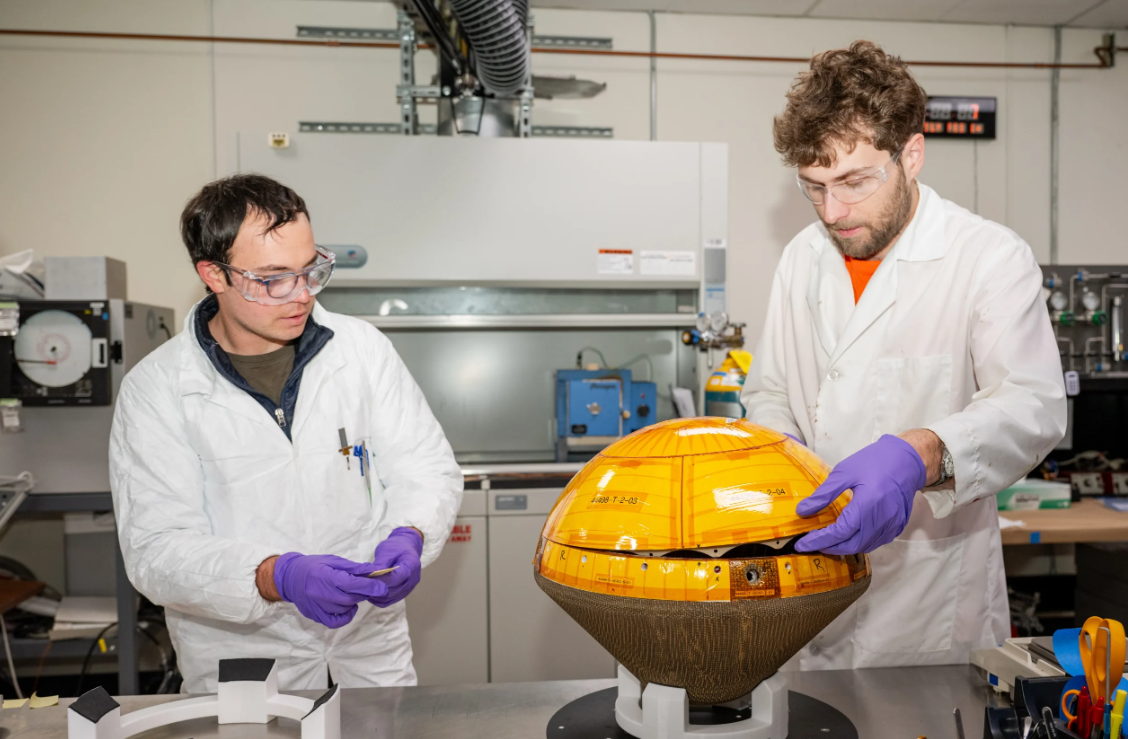
Engineers at NASA’s Ames Analysis Middle in California’s Silicon Valley report progress in putting in a warmth defend on the primary non-public spacecraft focused for Venus.
Rocket Lab of Lengthy Seaside, California, is main the hassle, together with their companions on the Massachusetts Institute of Expertise (MIT) in Cambridge, Massachusetts.
NASA’s Heatshield for Excessive Entry Atmosphere Expertise (HEEET) was invented on the NASA Ames middle.
NASA’s Small Spacecraft Expertise program, a part of the company’s Area Expertise Mission Directorate, supported the event of the warmth defend for Rocket Lab’s Venus mission.
Woven warmth defend
HEET is a textured materials masking the underside of the capsule, a woven warmth defend designed to guard spacecraft from temperatures as much as 4,500 levels Fahrenheit (2482 levels Celsius).
The non-public Venus probe can be deployed from Rocket Lab’s Photon spacecraft bus.
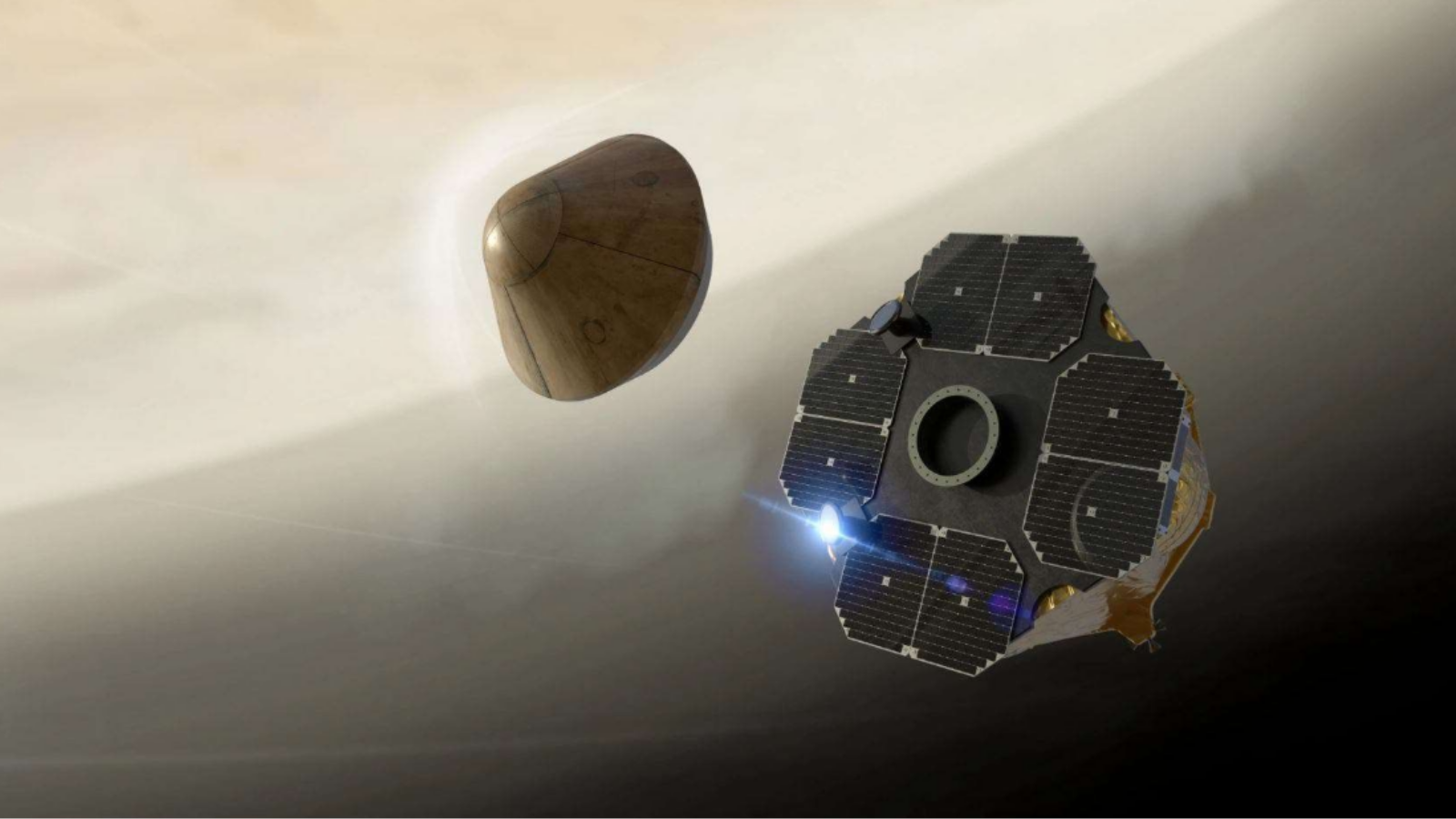


This probe will take measurements because it descends by the clouds of Venus.
“We missed our January 2025 launch window and now wait till the subsequent one summer season 2026,” mentioned MIT’s Sara Seager, a professor of planetary science and chief of the Morningstar Missions to Venus staff – a sequence of deliberate missions designed to research the potential of life in Venus’ clouds.
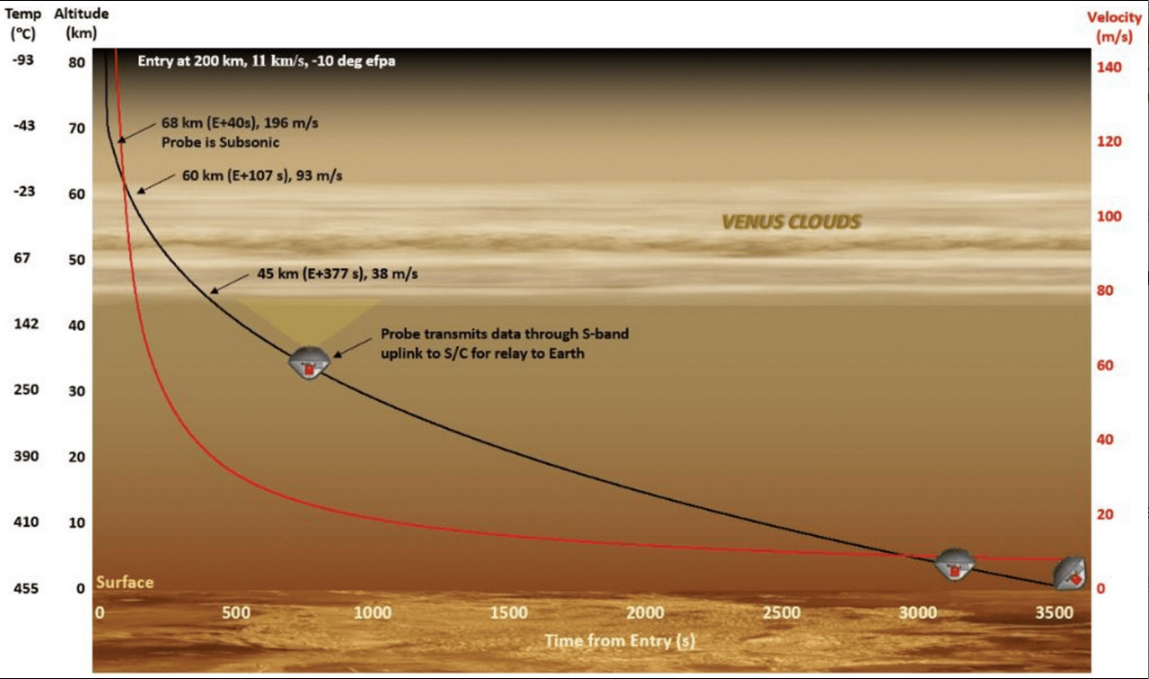
The primary mission, a collaboration with Rocket Lab, is the small, low-cost probe designed to measure autofluorescence and backscattered polarized radiation to detect the presence of natural molecules within the clouds.
That spacecraft is now happening Rocket Lab’s yet-to-fly Neutron booster, as a substitute of an Electron launcher, so the non-public Venus mission is tied to the Neutron coming on-line, Seager instructed Inside Outer Area.
“On my facet, we accomplished the instrument construct and had our first integration exams with the probe, the half that will likely be dropped off into the Venus ambiance. All is progressing,” mentioned Seager.

