Astronomers have been pressured to reassess the origins of mysterious, fast radio wave blasts referred to as “quick radio bursts” (FRBs).
This rethink was led to by an FRB first detected final yr, which has been traced again to the “cosmic graveyard” of a large “useless” galaxy crammed with historic stars positioned 2 billion light-years from Earth.
FRBs are often attributed to the supernova deaths of large younger stars in youthful galaxies experiencing bouts of star formation. This occasion additionally triggers the beginning of extremely magnetic neutron stars, or “magnetars.” Nevertheless, this FRB supply galaxy seems to lack such parts, that means FRB-producing occasions could also be extra various than beforehand thought.
“This new FRB exhibits us that simply if you suppose you perceive an astrophysical phenomenon, the universe turns round and surprises us,” workforce member and Northwestern College scientist Wen-fai Fong stated. “This ‘dialogue’ with the universe is what makes our subject of time-domain astronomy so extremely thrilling.”
A mysterious repeating radio sign
This theory-altering analysis started in Feb. 2024 when the Canadian Hydrogen Depth Mapping Experiment (CHIME) detected a brand new FRB, which was later designated FRB 20240209A.
Most FRBs flare as soon as, lasting mere milliseconds and emitting extra vitality than the solar radiates in a yr. Nevertheless, FRB 20240209A flared repeatedly, with the identical supply producing 21 pulses between February and July 2024.
Six of those pulses had been detected by a smaller model of CHIME, an “outrigger” telescope positioned round 37.3 miles (60 kilometers) from the primary instrument. These outriggers exist to permit astronomers to pinpoint the supply of the FRBs CHIME detects. Thus, the workforce was ready to do that backtracking train for FRB 20240209A.
With the supply of FRB 20240209A positioned, the workforce carried out follow-up observations with the W.M. Keck and Gemini observatories to study as a lot as they may about its surroundings.
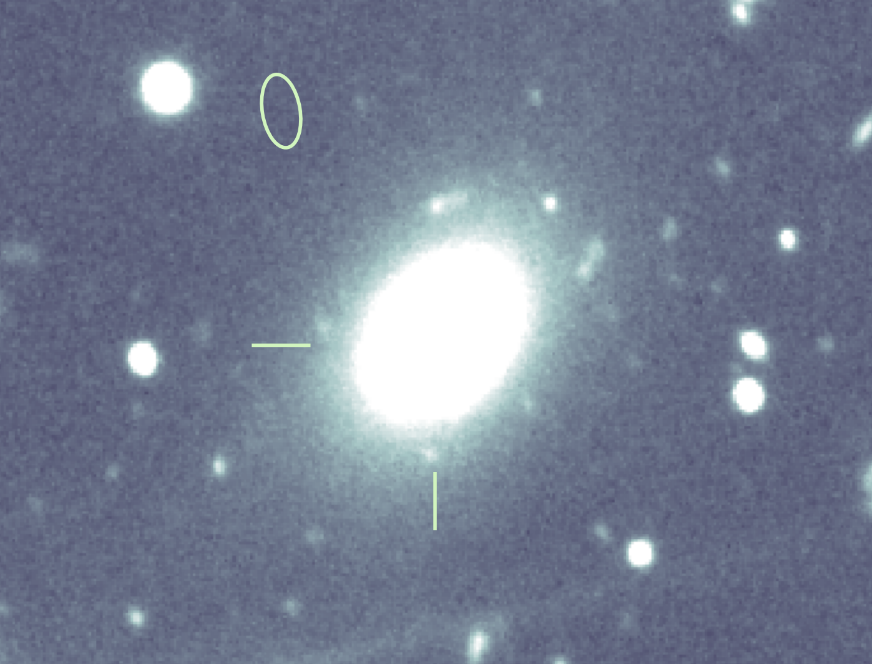
If the scientists had been anticipating a younger galaxy like the standard FRB supply, they had been in for a shock. Their follow-up investigation confirmed FRB 20240209A originated from the sting of an 11.3-billion-year-old galaxy.
The workforce set about studying extra about this galaxy by performing superior laptop simulations. This revealed that the galactic host of this FRB is extraordinarily luminous and has a mass of round 100 billion occasions the mass of our solar.
“It appears to be probably the most large FRB host galaxy so far,” workforce member and Northwestern Middle for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Analysis in Astrophysics (CIERA) scientist Tarraneh Eftekhari stated. “It is amongst a number of the most large galaxies on the market.”
An FRB on the sting
The supply of this FRB inside the galaxy additionally presents a conundrum. That’s as a result of FRBs often originate effectively inside their galaxies. FRB 20240209A, nevertheless, got here from the outskirts of its host galaxy, round 130,000 lightyears from the galactic heart.
“Among the many FRB inhabitants, this FRB is positioned the furthest from the middle of its host galaxy,” stated Vishwangi Shah, a graduate scholar at McGill, who led the hassle to pinpoint the supply of FRB 20240209A. “That is each stunning and thrilling, as FRBs are anticipated to originate inside galaxies, usually in star-forming areas.
“The situation of this FRB to this point outdoors its host galaxy raises questions as to how such energetic occasions can happen in areas the place no new stars are forming.”
Previous to this, just one FRB had ever been traced to the outer limits of a galaxy.
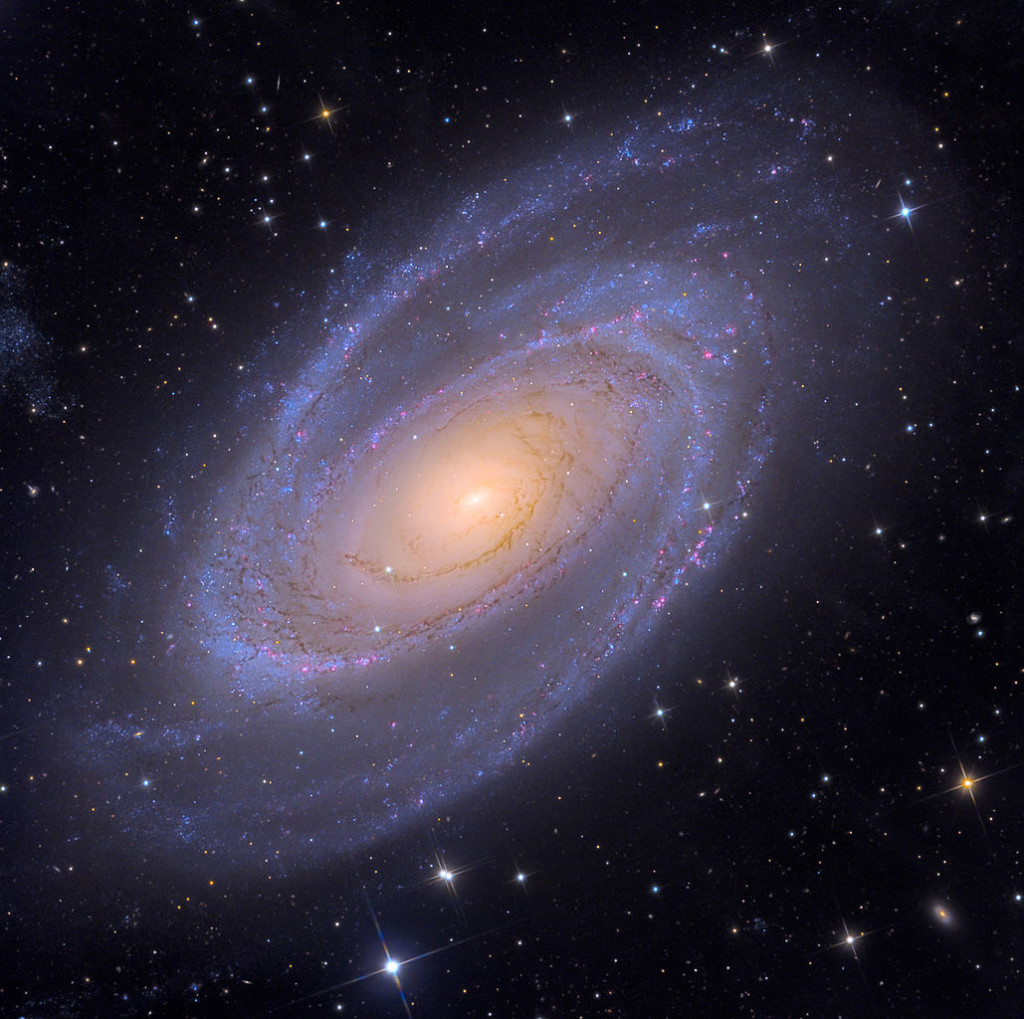

In 2022, FRB 20200120E was traced to a dense star cluster, or globular cluster, on the outskirts of Messier 81 (M81), a spiral galaxy round 12 million light-years from Earth within the constellation Ursa Main.
Regardless of rising from very completely different galaxies, FRB 20240209A and FRB 20200120E shared many similarities.
“A couple of years in the past, the M81 FRB was surprisingly found inside a dense cluster of stars referred to as a globular cluster,” Fong stated. “That occasion single-handedly halted the standard practice of thought and made us discover different progenitor eventualities for FRBs.”
Since FRB 20200120E was detected, no FRB had prefer it had been noticed. That led Fong and the workforce to consider FRB 20200120E was a one-off discovery — till now.
“Actually, this CHIME FRB could possibly be a twin of the M81 occasion. It’s removed from its residence galaxy, far-off from the place any stars are being born, and the inhabitants of stars in its residence galaxy is extraordinarily outdated. It is had its heyday and is now coasting into retirement,” Fong stated. “On the similar time, this kind of outdated surroundings is making us rethink our commonplace FRB progenitor fashions and turning to extra unique formation channels, which is thrilling.”
FRBs with out the supernovas
To this point, round 100 FRBs have been linked to a galactic host, and most of those have been linked to a magnetar — a extremely magnetic type of neutron star.
Like all neutron stars, magnetars are fashioned when large stars run out of their gas for nuclear fusion. This implies the outward movement of vitality that helps them towards collapse is reduce off, and the star can now not help itself towards the crushing inward power of its personal gravity.
Because the star’s core quickly crushes all the way down to type a neutron star, the outer layers and many of the star’s mass are blown away in a core-collapse supernova.
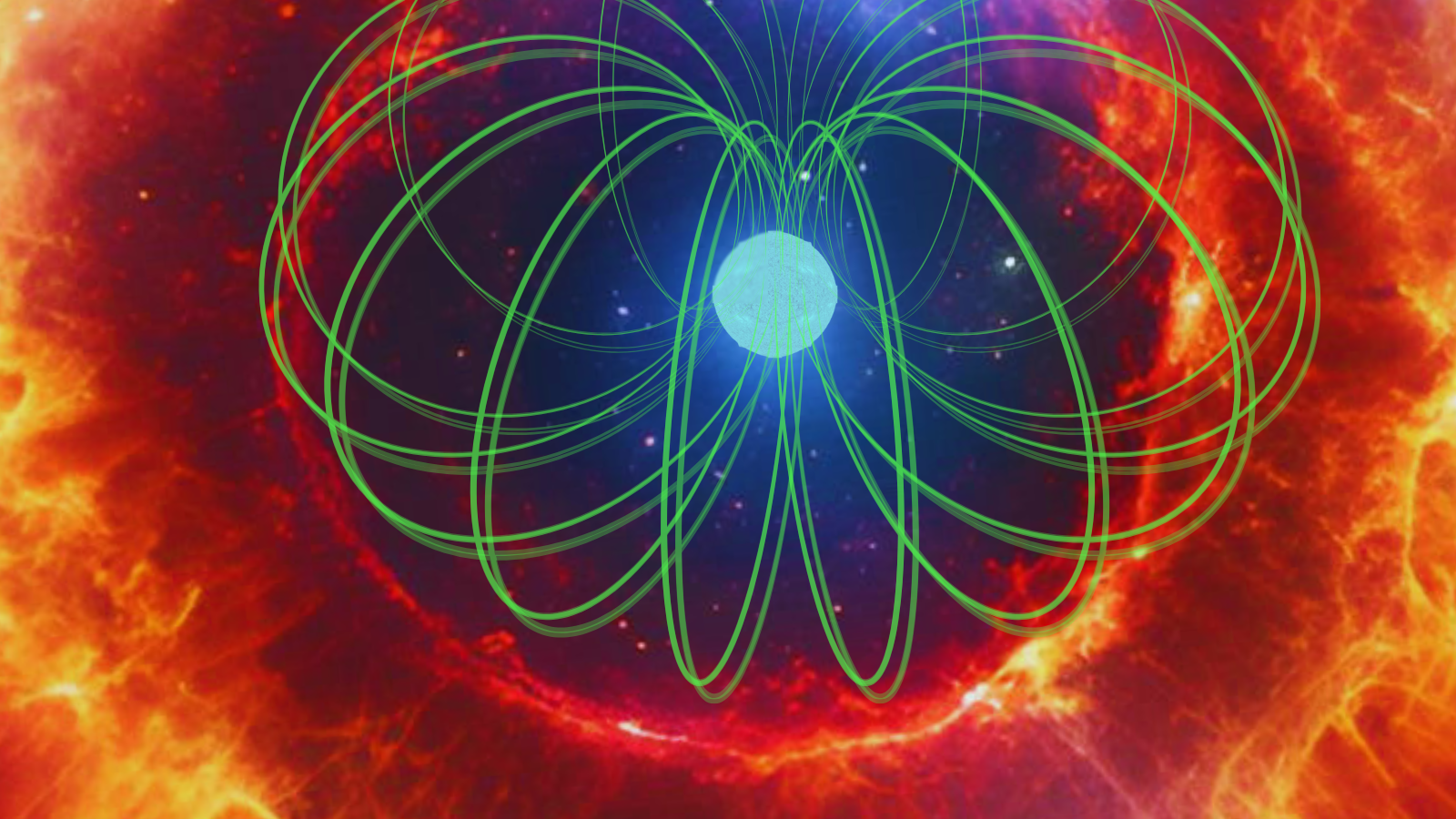

“The prevailing concept is that FRBs come from magnetars fashioned by way of core-collapse supernovae,” Eftekhari stated. “That doesn’t look like the case right here. Whereas younger, large stars finish their lives as core-collapse supernovae, we don’t see any proof of younger stars on this galaxy.
“Due to this new discovery, an image is rising that exhibits not all FRBs come from younger stars. Perhaps there’s a subpopulation of FRBs which might be related to older programs.”
The researchers consider that identical to FRB 20200120E, FRB 20240209A could have come from a globular cluster. That is important as a result of globular clusters are related to different highly effective occasions related to older stars, together with the collisions and mergers of two neutron stars or a white dwarf collapsing below its personal gravity. Occasions that might additionally give rise to FRBs.
“A globular cluster origin for this repeating FRB is the most probably state of affairs to elucidate why this FRB is positioned outdoors its host galaxy,” Shah stated. “We have no idea for a truth if there’s a globular cluster current on the FRB place and have submitted a proposal to make use of the James Webb House Telescope for follow-up observations of the FRB location. If sure, it will make this FRB solely the second FRB identified to reside in a globular cluster.
“If not, we must contemplate different unique eventualities for the FRB’s origin.”
“It is clear that there is nonetheless a variety of thrilling discovery area in the case of FRBs and that their environments may maintain the important thing to unlocking their secrets and techniques,” Eftekhari concluded.
The workforce’s analysis was detailed on the finish of January in two papers printed in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.

