
Folks have noticed the intense Martian poles wax and wane for hundreds of years, however solely throughout the final 50 years have scientists found that they’re largely comprised of carbon dioxide biking out and in of the ambiance to the rhythm of the seasons. However precisely how this occurs is a posh interaction of planetary processes that scientists are frequently teasing out.
The analysis is published within the journal Icarus.
PSI Senior Scientist Candice Hansen leads a brand new paper printed in Icarus that weaves collectively many years of previous analysis with newer observations collected by the Excessive-Decision Imaging Experiment, or HiRISE, instrument on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to match how the Martian poles differ of their seasonal uptake and launch of carbon dioxide.
“Everyone is aware of there is a distinction in how carbon dioxide interacts with the poles, however how many individuals perceive why?” Hansen stated. “That was what I used to be getting down to describe. And happily, I’ve an entire bunch of actually proficient co-authors who have been keen to fill in their very own items.”
The purpose was to make clear the processes that form the planet’s floor in addition to Mars’ general local weather—since Mars cycles a couple of quarter of its ambiance all through the Martian yr.
Like Earth, Mars spins at a tilt of about 25 levels, so it experiences seasons, however Mars’ for much longer path across the solar can be extra rectangular—or what scientists name eccentric—than Earth’s.
If Mars’ path across the solar was an ideal circle, then all of its seasons can be equally lengthy. However its eccentricity situates Mars farthest from the solar throughout southern fall and winter—which is concurrently northern spring and summer time—that means these seasons for every hemisphere are the longest for the planet. Mars’ southern hemisphere can be considerably extra elevated than the northern hemisphere.
“So finally, southern fall and winter convey essentially the most freezing and lowest atmospheric strain,” since a lot of the ambiance is frozen as dry ice, Hansen stated. “These are the main drivers of variations in seasonal conduct of carbon dioxide between the hemispheres.”

Mars’ northern winter, in contrast, isn’t solely shorter than southern winter, nevertheless it additionally coincides with mud storm season. Because of this, the northern polar seasonal cap incorporates a better focus of mud than the south polar cap, making the ice much less sturdy.
“They are not symmetric seasons,” Hansen stated.
Variations within the northern and southern polar terrains additionally affect how carbon dioxide ice and fuel form the panorama, in accordance with the paper. For instance, within the southern hemisphere, black mud followers are distributed throughout the panorama.
“A layer of carbon dioxide ice builds within the southern hemisphere fall, and over the course of the winter, it thickens and it turns into translucent,” Hansen stated. “Then within the spring, the solar comes up, and light-weight penetrates this ice layer to the underside sufficient that it warms up the bottom beneath.”
The nice and cozy floor then turns the carbon dioxide ice into fuel, a course of known as sublimation.
“Now, fuel is trapped underneath strain,” Hansen stated. “It will search for any weak spot within the ice and rupture like a champagne cork.”
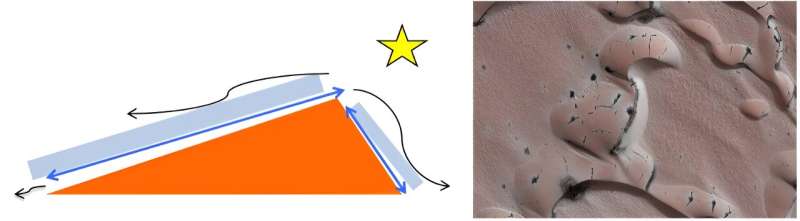
As quickly because it finds a weak spot, the ice ruptures and fuel rushes over to the break, carving on the floor alongside the best way, making a community of gully channels that splay out throughout the panorama. These are known as araneiforms due to their spider-like look.
As soon as the fuel breaks via the ice, it blows darkish mud into the ambiance.
“It seems that meteorology is de facto essential on this image too, as a result of from there, the mud is blown by no matter wind occurs to be current and lands in a fan-shaped deposit,” Hansen stated.
Geophysicist Hugh Kieffer described that course of in 2006. Just a few years later, Hansen adopted up along with her personal mannequin for the north polar cap, which additionally shows followers within the spring.
She discovered that the identical phenomena happen within the north, however fairly than comparatively flat terrain, these processes play out throughout sand dunes.
“When the solar comes up and begins to sublimate the underside of the ice layer, there are three weak spots—one on the crest of the dune, one on the backside of the dune the place it meets the floor after which the ice itself can crack alongside the slope,” Hansen stated. “No araneiform terrain has been detected within the north as a result of though shallow furrows develop, the wind smooths the sand on the dunes.”
As a member of the HiRISE imaging crew, Hansen sees adjustments on the Martian floor over the course of years, months, even days.
“Most of my colleagues research the adjustments that occurred on Mars 3.5 billion years in the past, however I am speaking about issues that occurred final month,” Hansen stated. “Mars is energetic immediately.”
Extra data:
C.J. Hansen et al, A comparability of CO2 seasonal exercise in Mars’ northern and southern hemispheres, Icarus (2023). DOI: 10.1016/j.icarus.2023.115801
Quotation:
The Martian polar caps aren’t created equally—this is why (2024, September 3)
retrieved 3 September 2024
from
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.

