What occurs when two carbon-rich area rocks slam into one another?
You’d count on to see clear indicators of affect within the ensuing meteorites — however for over 30 years, scientists have puzzled over why meteorites that comprise carbon seem much less affected by such violent encounters than those who do not.
Understanding why carbon-rich meteorites seem “much less shocked” helps scientists interpret the historical past and evolution of photo voltaic system our bodies extra precisely. Shock options in meteorites are a type of forensic proof — they reveal how usually, and the way violently, area rocks have collided with one another, and with planetary our bodies, over the eons.
If sure supplies obscure or erase that proof, it might skew our understanding of planetary formation, the circumstances on early asteroids, and even how life-essential parts, like carbon, have been distributed all through the photo voltaic system.
Associated: What are meteorites?
To discover a resolution, Kosuke Kurosawa, an astrophysicist at Kobe College in Japan, turned to an outdated concept: that asteroid collisions launch vapor from water-bearing minerals within the rocks, which then carries the proof away into area.
“I specialise in affect physics and am interested by how the meteorite materials adjustments in response to impacts, one thing known as ‘shock metamorphism,'” Kurosawa defined in a statement.
“And so, I used to be very on this query,” the researcher added. “I assumed the [old theory] was good, but it surely had issues.”
For one, the unique proponents by no means calculated whether or not the method would generate sufficient vitality — or water vapor — to really blast affect proof into area. After which there is a larger concern: some carbon-rich meteorites nonetheless seem “much less shocked,” regardless of missing any water-bearing minerals.
However Kurosawa wasn’t able to abandon the speculation simply but. To analyze how carbon-bearing minerals behave throughout collisions, his group constructed a two-stage gentle fuel gun linked to a pattern chamber designed to research gases launched after high-speed collisions.
The design allowed the researchers to isolate and analyze gases from the affect alone, by separating the pattern chamber from the gun mechanism — stopping contamination from gases generated throughout the shot itself.
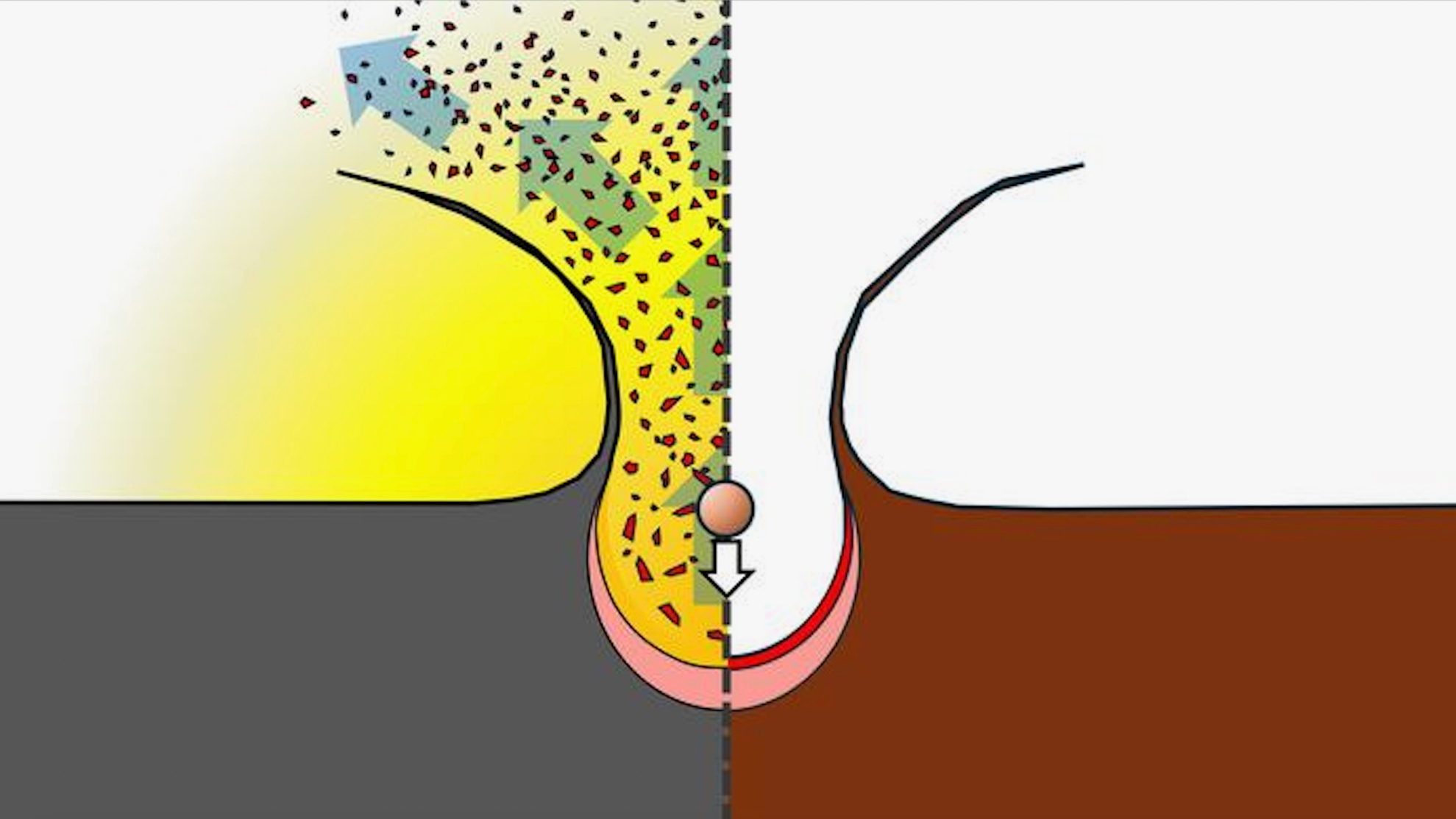
The experiments revealed that impacts by carbon-rich area rocks set off chemical reactions that generate not water vapor however extraordinarily sizzling carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide gases.
“We discovered that the momentum of the following explosion is sufficient to eject the encircling extremely shocked rock materials into area,” Kurosawa mentioned. “Such explosions happen on carbon-rich meteorites, however not on carbon-poor ones.”
Kurosawa believes that, whereas proof of such collisions is likely to be tough to acquire on smaller objects, bigger our bodies just like the dwarf planet Ceres ought to have sufficient gravity to to tug the ejected materials again to the physique’s floor.
“Our outcomes predict that Ceres ought to have collected extremely shocked materials produced by these impacts, and so we imagine that this offers a tenet for planning the following era of planetary exploration missions,” mentioned Kurosawa.
The brand new research was printed on-line Thursday (April 24) within the journal Nature Communications.

