Starliner’s lengthy area odyssey is over.
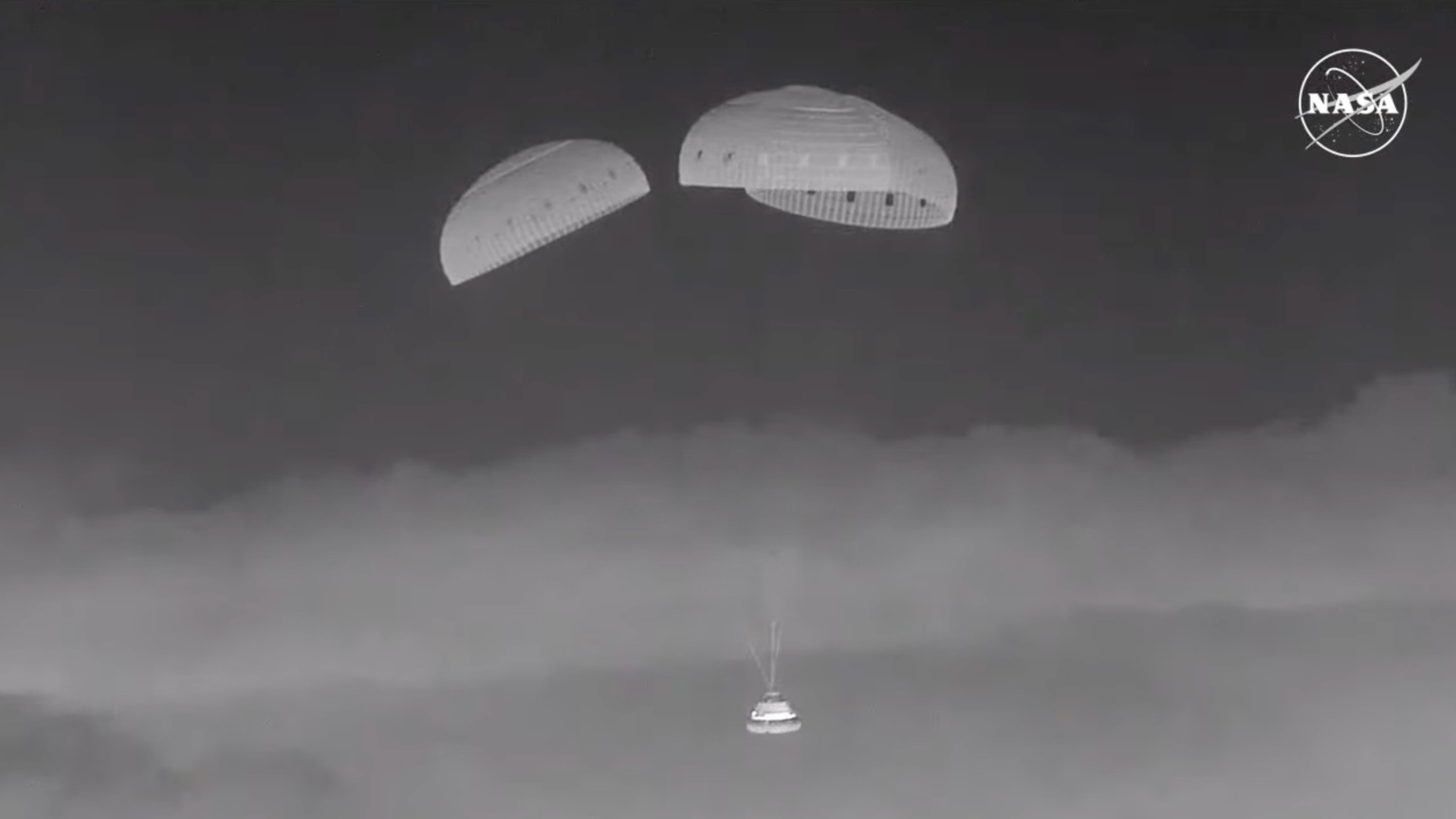
The Boeing capsule, named Calypso, returned to Earth early this morning (Sept. 7), touching down within the New Mexico desert at 12:01 a.m. EDT (0401 GMT; 11:01 p.m. native time on Sept. 6).
“Nice touchdown of Calyspo!” NASA astronaut Suni Williams stated on the company’s webcast. “I do not assume that might have gone higher.”
The touchdown was long-delayed, coming greater than three months into an orbital mission initially anticipated to final about 10 days. And, whereas Starliner launched with two NASA astronauts aboard — Williams and Butch Wilmore — no person rode it residence.
It wasn’t supposed to finish like this.

Construct Boeing’s Starliner!
You may construct your individual Boeing Starliner area capsule with this Steel Earth Boeing CST-100 Starliner 3D Steel Mannequin Package, available for $10.95 at Amazon.
An important take a look at flight
The roots of the just-completed mission, referred to as Crew Flight Take a look at (CFT), return a decade. In 2014, NASA gave SpaceX and Boeing multibillion-dollar contracts to complete work on their astronaut taxis — capsules referred to as Crew Dragon and Starliner, respectively.
The company wished one or each of these automobiles to begin flying astronauts to and from the Worldwide Area Station (ISS) by 2017, reestablishing a homegrown orbital human spaceflight functionality — one thing the U.S. had lacked for the reason that retirement of the area shuttle in 2011.
Associated: NASA’s area shuttle program in footage: A tribute
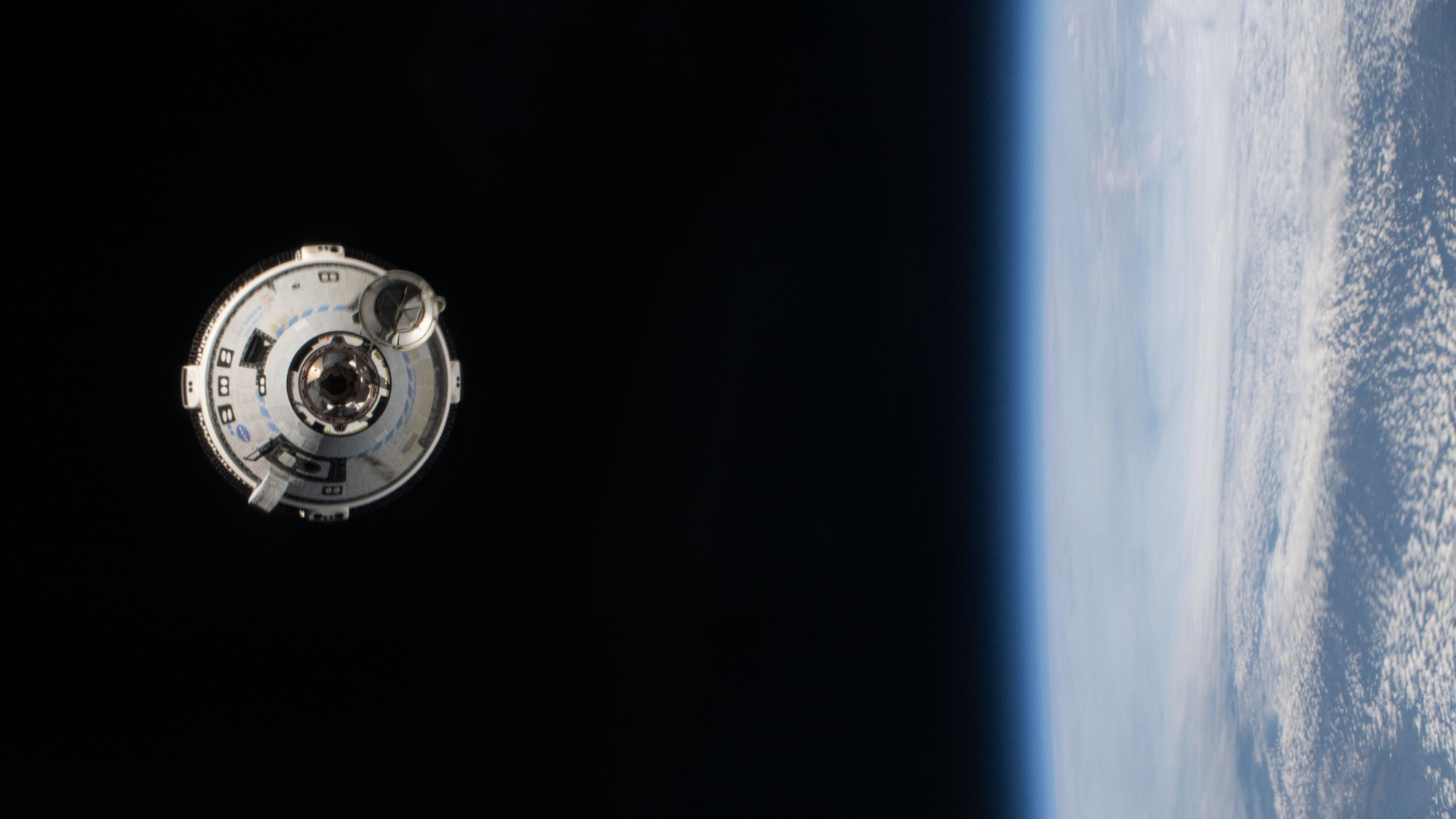
Neither capsule hit that bold goal. SpaceX’s first astronaut mission, a take a look at flight to the ISS referred to as Demo-2, lifted off in Could 2020. Starliner’s crewed debut was CFT, which launched atop a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket on June 5, sending Williams and Wilmore to the orbiting lab for a deliberate eight-day keep.
CFT had been slated to fly final yr, nevertheless it was delayed to cope with parachute points and to take away massive quantities of insulating tape from the capsule’s wiring system. (Analsyes decided that the tape was flammable and thus posed a security threat.)
The mission encountered points extra just lately as effectively. A deliberate Could 25 launch try was scrubbed, for instance, after crew members observed a small helium leak in Starliner’s service module. Extra helium leaks popped up after launch, as Starliner chased the ISS down in orbit. And, extra concerningly, the capsule skilled propulsion issues: 5 of its 28 response management system (RCS) thrusters conked out not lengthy after liftoff.
The thruster issues scuttled Starliner’s first ISS docking try on June 6. The capsule succeeded on its second attempt that day, and crew members ultimately introduced 4 of the 5 defective thrusters again on-line. However the difficulty loomed massive over the remainder of the mission.

A troublesome determination
NASA prolonged CFT’s orbital keep repeatedly, giving mission crew members extra time to research and troubleshoot the thruster issues. Such work included modeling research and testing each in area (with Starliner) and on the bottom (with a Starliner RCS thruster at NASA’s White Sands Take a look at Facility in New Mexico).
In the end, NASA concluded that bringing Williams and Wilmore residence on Starliner posed an unacceptable security threat.
“The choice to maintain Butch and Suni aboard the Worldwide Area Station and produce Boeing’s Starliner residence uncrewed is the results of our dedication to security: our core worth and our North Star,” NASA Administrator Invoice Nelson said in a statement on Aug. 24, the day the company introduced the information.
Associated: Boeing Starliner astronauts will return residence on a SpaceX Dragon in 2025, NASA confirms
Williams and Wilmore will keep aboard the ISS till February, after they’ll hitch a trip residence on a SpaceX Crew Dragon — the one flying the corporate’s Crew-9 mission, which is about to raise off later this month. To make room for them, Crew-9 will raise off with two astronauts as an alternative of the same old 4.
Starliner, in the meantime, was packed up for an uncrewed return to Earth. Among the many gear that it carried residence had been the “Boeing Blue” spacesuits that Williams and Wilmore wore aboard the capsule. The astronauts don’t have any want for them now.
“The fits should not appropriate,” Steve Stich, supervisor of NASA’s Industrial Crew Program, stated throughout a press convention on Wednesday (Sept. 4). “So the Starliner fits wouldn’t work in Dragon, and vice versa.”
Starliner undocked from the ISS on Friday (Sept. 6) at 6:04 p.m. EDT (2204 GMT) as deliberate. It carried out a collection of burns to set itself up for the uncrewed touchdown, which occurred below parachutes in New Mexico’s White Sands Area Harbor simply after midnight as we speak.
It was the third landing general for Starliner. The capsule additionally flew two uncrewed take a look at flights to the ISS, one in December 2019 and one in Could 2022. Starliner failed to satisfy up with the orbiting lab on the primary flight after struggling a number of glitches. The second uncrewed mission was a hit, although Starliner skilled some thruster points on that flight as effectively. (These had been a distinct set, related not with the RCS however with Starliner’s orbital maneuvering and management system.)
A cloudy future
Boeing and NASA had hoped that CFT would pave the way in which for Starliner’s certification, permitting the capsule to start flying six-month-long astronaut missions to the ISS.
The primary such operational flight, Starliner-1, had been focused for February 2025. That launch has already been pushed again, nevertheless, to August 2025 on the earliest. And it is unclear in the intervening time if Starliner can be licensed by then — or what extra exams, if any, NASA would require earlier than certification can happen.
“I believe what we have to do now could be actually lay out the general plan, which we now have not had time to do,” Stich stated within the Sept. 4 press convention.
“We’ve not, as a result of the groups have been so centered on this flight, laying out that general search technique, the general quantity of labor we have to go do,” he added. “After which after we do this, we’ll have a greater understanding of, When can we certify the automobile, and when can we resume flights?”
Crew Dragon, in the meantime, was licensed shortly after Demo-2’s profitable conclusion in 2020. The SpaceX automobile is now gearing up for its ninth operational astronaut flight to the ISS for NASA. (That will be Crew-9, because the identify suggests.)
SpaceX has additionally flown a handful of personal crewed missions to the station, in addition to the Inspiration4 astronaut flight to Earth orbit, which didn’t meet up with the orbiting lab. And it is getting ready to launch Polaris Daybreak, one other free-flying industrial astronaut mission, which goals to conduct the first-ever personal spacewalk.

