MILAN — The European House Company (ESA) is constructing infrastructure to assist lunar exploration.
ESA formally launched the Moonlight Lunar Communications and Navigation Providers (LCNS) program right here on the Worldwide Astronautical Congress on Tuesday (Oct. 15), with the purpose of offering providers for the greater than 400 moon missions deliberate by house companies and personal corporations over the following 20 years.
Moonlight will probably be a constellation of 5 lunar satellites, which collectively will allow exact, autonomous landings and floor mobility, in accordance with ESA, whereas facilitating high-speed communication and knowledge switch throughout the roughly 250,000 miles (400,000 kilometers) between Earth and the moon.
“ESA is taking the essential step in supporting the longer term industrial lunar market, in addition to ongoing and future lunar missions,” Josef Aschbacher, ESA director basic, mentioned on the Moonlight signing ceremony in Milan.
Associated: The moon: Every thing it is advisable to find out about Earth’s companion
Step one will probably be launching Lunar Pathfinder, a precursor communications relay satellite tv for pc manufactured by Surrey Satellite tv for pc Expertise Ltd (SSTL), in 2026. Moonlight’s preliminary providers are scheduled to start by the top of 2028, and the system is to be totally operational by 2030.
Moonlight will prioritize protection on the south pole of the moon, which is the main focus of many missions resulting from its distinctive and helpful lighting situations and the prospect of water ice saved in completely shadowed craters.
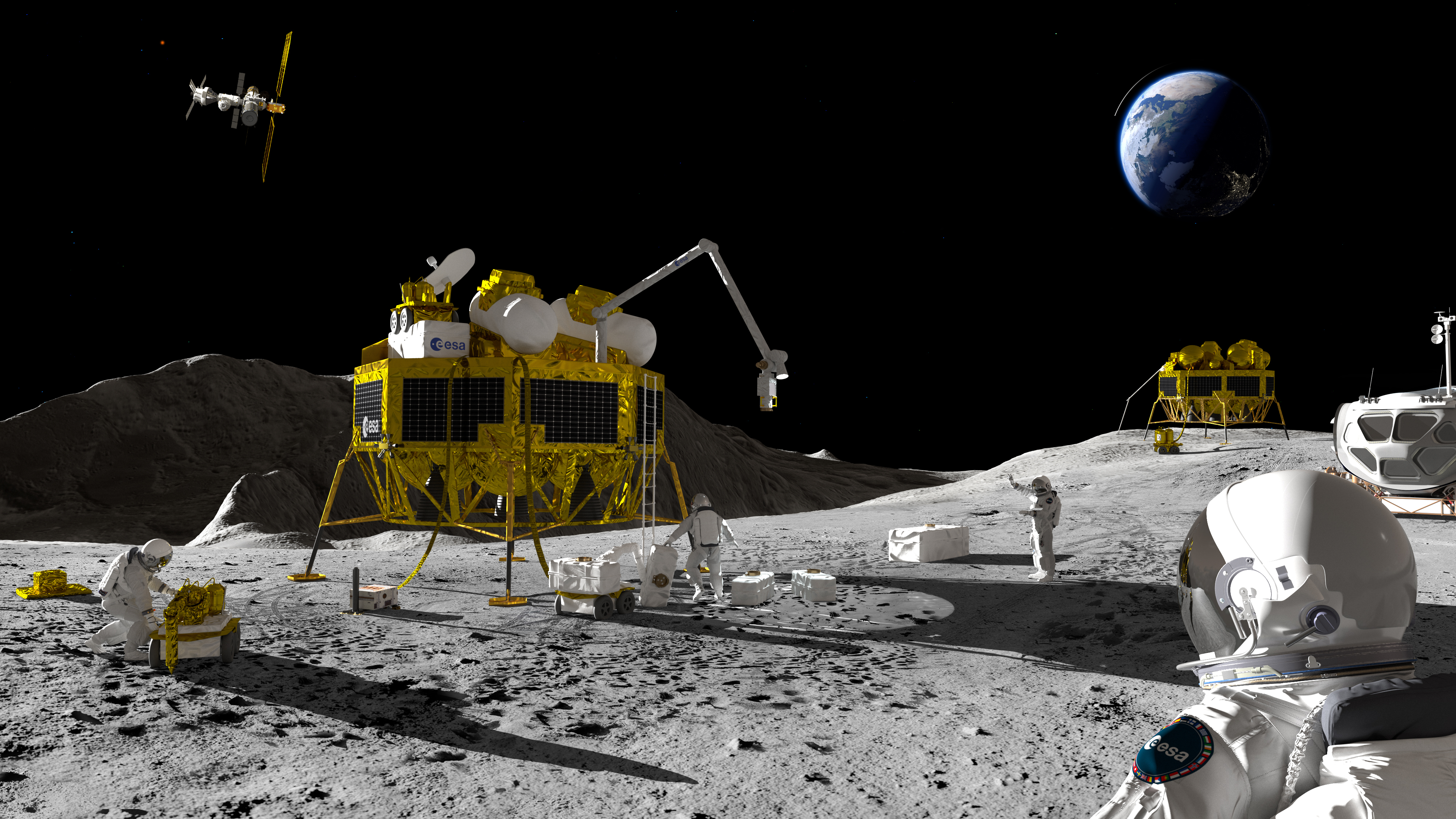
The NASA-led Artemis program goals to get astronauts again onto the moon in coming years, and construct a sustainable presence there. ESA is engaged in this system and contributing to Artemis’ Gateway challenge. Europe additionally plans to land its Argonaut spacecraft on the moon round 2031, whereas quite a few non-public missions are deliberate for the moon.
“It is a very particular second for Europe,” mentioned Javier Benedicto, ESA’s director of navigation. “The Moonlight [agreement] we’re signing right this moment is the spine of the longer term navigation system round and on the floor of the moon.”
This system entails plenty of directorates at ESA and engages quite a few nations, industrial and institutional companions.
“Main a prestigious pan-European group, Telespazio is dedicated to creating the situations for a secure and safe presence on the moon whereas concurrently opening up extraordinary industrial alternatives for Europe in cislunar house,” mentioned Gabriele Pieralli, CEO of Telespazio, said in a statement.
One huge good thing about Moonlight in its quest to make it a key lunar service is that its communications capabilities will scale back the necessity for particular person communication programs, permitting prospects to focus extra on the astronauts and robotics concerned of their missions.
“We’re beginning one thing enormous,” mentioned Pieralli. “I’m satisfied we don’t even notice the significance of what’s taking place right this moment, however the future is in entrance of us.”
The required work on worldwide collaboration and coordination can also be underway. As a part of this system, ESA can also be collaborating with NASA and Japanese house company JAXA on LunaNet, a framework for lunar communication and navigation requirements. This, crucially, goals to make sure compatibility with future lunar infrastructures and applied sciences. The primary and pioneering lunar navigation interoperability assessments are deliberate for 2029.
The imaginative and prescient and ambition for supporting exploration would not cease there. Past Moonlight, ESA will look to leverage the applied sciences and experiences gained from this system to construct the Mars Communication and Navigation Infrastructure (MARCONI) sooner or later.

