The brand new moon of January can be at 7:36 a.m. Japanese Time on Jan. 29, in response to the U.S. Naval Observatory, and two days later a younger moon will move close to Saturn and close to Venus as they cluster collectively within the night sky.
A brand new moon is when the solar and moon share the identical celestial longitude, a place additionally referred to as conjunction. At new part, you’ll be able to’t see the moon from Earth as a result of the illuminated facet is dealing with away from us, and on prime of that new moons rise and set with the solar; even when one might mild up the facet of the moon dealing with Earth it could be misplaced within the photo voltaic glare. The one approach to see the new moon is when it passes in entrance of the solar, inflicting a photo voltaic eclipse; the following is not due till March 29.
On the day of the brand new moon, Jan. 29, Venus continues to be a vivid night star, and when the moon is just not out it’s the first celestial object one can see with the bare eye; it’s a distinct, vivid star even comparatively near sundown. By 6 p.m. in New York Metropolis the sky is darkish sufficient to see Venus within the west and Saturn just under it; the latter is at an altitude of about 22 levels; Venus is about 9 levels greater. Saturn units at 8:13 p.m. on Jan. 29 in New York; Venus follows at 9:13 p.m. Japanese Time.
Seen Planets
TOP TELESCOPE PICK:

Wish to see planets up shut within the evening sky? The Celestron NexStar 4SE is right for inexperienced persons wanting high quality, dependable and fast views of celestial objects. For a extra in-depth take a look at our Celestron NexStar 4SE assessment.
On Feb. 1, three days after the brand new moon, observers within the japanese half of Asia will see the moon occult Saturn, although it’ll happen within the daytime; whereas observing it’s potential one should train excessive warning as the skinny crescent moon can be slightly near the solar within the sky. (Some observers will be capable of see the moon occult Saturn within the night and even at evening; however that is solely in case you are within the very far north of Alaska or Siberia).
For observers within the Americas, Africa and Europe, the second of conjunction will not be seen, as by the time it occurs the moon may have set, but when one appears to the southwest within the night on Jan. 31 one will see the younger moon – a skinny crescent nonetheless – can be simply seen above the southwestern horizon, beneath and to the best of Saturn. From New York Metropolis, for instance, the solar units at 5:12 p.m. and by the top of civil twilight at 5:41 p.m., the moon units at 7:54 p.m. and Saturn at 8:06 p.m.; the precise conjunction is at 11:52 p.m. Japanese. Nonetheless one will see the moon, Saturn and Venus in a tough line; making them a simple trio to identify.
Australians (and others within the Southern Hemisphere) will see the three-day-old moon close to Saturn as nicely, however in the meanwhile of closest strategy the planet will look like above the moon – in Melbourne, Australia the shut move can be at 3:01 p.m. native time. By nightfall (sundown is at 8:33 p.m. on Feb. 1) Saturn can be to the left of, and in mid-southern latitudes, virtually stage with the moon at nightfall. Moonset in Melbourne is at 10:13 p.m. native time; Saturn additionally units at 10:13 p.m. by 9 p.m. Saturn, the moon, and Venus will kind a tough horizontal line within the west operating from south to north about 13 levels above the western horizon.
To see the moon occult Saturn one have to be in Asia; for instance in Hanoi the conjunction is at 9:43 a.m., when Saturn disappears behind the moon. Saturn will not be simply seen with no telescope and if utilizing one care have to be taken – daytime observations of any objects close to the solar may be harmful; by accident pointing any optical aids on the solar whereas wanting by way of them can lead to everlasting blindness. (It is usually a good suggestion to first look by way of the eyepiece of a telescope utilizing a telephone or different system, for instance, to verify it’s aligned with the moon accurately). The planet reappears at 10:27 a.m.
As one strikes north and east the conjunction will get later within the day; from Seoul, South Korea, the moon passes in entrance of Saturn from 11:39 a.m. to 2:23 p.m. native time; the occultation occurs an hour later (native time) in Vladivistok, and an hour later in Sapporo, Japan. Nonetheless, the one locations the place the occultation can be seen after darkish are within the far north of Siberia and the Arctic Ocean. One such location is the distant metropolis of Anadyr, Russia, the place sundown is at 3:52 p.m. native time. The occultation begins at 4:56 p.m. and ends at 5:13 p.m. native time.
Turning eastward, Mars rises in New York at 3:10 p.m. on Jan. 29; by 6 p.m. it’s about 29 levels above the horizon and simply to the best of Pollux, one of many vivid stars in Gemini, the Twins. Mars is recognizable as a result of it’ll look distinctly red-ornage in comparison with Pollux, which is extra yellow-white. The planet is seen a lot of the evening; it does not set till 6:32 a.m. on Feb. 1.
Jupiter is excessive within the southeast from mid-northern latitudes; on Jan. 29 it rises in New York at 12:35 p.m. Japanese and transits at 7:57 p.m. By 6 p.m. it’s already a superb 58 levels excessive; practically two thirds of the way in which to the zenith. Within the constellation Taurus, the Bull, Jupiter is simply above Taurus’ brightest star, Aldebaran. One can inform the 2 aside due to Aldebaran’s extra orange hue.
For Southern Hemisphere observers, the place the Solar units a lot later, the sky does not get absolutely darkish till about 9:30 p.m. By 9 p.m. on Jan. 30 in Melbourne, Australia, Saturn is simply turning into seen above the western horizon, about 14 levels excessive; the planet units at 10:21 p.m. native time. Venus is to the best (northward) and units at 10:26 p.m.
As within the Northern Hemisphere Mars is within the east, although decrease within the sky; in Melbourne the Crimson Planet is barely 11 levels excessive at 9 p.m. (Mars rises in Melbourne at 7:40 p.m. on Jan. 30). Mars units the following morning at 4:47 p.m. Fairly than being above Pollux within the sky, it’ll appear to be nearer to the horizon because the sky is “the wrong way up” within the Southern Hemisphere.
Jupiter, in the meantime, is sort of due north by 9 p.m.; the planet transits at 9:20 p.m. and in Melbourne is about 31 levels excessive, and units Jan. 31 at 2:11 a.m. AEDT. As with Mars, with the sky “reversed” Jupiter will seem beneath Aldebaran slightly than above it.
Stars and Constellations
Winter constellations are in full swing for Northern Hemisphere observers on the finish of January. On the evening of the brand new moon in mid-northern latitudes the solar has set by 6 p.m. At that time the brightest stars are already above the horizon; Sirius, the brightest of them, rises at 5:01 p.m. in New York Metropolis (and related native occasions in Chicago, Denver, or Sacramento). A enjoyable remark train is to see how quickly after it rises one can spot it; in New York it’s only 9 levels excessive by 6 p.m. and the sky is simply beginning to get actually darkish because the final mild of night fades. Sirius is vivid sufficient that it’s shortly recognizable, as it’s a vivid blue-white.
By 7 p.m. everything of Sirius’ guardian constellation, Canis Main, the Massive Canine, is above the horizon. Trying upwards from Sirius one will see the three stars of Orion’s Belt. They’re named (from left to proper) Alnitak, Alnilam, and Mintaka. Under the Belt and to the best is Rigel, additionally a white (or for some individuals, blue-white) star, marking Orion’s left foot. Above the Belt and to the left is Orion’s proper shoulder, the intense and ruddy Betelgeuse. If one appears to the left (northward) of Sirius, in the direction of the East, one can see a whitish star, Procyon, the brightest star in Canis Minor, the Little Canine.
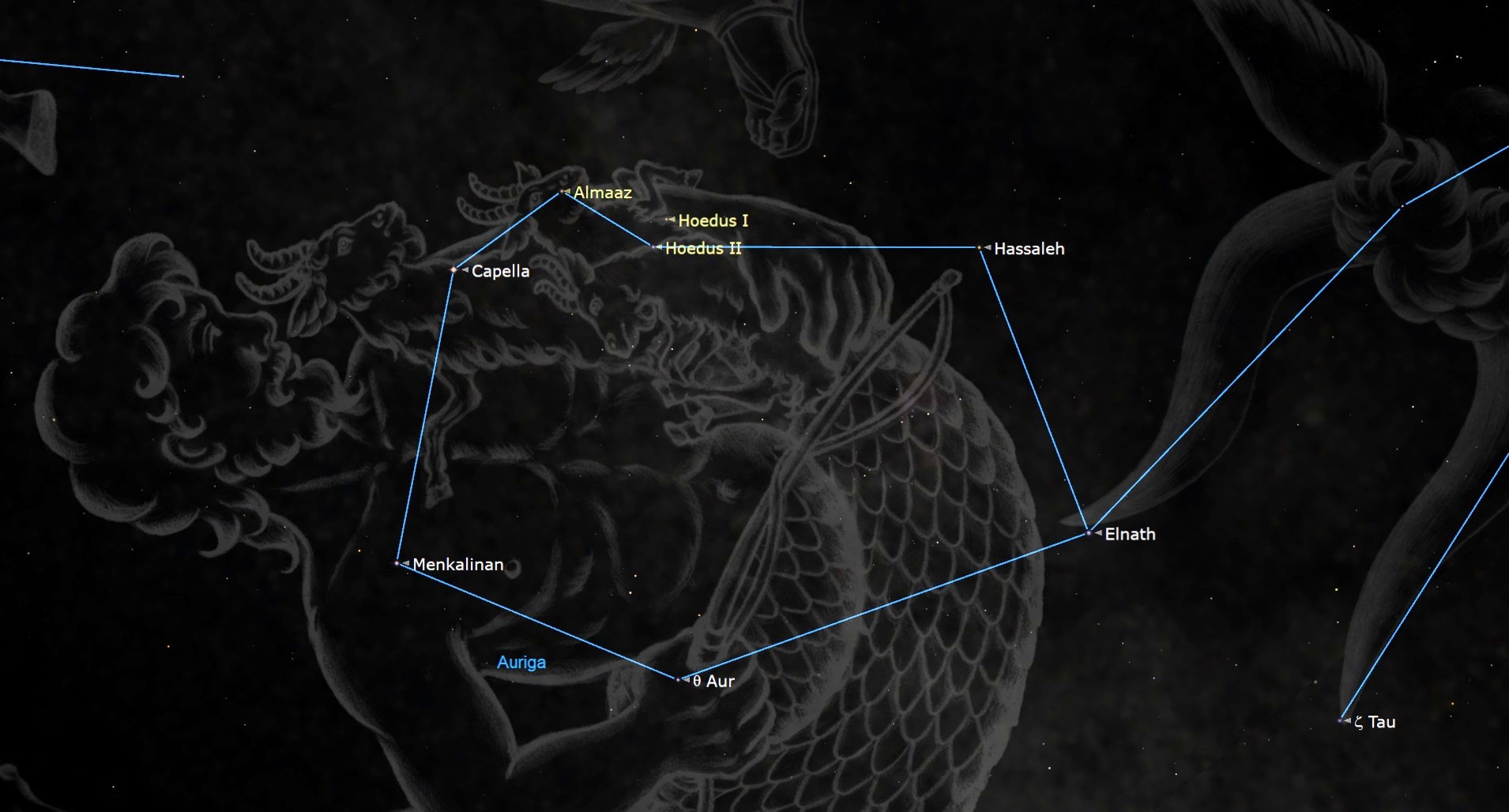
Above Procyon and to the left of Orion one can see Gemini, the Twins, and the 2 stars Castor and Pollux. Castor is the uppermost of the 2 stars, because the Twins are on their “facet” simply after they get above the horizon. North and west of the Twins is Auriga, the Charioteer. Auriga comprises the intense star Capella, which from the latitude of New York Metropolis and above by no means units – it is without doubt one of the circumpolar stars. At 7 p.m. on Jan. 29 it is going to be about 72 levels above the Japanese horizon.
Close to Capella are 4 different stars that with it kind a pentagonal form; the “backside” star nearest Orion is Elnath, which was as soon as “shared” by Taurus, however now could be designated as Beta Tauri, the higher “horn” of the Bull. To the south and west of Elnath (in the direction of the best from the perspective of an observer) is Aldebaran.
By 9 p.m. The Massive Dipper is sort of vertical and within the northeast; the “bowl” faces west (left). One can use it to seek out Polaris, the Pole Star, through the use of the 2 stars which can be the entrance of the bowl (the highest of the asterism presently of evening). The celebs are referred to as Dubhe and Merak, the previous is the one to the left. Drawing a line between them to the left takes one to Polaris. However Polaris is not the one star the Dipper can level to. If one attracts a line to the best, connecting the celebs behind the bowl (these would be the two decrease within the sky) one reaches Regulus, the brightest star in Leo, the Lion, which at 9 p.m. can be virtually due east and about 27 levels excessive (it will fluctuate relying on one’s actual latitude however it is going to be related in any mid-Northern latitude metropolis).
For Southern Hemisphere observers, January is when Puppis, Carina and Vela, the three constellations that make up the ship (linked to the Argo, the well-known ship of Jason and the Argonauts) are distinguished. As it’s the austral summer time the solar does not set till after 8 p.m.; for the sky to get absolutely darkish one should wait till about 9:30 p.m. At that time within the northeastern sky one would see an “the wrong way up” Orion, with the Belt stars above Betelgeuse, which from locations similar to Melbourne, Australia is beneath them and to the best. Rigel, in the meantime, is upwards and to the left, and this time when one follows the River from Cursa, one goes up a full 62 levels to some extent simply west of north to Achernar.
Sirius is above and to the best of Betelgeuse, and one can draw a line between them southwards (this can be to the best) and above that line is the intense Canopus, the brightest star in Carina, the Ship’s Keel, about 52 levels excessive and due east. Carina is one among three constellations that make up the legendary Argo, the ship Theseus the hero of Greek legend sailed. Between Canopus and Sirius is a bunch of seven fainter stars that kinds a protracted form one thing like a foot and an ankle; that is Puppis, the Poop Deck. Look just under that in the direction of the horizon and one can see a ring-shaped group of eight stars that’s Vela, the Sail.
Turning a bit additional south – it is going to be to the best and additional in the direction of the horizon – one can see Crux, the Southern Cross, simply between 12 and 17 levels excessive within the south-southeast. From the latitude of Melbourne Crux is circumpolar – it by no means units. Crux is without doubt one of the smallest of the 88 constellations within the sky; at that hour in January the highest of the cross is pointed in the direction of the horizon. If one turns practically due south one will see Rigil Kentaurus, in any other case generally known as Alpha Centauri. The Centaur is usually beneath the horizon, however by midnight the constellation has virtually utterly risen.

