Continent-size islands deep inside Earth’s mantle could possibly be greater than a billion years previous, a brand new examine finds.
Often known as massive low-seismic-velocity provinces (LLSVPs), these blobs are each hotter and older than close by areas of the mantle. The findings, printed Jan. 22 within the journal Nature, make clear Earth’s deep inside and will assist clarify how the mantle strikes over time.
Scientists have identified about these LLSVPs for just a few a long time. The 2 big blobs — one beneath the Pacific Ocean and one beneath Africa — lie on the boundary between Earth’s mantle and its outer core, some 1,900 miles (3,000 kilometers) beneath the floor.
“Individuals have been questioning for all this time what they’re,” examine co-author Arwen Deuss, a seismologist at Utrecht College within the Netherlands, informed Stay Science. “The one factor that we all know of those is that when seismic waves journey by these locations, they decelerate.”
To higher perceive the character of the LLSVPs, Deuss and her colleagues pored by seismic knowledge from greater than 100 earthquakes sturdy sufficient to reverberate by the entire planet, together with the LLSVPs and the encircling mantle.
From these knowledge, the researchers calculated each the velocity of the seismic waves and the way shortly they misplaced vitality as they traveled by completely different components of the mantle. In settlement with earlier work, the staff discovered that the seismic waves moved extra slowly by the LLSVPs than by different components of the mantle, suggesting that the blobs run hotter than their environment. However the waves misplaced a lot much less vitality than anticipated when touring by the LLSVPs. One other function, equivalent to a change in composition, have to be answerable for the sudden end result, the staff suspected.
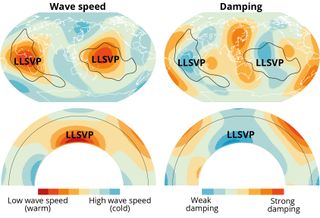
Laptop fashions urged that the dimensions of crystalline minerals within the LLSVPs may play a task. Each time a wave crosses a boundary between two crystals, often called a grain boundary, it loses vitality. If the crystals are smaller, there are extra of those grain boundaries in a given quantity.
Deuss likened the seismic waves to operating. “When you run in dune sand, when you might have a whole lot of small grains, then you definitely get actually drained since you type of sink into the sand,” she mentioned. The identical factor occurs to seismic waves once they cross by areas of the mantle across the LLSVPs. That a part of the mantle is product of previous tectonic plates that break into tiny items once they sink deep sufficient into the planet.
The LLSVPs, against this, include bigger crystals than their environment. As a result of the waves do not run into grain boundaries as typically when passing by the LLSVPs, they do not lose as a lot vitality as they do in surrounding rock. Crystals within the mantle take a very long time to develop, Deuss mentioned, so the bigger crystals within the LLSVPs have probably been undisturbed for fairly a while.
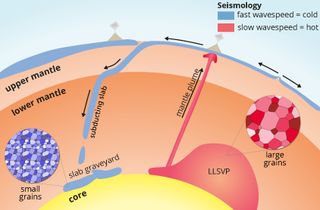
“They should have been there for no less than a billion years,” Deuss mentioned. “After which every part instantly fell into place, as a result of many individuals have been suspecting that they may nicely be previous, however no one had any solution to show it.”
These older sections of the mantle may present perception into how the mantle strikes and mixes over time. The steady LLSVPs may assist clarify why volcanic rocks in several components of the world have completely different compositions or how tectonic plates are organized on the floor, Deuss informed Stay Science. However determining precisely how these impacts present up within the geological document would require additional area analysis.
With the brand new findings, “now individuals can do a lot of different investigations to determine, what’s the origin of those locations? Why have they been sitting there? And which may result in a whole lot of different excellent questions in science that also want solutions,” Deuss mentioned.
What’s inside Earth quiz

