Astronomers making an attempt to measure the solar’s age by analyzing vibrations rippling inside the solar have realized one thing troubling. It appears that evidently the photo voltaic cycle of magnetic exercise is interfering with their efforts. In fact, we are able to confirm the solar’s true age via unbiased means — and we due to this fact know it is about 4.6 billion years outdated — however this concern with vibrational measurements of stellar age threatens to thwart makes an attempt to measure the elemental traits of different stars.
We all know the solar’s age as a result of, for example, scientists have managed to measure the radioactive decay of atoms in our photo voltaic system that fashioned alongside the planets and the solar. Radioactive decay refers to when the nucleus of an atom loses vitality by way of radiation and decays right into a extra steady aspect. The speed of decay of a amount of radioactive materials is described as its half-life, which is the time taken for half of that amount to decay, so we are able to backtrack and work out how outdated it’s based mostly on how a lot has decayed over time. Thus, by monitoring the timeline of radioactive decay for atoms inside our photo voltaic system, we are able to deduce the age of our photo voltaic system. As well as, scientists’ detailed fashions of stellar evolution are key in figuring out the solar’s age.
There’s additionally one other technique to decide the age of the solar, or any star for that matter. It is known as helioseismology when associated to the solar, and asteroseismology when referring to different stars.
“You will need to think about a star as an enormous ball of fuel in fixed movement,” stated Jérôme Bétrisey of the College of Geneva in a statement. “Inside this star there are waves or pulsations that make it vibrate, slightly just like the sound that resonates in a musical instrument. These vibrations trigger the star’s floor to maneuver barely and alter luminosity frequently. Because of very exact devices, we are able to detect these variations in luminosity.”
Associated: Scientists accumulate high-resolution pictures of the North Star’s floor for 1st time
There are a number of completely different patterns, or modes, of oscillation overlapping within the solar, all with completely different durations and frequencies. And simply as finding out seismic waves on Earth can inform us in regards to the inside of our planet because the tremors cross via, oscillations within the solar are informative of its inside construction. By evaluating what these oscillations are telling us with detailed fashions of what the inside of the solar ought to appear like at completely different ages, photo voltaic physicists can decide what age the solar presently is.
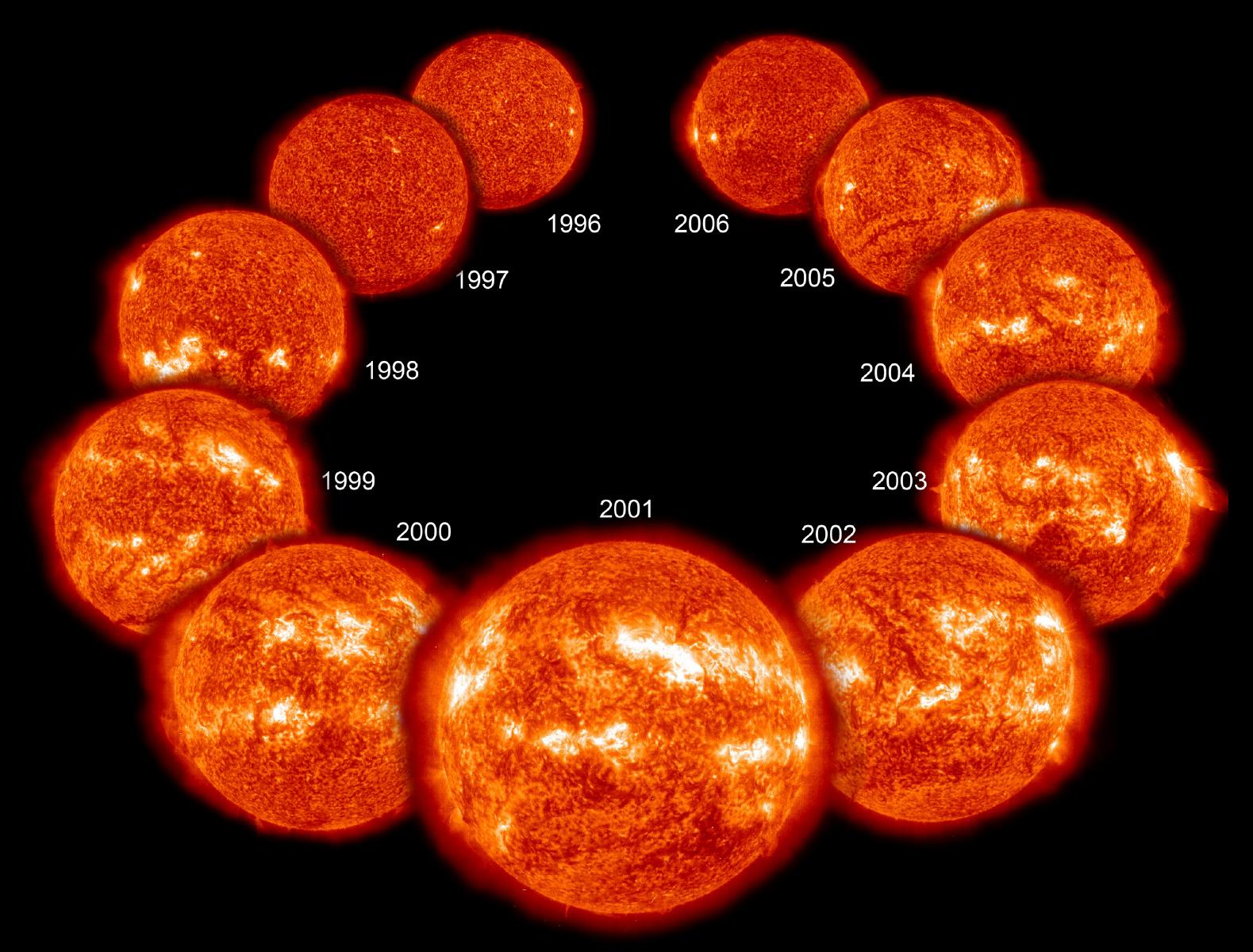
Nonetheless, earlier measurements have revealed discrepancies between photo voltaic age observations and theoretical fashions — and now, a group led by Bétrisey has proven that it is most likely the solar’s personal magnetic exercise that’s at fault. That is stunning, as a result of the consensus had beforehand been that magnetic exercise should not have any affect in any respect.
Bétrisey’s group checked out 26.5 years’ price of knowledge from two sun-observing applications. One was BISON, the Birmingham Photo voltaic Oscillations Community, which is a set of ground-based photo voltaic observatories overseen by scientists on the College of Birmingham within the U.Ok. The opposite was GOLF, the World Oscillations at Low Frequency instrument on the joint NASA–ESA SOHO (Photo voltaic and Heliospheric Observatory) mission that was launched in 1995.
Our solar undergoes an 11-year cycle of magnetic exercise, rising from photo voltaic minimal when there are hardly any sunspots seen, to photo voltaic most when there are sunspots, prominences, coronal mass ejections and flares aplenty.
The BISON and GOLF knowledge each confirmed a 6.5% distinction when measuring the solar’s age by way of helioseismology at photo voltaic minimal in comparison with at photo voltaic most. Moreover, of the 2 photo voltaic cycles encompassed by the 26.5 years’ price of observations, each BISON and GOLF indicated that the cycle with stronger magnetic exercise had a higher affect upon the discrepancy within the age measurement.
As a result of, within the grand scheme of issues, the solar just isn’t a really lively star, the outcomes from BISON and GOLF recommend that “the affect of magnetic exercise might be very vital for extra lively stars similar to people who PLATO will detect,” stated Bétrisey.
PLATO, or the Planetary Transits and Oscillations of Stars, which is a forthcoming mission to be launched by the European Area Company in 2026, will survey stars in search of dips of their mild. A few of these dips shall be brought on by transiting exoplanets, however PLATO may even be capable to detect dips within the luminosity of stars ensuing from asteroseismic oscillations, from which astronomers ought to be capable to decide important stellar statistics together with mass, radius and, certainly, age. Though the explanation why magnetic exercise can have an effect on asteroseismic measurements just isn’t but clear, it should be taken into consideration for PLATO’s observations, whereas Bétrisey’s group additionally means that previous measurements, similar to these made with NASA’s Kepler Area Telescope, can also want revisiting.
As Bétrisey and colleagues describe it of their analysis paper, this can be a “looming problem” for the way forward for asteroseismology.
The findings have been printed on Aug. 8 within the journal Astronomy and Astrophysics.

