Two personal lunar landers are set to launch this week aboard the identical rocket, kicking off a busy yr of missions to the moon.
A six-day window for the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket launching the missions begins early Wednesday morning (Jan. 15), with liftoff scheduled for 1:11 a.m. EST (0611 GMT) from Launch Complicated-39B at NASA’s Kennedy House Middle (KSC) in Florida.
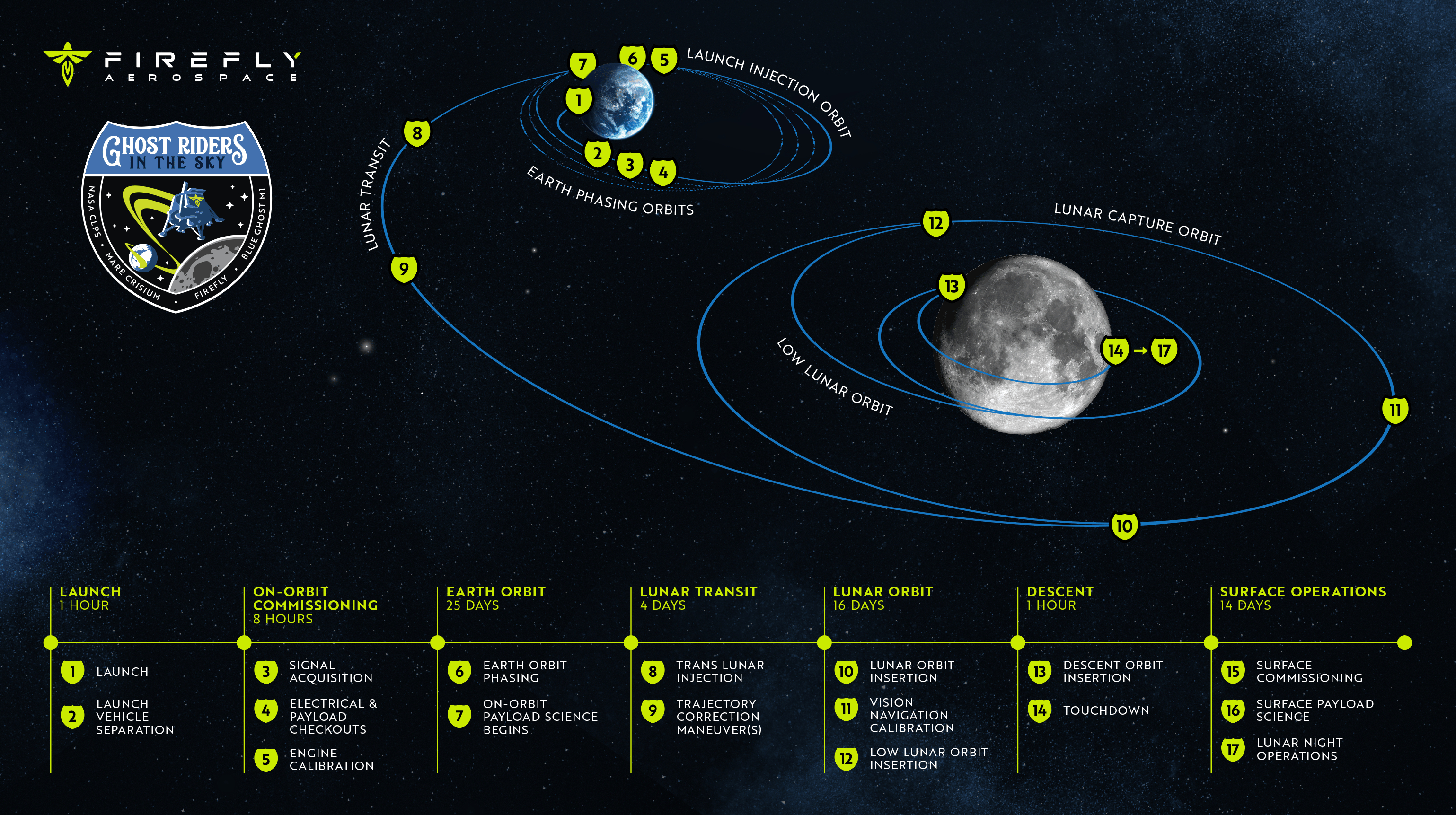
The Falcon 9 will carry each landers to Earth orbit, the place every will start unbiased trajectories towards the moon. Ghost Riders in the Sky, the mission for Firefly Aerospace’s Blue Ghost Mission 1 lunar lander, is a part of NASA’s Business Lunar Payload Providers (CLPS) program to ship scientific payloads to the floor of the moon. The second lander, Resilience, comes from Japan-based firm ispace, and is the second mission the corporate has flown in an try and land on the moon. ispace’s Mission 2 will deploy after Blue Ghost and can take about 4 occasions longer to finish its mission.
Blue Ghost will spend 25 days orbiting Earth forward of an engine burn to set its trajectory towards the moon. After one other 20 days — 4 in transit, plus one other 16 in lunar orbit — if every thing performs nominally, the lander will autonomously contact down in Mare Crisium (“Sea of Crises”) to start two weeks of lunar science.
Blue Ghost’s 60-day mission from Earth to the moon will finish about 5 hours after night time falls on the lander’s location. The spacecraft will protect the final of its battery energy to seize a picture of the lunar sundown earlier than powering down.
Associated: Double moon mission! SpaceX to launch 2 personal lunar landers in January
The Resilience lander will fly a a lot slower trajectory to the moon, with touchdown focused for 4 to 5 months after launch. The second mission for ispace’s Hakuto-R program, Resilience is provided with {hardware} and software program upgrades based mostly on classes discovered throughout Hakuto-R Mission 1. That mission efficiently reached lunar orbit however failed its touchdown try in April 2023, after an altitude sensor on the lander did not carry out as anticipated, leading to a crash on the lunar floor.
ispace is taking a step-by-step strategy with Hakuto-R Mission 2, laying out a 10-step record of milestones Resilience will full on its option to the moon, with a separate guidelines for objectives reached following a profitable landing on the lunar floor. The lander is aiming for Mare Frigoris (Sea of Chilly), within the moon’s northern hemisphere, the place it’ll start floor operations, together with the deployment of an onboard microrover named Tenacious, which is able to acquire a pattern of regolith (moon mud) as a part of a contract with NASA.

Extra moon missions in months forward
This week’s Falcon 9 launch to the moon shall be adopted, in comparatively quick order, by that of one other lunar launder, this time from the one personal firm to have efficiently landed on the lunar floor thus far.
Intuitive Machines launched its first Nova-C lander, named Odysseus, in February 2024, which carried six NASA CLPS payloads together with one other half dozen industrial payloads. On that mission, referred to as IM-1, Odysseus executed a principally profitable touchdown close to the crater Malapert A, about 190 miles (300 kilometers) from the lunar south pole.
IM-2 is predicted to launch someday in February, and can also be headed to the moon’s south polar area — this time, to a ridge close to Shackleton Crater. IM-2 will carry a lot of CLPS payloads for NASA, together with an instrument referred to as PRIME-1 (Polar Sources Ice Mining Experiment-1) that may assist verify the abundance of water ice within the space.
A 3rd Nova-C lander will ship one other spherical of CLPS experiments and expertise demonstrations to the lunar floor for the area company, and is slated to launch someday later in 2025 on the IM-3 mission.
Pittsburgh-based firm Astrobotic can also be concentrating on this yr for its Griffin Mission One, one other probe carrying NASA CLPS payloads. The corporate’s Peregrine lunar lander launched final yr however failed to achieve the moon as a consequence of a gas leak. As a substitute, the probe’s handlers introduced it again to Earth, the place it burned up throughout atmospheric reentry above the Pacific Ocean.
NASA’s many CLPS contracts are targeted on forwarding the efforts of the company’s Artemis program, which goals to land astronauts on the moon in 2027, and ultimately to arrange a base within the lunar southern polar area, the place water ice seems to be plentiful. Much like CLPS, NASA awarded Human Touchdown Providers (HLS) contracts to corporations to ship astronauts to the floor of the moon. SpaceX’s Starship rocket received NASA’s first HLS contract and is predicted to launch dozens of check flights in 2025, together with, probably, one across the moon.
Blue Origin received NASA’s second HLS contract, tapping the corporate’s Blue Moon lander to ship astronauts to the lunar floor for missions past Artemis 3. TKThe profitable maiden launch of Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket Jan. 12 places the corporate’s MK1 Lunar Lander pathfinder mission on the right track for a potential 2025 launch as effectively.

