
2 Pallas is the third largest asteroid within the asteroid belt, with a diameter of around 512 kilometers. Its excessive inclination, together with its orbit eccentricity, piques astronomers’ curiosity.
Nonetheless, it has some traits in widespread with different celestial our bodies, together with Ceres and Vesta. Learning the character of two Pallas has essential implications for our photo voltaic system. This topic is fascinating to each novice {and professional} astronomers.
What’s 2 Pallas
Classification and Traits
Pallas is an fascinating world, positioned properly inside our photo voltaic system’s asteroid belt. It’s the third-largest asteroid, barely smaller than Vesta, with a diameter of about 512 km. Its measurement and construction recommend it isn’t only a common asteroid however doubtless a remnant protoplanet. This implies it might have been on its solution to changing into a planet if situations had been totally different.
The asteroid spins comparatively quick on its axis, with a rotation period of about 7.81 hours. What’s fascinating about 2 Pallas is its orbit. Not like most asteroids within the belt, it has a extremely inclined and eccentric orbit. This unusual path doesn’t merely go across the Solar in a flat airplane like Earth does. As an alternative, it takes a extra tilted and stretched route.
It completes an orbit across the Solar each 4.611 Earth years, a journey influenced by its near-18:7 resonance and approximate 5:2 resonance with Jupiter. These relationships with Jupiter pull on it gravitationally and affect its orbit over prolonged time. The composition of two Pallas provides one other layer to its uniqueness. Its floor is predominantly silicate, with little iron and water.
This provides hints at the way it shaped and what supplies had been obtainable within the early photo voltaic system. Not less than 9% of its surface has craters larger than 40 km. This reveals an interesting historical past of cosmic collisions.
Discovery and Historic Context
2 Pallas holds a really particular place in astronomical historical past. It was the second asteroid found, coming in proper after Ceres. On March 28, 1802, German astronomer Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers made a major discovery. This second struck a key change in how we seen the small our bodies of the photo voltaic system. That discovery stuffed a long-standing hole between Mars and Jupiter. For hundreds of years, astronomers had puzzled about this vacuous house.
The discovering of two Pallas has significantly enhanced our data of the asteroid belt. Its follow-up research has illuminated the early photo voltaic system. It acts like a window into the previous, telling us essential particulars of the situations and processes concerned within the formation of our photo voltaic system.

Bodily and Orbital Options
Floor and Composition
Pallas largely incorporates silicate supplies with little iron or water in comparison with the spectroscopic observations. That offers us clues concerning the situations within the early photo voltaic system by which it shaped.
Pallas’s form tells a narrative too. It goes means out of its equilibrium form, and in consequence, it hasn’t but reached the rounded form that’s widespread amongst dwarf planets. Its non-spherical form comes from its present rotation interval and mass distribution. This uncommon kind provides us a glimpse of its dynamic historical past.
Orbital Dynamics and Path
Now, let’s discuss Pallas’s journey via house. Its orbit is sort of the spectacle. With an orbital inclination of 34.8°, Pallas takes a steep path via the asteroid belt, making its presence distinctive amongst its friends.
The excessive inclination suggests a dynamic previous, probably involving gravitational interactions that knocked it into its present path. Pallas completes one orbit across the Solar in about 4.611 Earth years, which is comparatively fast in astronomical phrases.
Its axial tilt is one other fascinating characteristic; at 84°, it’s virtually on its aspect! This tilt means certainly one of its poles is sort of pointed instantly on the Solar throughout its orbit, creating excessive differences due to the season. With a rotation period of 7.8132 hours, Pallas spins quickly, offering a brief day-night cycle.
Regardless of its velocity, its imply opposition magnitude of +8.0 makes it seen with 10×50 binoculars, a deal with for novice astronomers.
Accessibility and Exploration
Commentary Strategies
If you’re speaking about observing 2 Pallas, it’s a matter of utilizing the appropriate instruments and methods. This asteroid, which loiters between Mars and Jupiter, is a troublesome cookie to crack. Why? It’s not a Close to Earth Object, so it’s at all times a secure distance from us.
For instance, the Hubble House Telescope has offered close-up views of Pallas. By inspecting how mild displays off the asteroid, scientists can decide its floor traits and chemical make-up.
House Missions and Research
Now with regards to house missions, 2 Pallas isn’t precisely on the high of the listing. NASA doesn’t view it as a vacation spot for human exploration. Why? It’s simply too far.
We don’t have any missions pointed instantly at Pallas. That doesn’t imply scientists aren’t . They use information from missions like Daybreak and different asteroid explorers to match and study extra about Pallas. These missions assist us perceive extra concerning the asteroid belt and the way Pallas matches into that puzzle.
Comparability with Related Objects
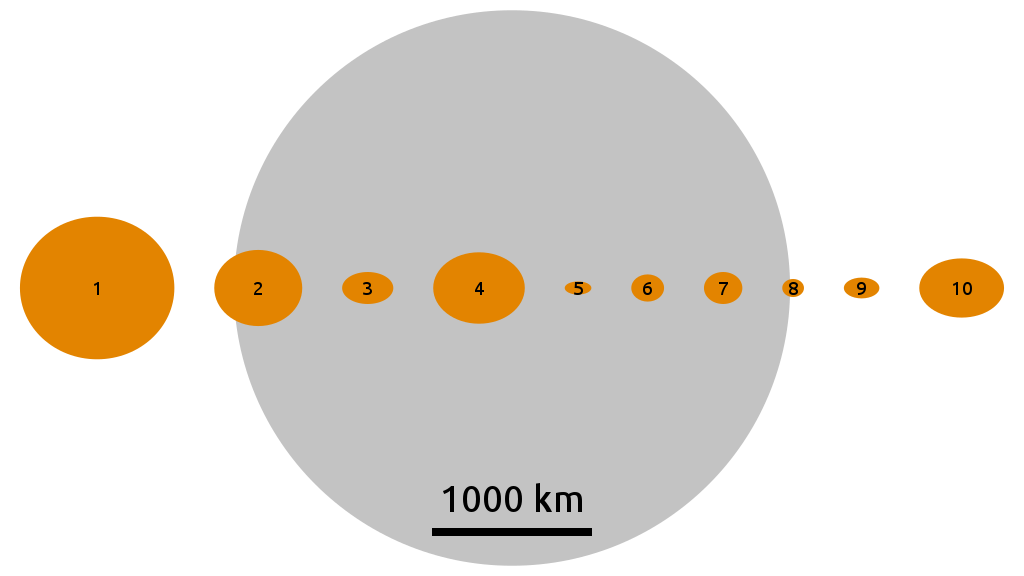
Taking a look at 2 Pallas, we discover curious similarities and variations. It actually jumps out after we evaluate it to different issues in our personal photo voltaic system, particularly Ceres and Vesta. These three are a few of the largest our bodies within the asteroid belt, so it’s solely pure to match them.
Pallas is one other large asteroid, like Ceres and Vesta. Its diameter is about 512 km, which is roughly 15 p.c of the moon’s diameter. This measurement places Pallas just a bit smaller than Vesta, which is measured to be about 525.4 km. All three our bodies have an identical composition, consisting primarily of rock and metallic — the type of materials you’d usually look forward to finding on a big asteroid.
One should observe the orbital patterns of those celestial our bodies. Pallas exhibits a near-1:1 orbital resonance with Ceres. This implies their orbits are synchronized in such a means that their gravitational interactions, whereas coincidental, create a secure stability. You may as well observe this phenomenon on different celestial our bodies. As an example, the moons of Jupiter have comparable patterns of their orbital house.
Pallas has a mass 79% that of Vesta. It additionally incorporates 22% of Ceres’s mass and only a quarter of a p.c of the Moon’s mass. This makes it a significant presence within the asteroid belt—however not the largest.
Conclusion
Exploring 2 Pallas opens doorways to new worlds. It looms even bigger than the asteroids round it, and it’s educating us issues about our photo voltaic system. Its distinctive options make it a gem for astronomers and house followers alike. The peculiar orbit of Pallas intrigues scientists and may make clear asteroid dynamics. Its sheer measurement and composition have fascinated those that surprise about house past our attain.
Ceaselessly Requested Questions
What’s 2 Pallas?
Pallas is the third-largest asteroid within the asteroid belt. It was found in 1802. Named after the goddess Pallas Athena, it’s a vital object within the research of the photo voltaic system.
What are the bodily options of two Pallas?
Pallas shouldn’t be spherical in form, having a diameter of roughly 512 kilometers. Its floor is rocky, and it displays mild comparatively properly. It is without doubt one of the largest asteroids, which makes it an fascinating topic for astronomers.
How does 2 Pallas orbit the Solar?
Pallas travels across the Solar in an ellipse. Its orbit is tilted, which means it strikes at an angle in comparison with most photo voltaic system objects. This unusual orbit makes it very fascinating for orbital research.
What are some notable information about 2 Pallas?
Pallas was the second asteroid ever found. It performs an essential function in understanding the composition of the early photo voltaic system. Its measurement and orbit make it a major object for scientific research.
How accessible is 2 Pallas for exploration?
Pallas is tough to review due to its distance and its inclination of orbit. No missions have but centered on it; future missions to house might examine it as expertise turns into extra superior.
How does 2 Pallas evaluate with comparable objects?
Asteroid 2 Pallas is comparable in measurement to Vesta and a bit smaller than Ceres. Its uncommon orbit and what it’s product of make it particular. It’s tipped greater than most massive asteroids, presenting a novel analysis alternative.
Why is finding out 2 Pallas essential?
Learning 2 Pallas helps scientists perceive asteroid composition and photo voltaic historical past. Its distinctive options present clues about planetary formation and potential sources for future exploration.

