The solar simply launched a burst of a uncommon type of helium often called helium-3 (3He). What’s peculiar is that this light-weight, elusive isotope is not normally seen in such excessive quantities.
“This uncommon isotope, which is lighter than the extra frequent 4He by only one neutron, is scarce in our photo voltaic system — discovered at a ratio of about one 3He ion per 2,500 4He ions,” Radoslav Bucik, lead scientist on the Southwest Analysis Institute within the U.S., mentioned in a statement. “Nevertheless, photo voltaic jets seem to preferentially speed up 3He to excessive speeds or energies, probably as a result of its distinctive charge-to-mass ratio.”
On Earth, 3He’s extremely prized for its potential makes use of in nuclear fusion, clear power analysis, cryogenics, quantum computing and even medical imaging and neutron detection. It’s, nonetheless, way more considerable on the moon as a result of, not like Earth, the moon lacks a magnetic subject, which might usually deflect particles from the solar — together with 3He. In contrast, these particles choose the floor of the moon, offering a possible lunar provide that has sparked rising curiosity in harvesting initiatives for future power and expertise purposes.
This latest surge of 3He particles was detected by the Photo voltaic Orbiter, a joint mission between NASA and the European House Company (ESA) designed to uncover the internal workings of our star. The spacecraft recorded a staggering 200,000-fold enhance in 3He particles, which had been accelerated to a lot greater speeds than sometimes seen with heavier parts.
NASA’s Photo voltaic Dynamics Observatory (SDO), which has been monitoring the solar from Earth orbit since 2010, adopted up on the occasion. Utilizing high-resolution imaging, SDO traced the outburst again to a small photo voltaic jet erupting from a coronal gap — a area the place the solar’s magnetic subject opens out into area. “Regardless of its tiny dimension, the jet was clearly linked,” Bucik mentioned.
What shocked scientists was that this small jet erupted from a area of the solar with a weak magnetic subject — a trait extra frequent in quiet photo voltaic areas than within the lively, explosive areas sometimes related to bursts of high-energy particles.
Though the precise mechanism behind the ejection of 3He stays a thriller, the discovering helps earlier theories that these uncommon particles usually tend to be enriched within the solar’s calmer, weakly magnetized zones.
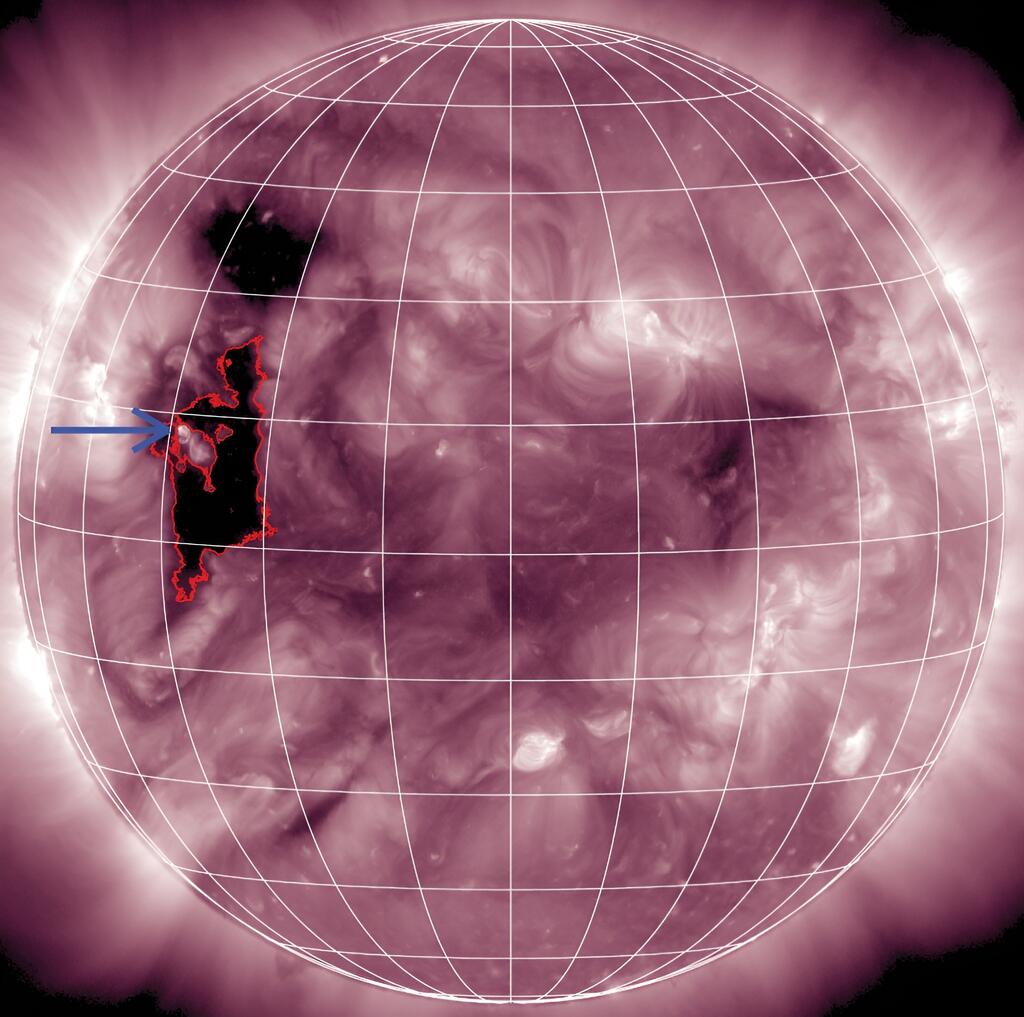
Researchers suppose that in these quieter areas, refined processes — like light waves or minimal turbulence — could create simply the best situations to spice up 3He in a novel method.
Apparently, the staff noticed an odd ion enhancement sample, the place the ionization or excitation of a component or molecule is elevated by the presence of one other. Usually, it will be anticipated that the jet would have ejected a larger abundance of heavier parts, corresponding to iron, particularly in areas with excessive ionization or excitation. Nevertheless, the jet as a substitute launched extra carbon, nitrogen, silicon and sulfur alongside helium, suggesting an sudden course of or interplay at play.
With solely 19 related occasions previously 25 years, this rarity is critical, providing potential new insights into the underlying phenomena.

