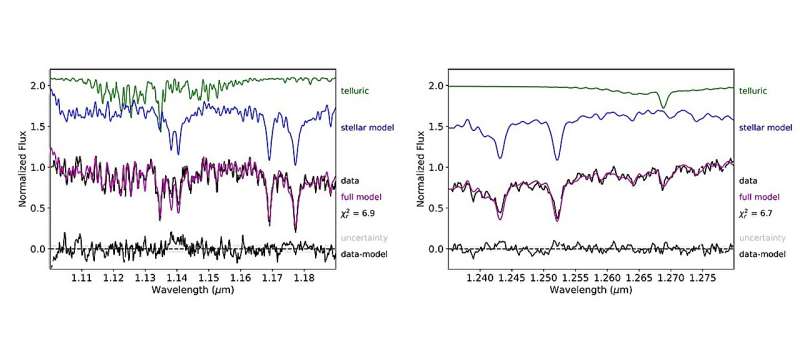
Utilizing the Close to-Infrared Echellette Spectrometer (NIRES) on the Keck II telescope, they investigated CWISE J124909.08+362116.0 (or CWISE J1249+3621 for brief)—a excessive correct movement faint pink supply first recognized by citizen scientists. Because of this, it turned out that the supply is a uncommon kind of hypervelocity subdwarf.
“We report the invention of a excessive velocity, very low-mass star or brown dwarf whose kinematics counsel it’s unbound to the Milky Method. (…) The quickest ‘hypervelocity’ stars are unbound to the Milky Method’s gravitational potential and should even have extragalactic origins,” the researchers defined.
In response to the research, CWISE J1249+3621 has a big radial velocity—at a degree of -103 km/s. This offers the galactic relaxation body velocity of 456 km/s, which corresponds to 1,530 mild years per a million years. Provided that this result’s just under the galactic escape velocity on the photo voltaic radius, which is presently estimated to be 521–580 km/s, the astronomers conclude that this object has a big chance of being unbound to the Milky Method.
The observations discovered that CWISE J1249+3621 has a mass of some 0.082 photo voltaic plenty and its efficient temperature is estimated to be 1,715–2,320 Ok. The metallicity of CWISE J1249+3621 was measured to be inside a variety of -1.4 and -0.5.
Primarily based on the collected information, the authors of the paper assume that CWISE J1249+3621 is probably going a hypervelocity metal-poor, early-type L subdwarf star moderately than a brown dwarf. They underline that it might due to this fact be the primary recognized low-mass hypervelocity star and the closest such object to Earth.
In attempting to find out the origin of CWISE J1249+3621, the researchers have in mind a number of totally different hypotheses, together with ejection from the galactic middle greater than three billion years in the past, or a survival because the companion to an accreting white dwarf that exploded.
Additional investigation into bodily and atmospheric properties of this object is required to be able to infer its true origin.
Extra info:
Adam J. Burgasser et al, Discovery of a Hypervelocity L Subdwarf on the Star/Brown Dwarf Mass Restrict, arXiv (2024). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2407.08578
© 2024 Science X Community
Quotation:
Observations detect a close-by hypervelocity stellar/substellar object (2024, July 18)
retrieved 18 July 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.

