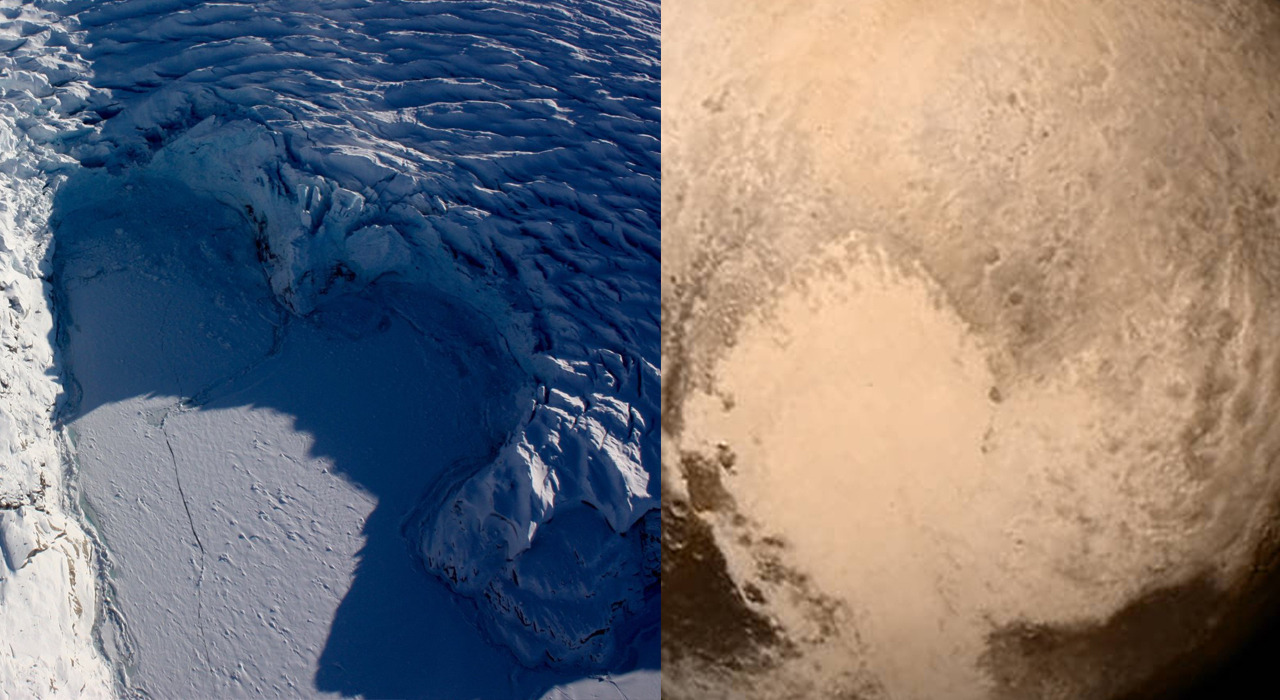

Icy Hearts: A heart-shaped calving front of a glacier in Greenland (left) and Pluto’s frozen plains (proper). Credit: NASA/Maria-Jose Viñas and NASA/APL/SwRI
From deep beneath the soil at Earth’s polar areas to Pluto’s frozen coronary heart, ice exists everywhere in the photo voltaic system…and past. From proper right here on our house planet to moons and planets hundreds of thousands of miles away, we’re exploring ice and watching the way it modifications. Right here’s 10 issues to know:
1. Earth’s Altering Ice Sheets
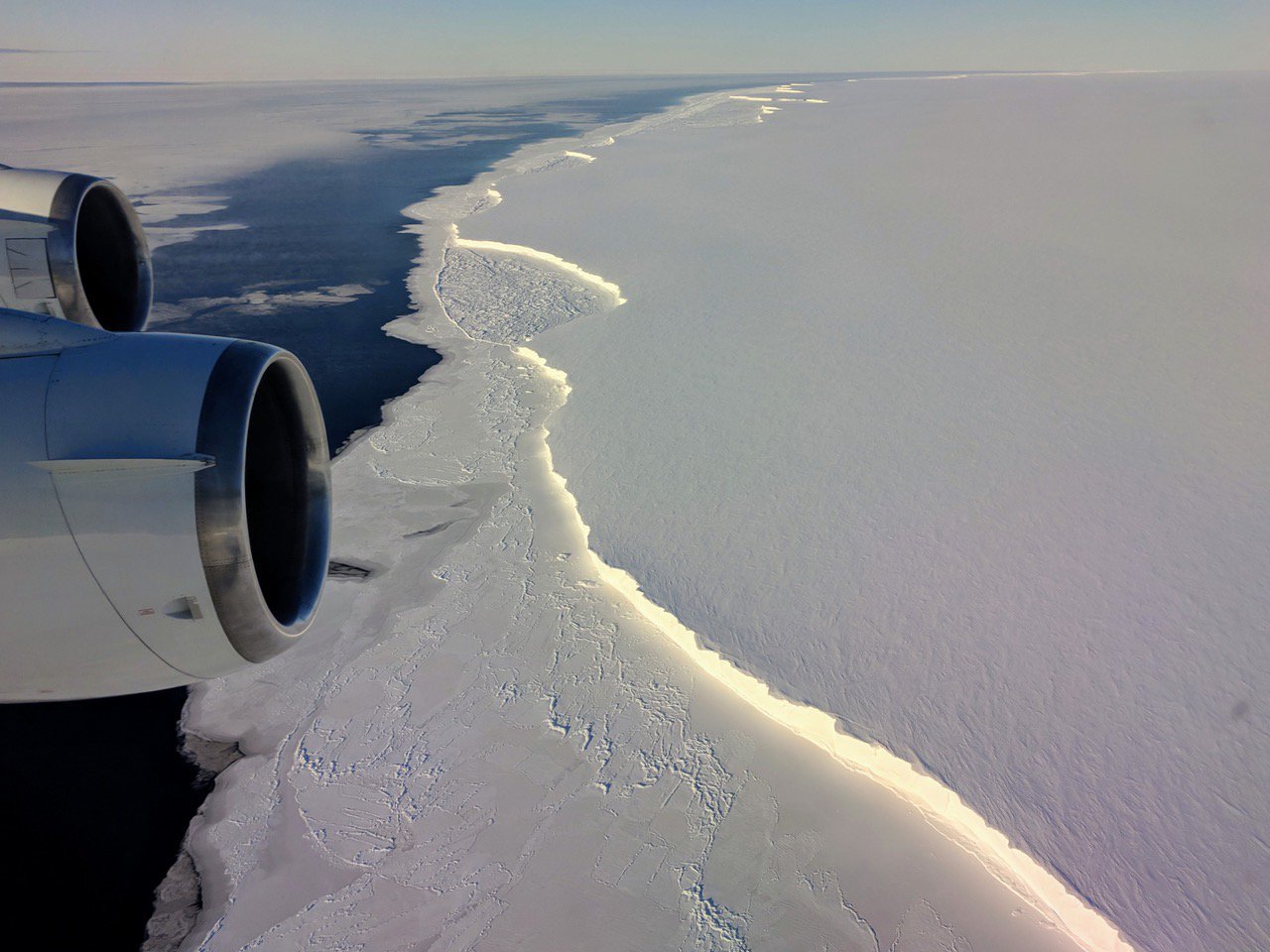

An Antarctic ice sheet. Credit score: NASA
Ice sheets are huge expanses of ice that keep frozen from 12 months to 12 months and canopy greater than 6 million sq. miles. On Earth, ice sheets prolong throughout most of Greenland and Antarctica. These two ice sheets include greater than 99 p.c of the planet’s freshwater ice. Nevertheless, our ice sheets are delicate to the altering local weather.
Knowledge from our GRACE satellites present that the land ice sheets in each Antarctica and Greenland have been dropping mass since a minimum of 2002, and the velocity at which they’re dropping mass is accelerating.
2. Sea Ice at Earth’s Poles

Earth’s polar oceans are coated by stretches of ice that freezes and melts with the seasons and strikes with the wind and ocean currents. Throughout the autumn and winter, the ocean ice grows till it reaches an annual most extent, after which melts again to an annual minimal on the finish of summer season. Sea ice performs a vital position in regulating local weather – it’s way more reflective than the darkish ocean water, reflecting as much as 70 p.c of daylight again into house; in distinction, the ocean displays solely about 7 p.c of the daylight that reaches it. Sea ice additionally acts like an insulating blanket on prime of the polar oceans, conserving the polar wintertime oceans heat and the ambiance cool.
Some Arctic sea ice has survived a number of years of summer season soften, however our analysis signifies there’s much less and fewer of this older ice annually. The utmost and minimal extents are shrinking, too. Summertime sea ice within the Arctic Ocean now routinely covers about 30-40 p.c much less space than it did within the late Nineteen Seventies, when near-continuous satellite tv for pc observations started. These modifications in sea ice circumstances improve the speed of warming within the Arctic, already in progress as extra daylight is absorbed by the ocean and extra warmth is put into the ambiance from the ocean, all of which can in the end have an effect on international climate patterns.
3. Snow Cowl on Earth

Snow extends the cryosphere from the poles and into extra temperate areas.
Snow and ice cowl most of Earth’s polar areas all year long, however the protection at decrease latitudes is determined by the season and elevation. Excessive-elevation landscapes such because the Tibetan Plateau and the Andes and Rocky Mountains preserve some snow cowl nearly year-round. Within the Northern Hemisphere, snow cowl is extra variable and in depth than within the Southern Hemisphere.
Snow cowl probably the most reflective floor on Earth and works like sea ice to assist cool our local weather. Because it melts with the seasons, it offers ingesting water to communities across the planet.
4. Permafrost on Earth
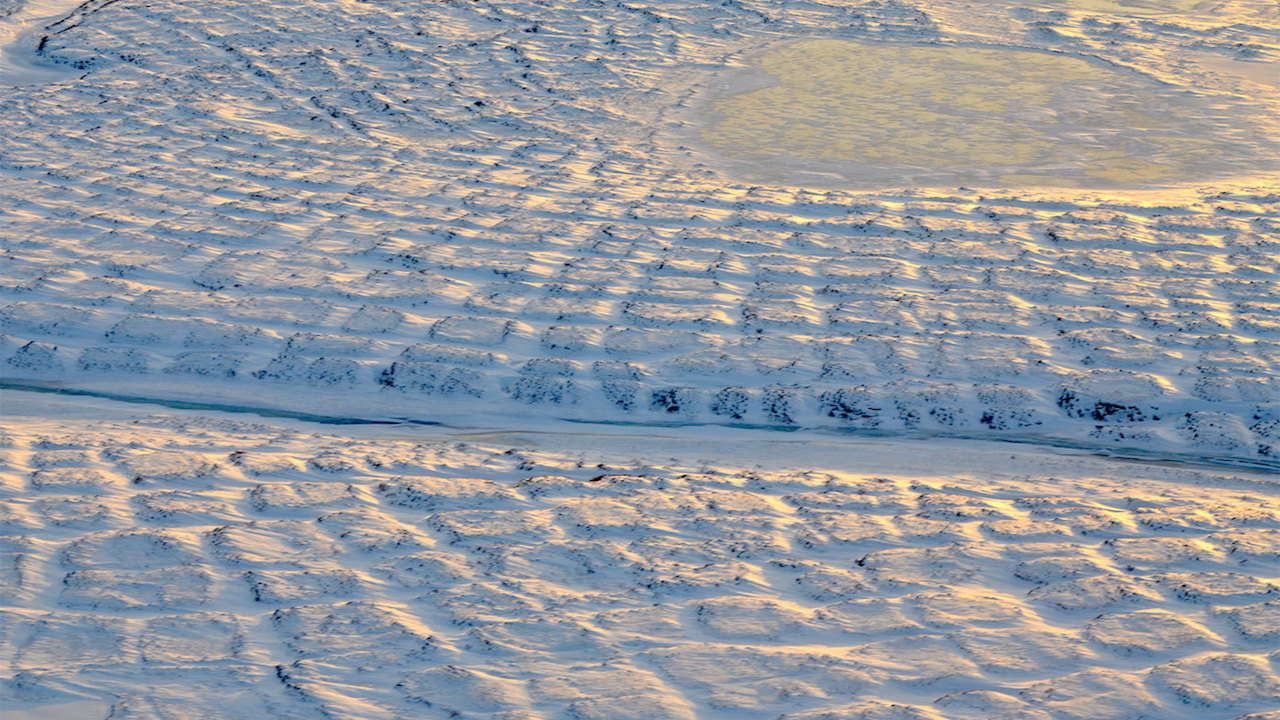

Tundra polygons on Alaska’s North Slope. As permafrost thaws, this space is prone to be a supply of atmospheric carbon earlier than 2100. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/Charles Miller
Permafrost is soil that stays frozen stable for a minimum of two years in a row. It happens within the Arctic, Antarctic and excessive within the mountains, even in some tropical latitudes. The Arctic’s frozen layer of soil can prolong greater than 200 ft beneath the floor. It acts like chilly storage for useless natural matter – vegetation and animals.
In elements of the Arctic, permafrost is thawing, which makes the bottom wobbly and unstable and may launch these natural supplies from their icy storage. Because the permafrost thaws, tiny microbes within the soil wake again up and start digesting these newly accessible natural supplies, releasing carbon dioxide and methane, two greenhouse gases, into the ambiance.
Two campaigns, CARVE and ABoVE, research Arctic permafrost and its potential results on the local weather because it thaws.
5. Glaciers on the Transfer

Do you know glaciers are always shifting? The plenty of ice act like slow-motion rivers, flowing below their very own weight. Glaciers are fashioned by falling snow that accumulates over time and the sluggish, regular creep of flowing ice. About 10 p.c of land space on Earth is roofed with glacial ice, in Greenland, Antarctica and excessive in mountain ranges; glaciers retailer a lot of the world’s freshwater.
Our satellites and airplanes have a chicken’s eye view of those glaciers and have watched the ice skinny and their flows speed up, dumping extra freshwater ice into the ocean, elevating sea degree.
6. Pluto’s Icy Coronary heart

The nitrogen ice glaciers on Pluto seem to hold an intriguing cargo: quite a few, remoted hills that could be fragments of water ice from Pluto’s surrounding uplands. NASA/Johns Hopkins College Utilized Physics Laboratory/Southwest Analysis Institute
Pluto’s most well-known characteristic – that coronary heart! – is stone chilly. First noticed by our New Horizons spacecraft in 2015, the guts’s western lobe, formally named Sputnik Planitia, is a deep basin containing three sorts of ices – frozen nitrogen, methane and carbon monoxide.
Fashions of Pluto’s temperatures present that, due the dwarf planet’s excessive tilt (119 levels in comparison with Earth’s 23 levels), over the course of its 248-year orbit, the latitudes close to 30 levels north and south are the coldest locations – far colder than the poles. Ice would have naturally fashioned round these latitudes, together with on the middle of Sputnik Planitia.
New Horizons additionally noticed unusual ice formations resembling large knife blades. This “bladed terrain” comprises constructions as tall as skyscrapers and made nearly solely of methane ice, seemingly fashioned as erosion wore away their surfaces, leaving dramatic crests and sharp divides. Related constructions may be present in high-altitude snowfields alongside Earth’s equator, although on a really completely different scale.
7. Polar Ice on Mars

This picture, combining knowledge from two devices aboard our Mars World Surveyor, depicts an orbital view of the north polar area of Mars. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
Mars has brilliant polar caps of ice simply seen from telescopes on Earth. A seasonal cowl of carbon dioxide ice and snow advances and retreats over the poles in the course of the Martian 12 months, very like snow cowl on Earth.
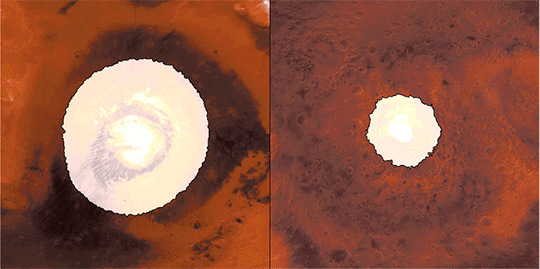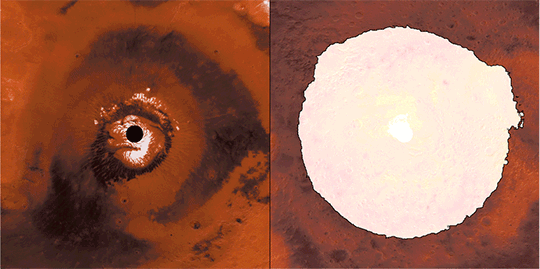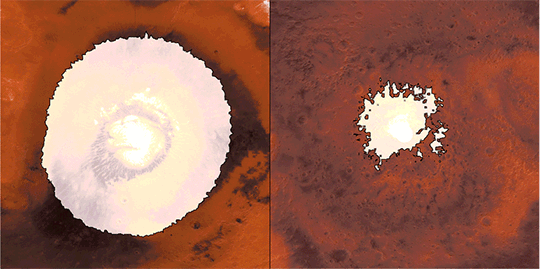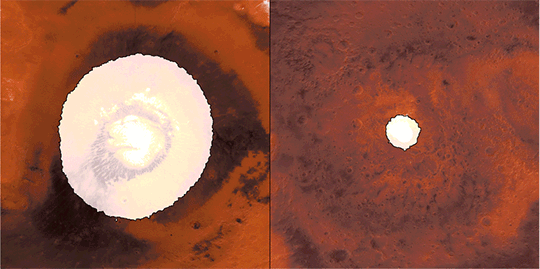
This animation reveals a side-by-side comparability of CO2 ice on the north (left) and south (proper) Martian poles over the course of a typical 12 months (two Earth years). This simulation isn’t based mostly on photographs; as an alternative, the info used to create it got here from two infrared devices able to finding out the poles even after they’re in full darkness. This knowledge had been collected by our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, and Mars World Surveyor. Credit score: NASA/JPL-Caltech
Throughout summertime within the planet’s north, the remaining northern polar cap is all water ice; the southern cap is water ice as effectively, however stays coated by a comparatively skinny layer of carbon dioxide ice even in summertime.
Scientists utilizing radar knowledge from our Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter discovered a document of the latest Martian ice age within the planet’s north polar ice cap. Analysis signifies a glacial interval ended there about 400,000 years in the past. Understanding seasonal ice habits on Mars helps scientists refine fashions of the Crimson Planet’s previous and future local weather.
8. Ice Feeds a Ring of Saturn

Wispy fingers of brilliant, icy materials attain tens of hundreds of kilometers outward from Saturn’s moon Enceladus into the E ring, whereas the moon’s lively south polar jets proceed to fireplace away. Credit score: NASA/JPL/House Science Institute
Saturn’s rings and plenty of of its moons are composed of principally water ice – and one among its moons is definitely creating a hoop. Enceladus, an icy Saturnian moon, is roofed in “tiger stripes.” These lengthy cracks at Enceladus’ South Pole are venting its liquid ocean into house and making a cloud of nice ice particles over the moon’s South Pole. These particles, in flip, kind Saturn’s E ring, which spans from about 75,000 miles (120,000 kilometers) to about 260,000 miles (420,000 kilometers) above Saturn’s equator. Our Cassini spacecraft found this venting course of and took high-resolution pictures of the system.

Jets of icy particles burst from Saturn’s moon Enceladus on this temporary film sequence of 4 pictures taken on Nov. 27, 2005. Credit score: NASA/JPL/House Science Institute
9. Ice Rafts on Europa
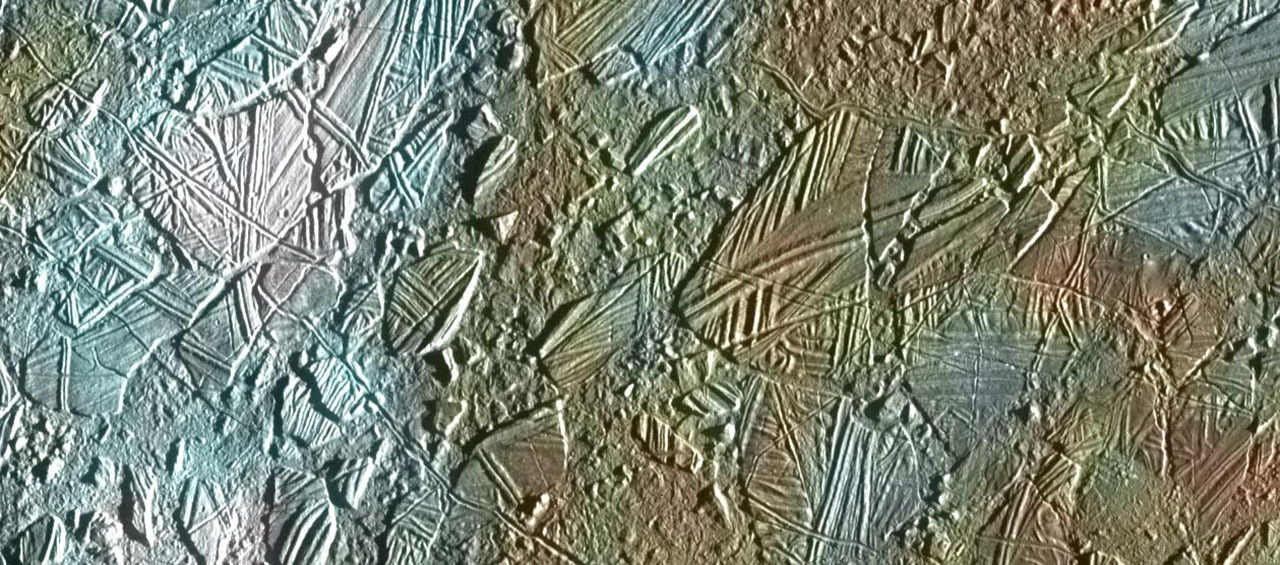

View of a small area of the skinny, disrupted, ice crust within the Conamara area of Jupiter’s moon Europa exhibiting the interaction of floor colour with ice constructions. Credit score: NASA/JPL/College of Arizona
The icy floor of Jupiter’s moon Europa is crisscrossed by lengthy fractures. Throughout its flybys of Europa, our Galileo spacecraft noticed icy domes and ridges, in addition to disrupted terrain together with crustal plates which are thought to have damaged aside and “rafted” into new positions. An ocean with an estimated depth of 40 to 100 miles (60 to 150 kilometers) is believed to lie beneath that 10- to 15-mile-thick (15 to 25 km) shell of ice.
The rafts, unusual pits and domes recommend that Europa’s floor ice may very well be slowly turning over as a result of warmth from beneath. Our Europa Clipper mission, focused to launch in 2022, will conduct detailed reconnaissance of Europa to see whether or not the icy moon may harbor circumstances appropriate for all times.
10. Crater Ice on Our Moon

The picture reveals the distribution of floor ice on the Moon’s south pole (left) and north pole (proper), detected by our Moon Mineralogy Mapper instrument. Credit score: NASA
Within the darkest and coldest elements of our Moon, scientists straight noticed definitive proof of water ice. These ice deposits are patchy and may very well be historical. Many of the water ice lies contained in the shadows of craters close to the poles, the place the warmest temperatures by no means attain above -250 levels Fahrenheit. Due to the very small tilt of the Moon’s rotation axis, daylight by no means reaches these areas.
A group of scientists used knowledge from a our instrument on India’s Chandrayaan-1 spacecraft to determine particular signatures that definitively show the water ice. The Moon Mineralogy Mapper not solely picked up the reflective properties we’d anticipate from ice, however was capable of straight measure the distinctive means its molecules soak up infrared gentle, so it will probably differentiate between liquid water or vapor and stable ice.
With sufficient ice sitting on the floor – throughout the prime few millimeters – water may be accessible as a useful resource for future expeditions to discover and even keep on the Moon, and probably simpler to entry than the water detected beneath the Moon’s floor.
11. Bonus: Icy World Past Our Photo voltaic System!
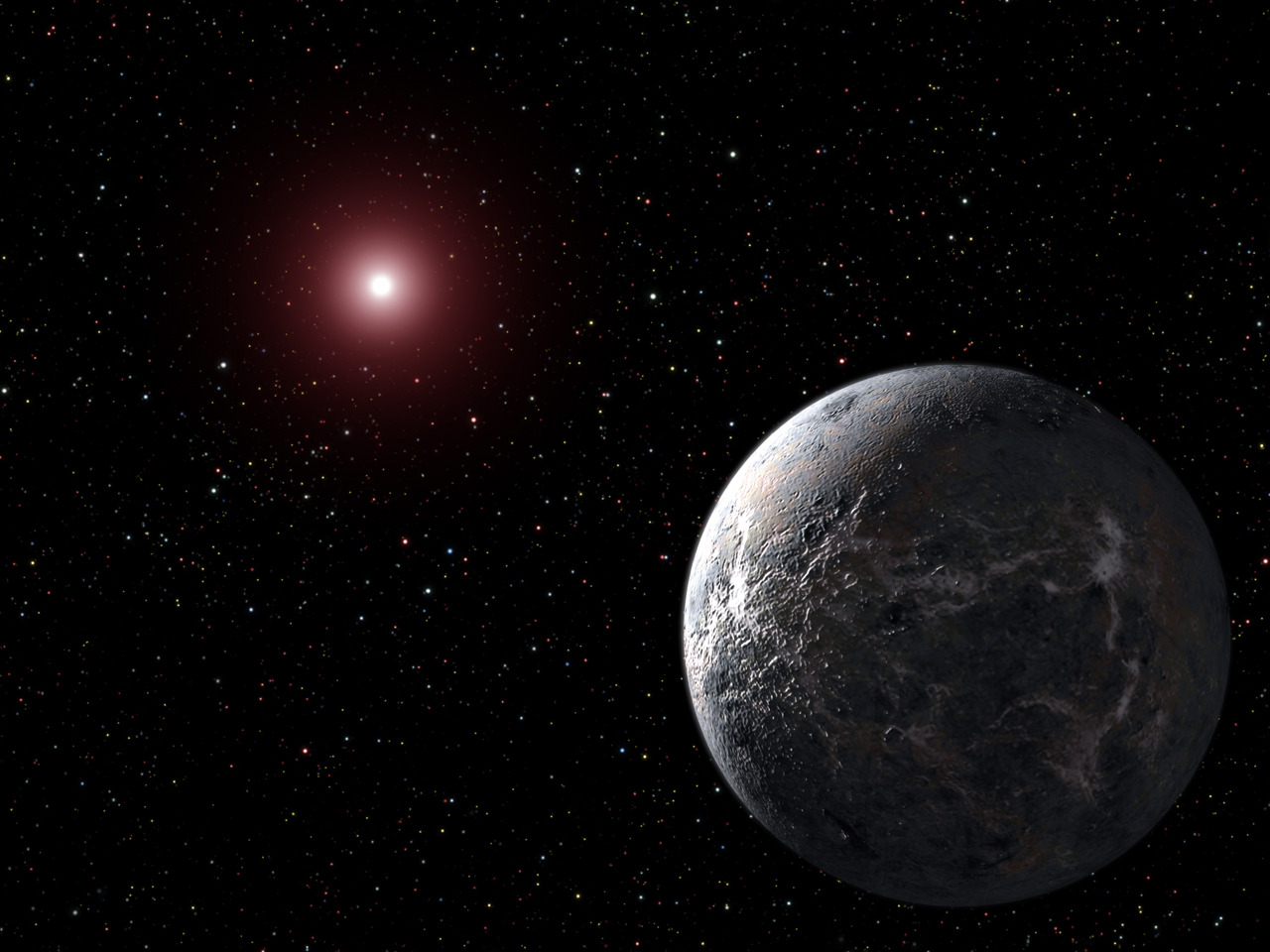

With an estimated temperature of simply 50K, OGLE-2005-BLG-390L b is the chilliest exoplanet but found. Pictured right here is an artist’s idea. Credit score: NASA
OGLE-2005-BLG-390Lb, the icy exoplanet in any other case referred to as Hoth, orbits a star greater than 20,000 gentle years away and near the middle of our Milky Means galaxy. It’s locked within the deepest of deep freezes, with a floor temperature estimated at minus 364 levels Fahrenheit (minus 220 Celsius)!
Make certain to comply with us on Tumblr on your common dose of house:

