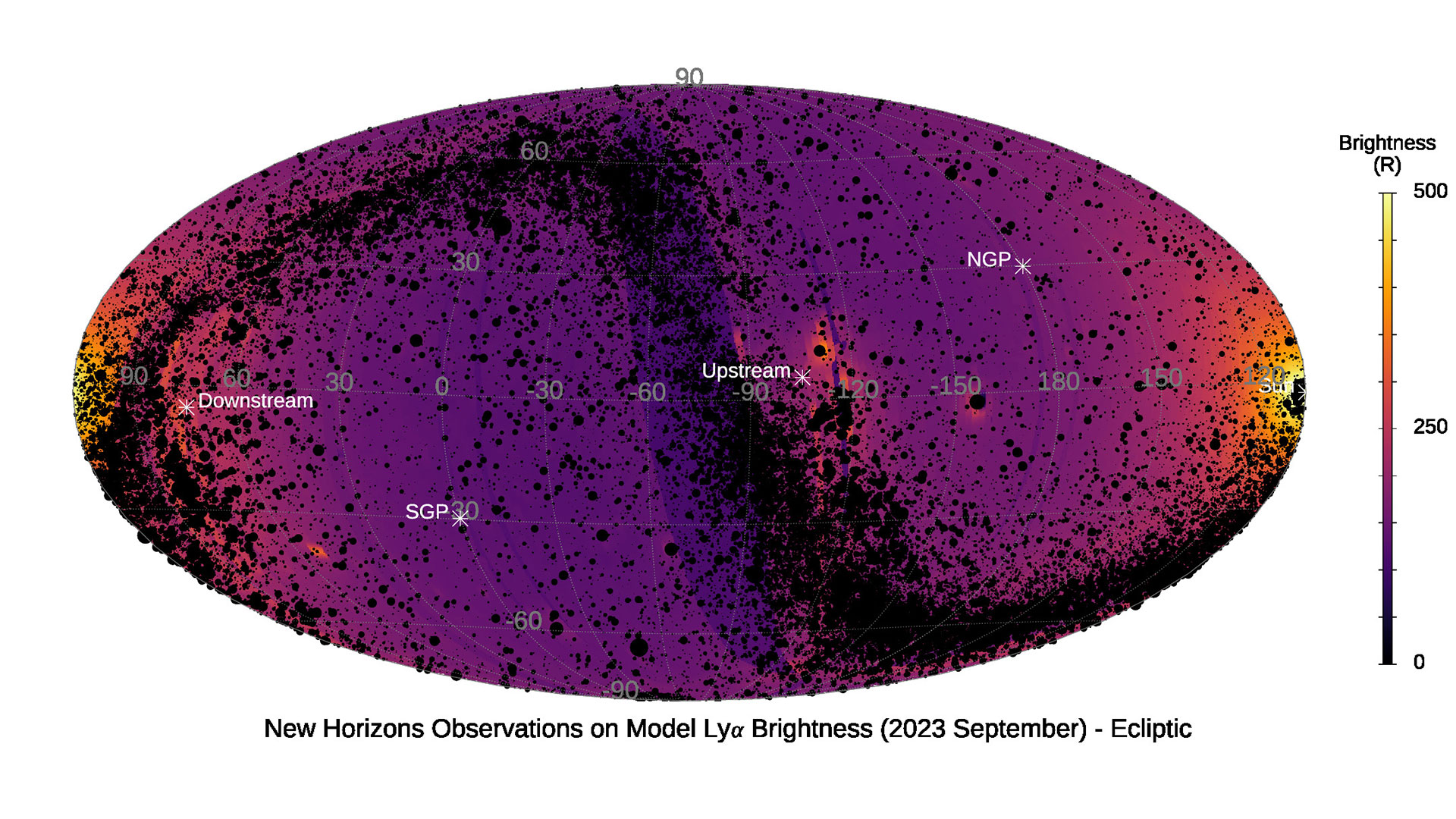
A brand new research from the NASA New Horizons mission group on the Southwest Analysis Institute have resulted in a first-of-its-type map from the Milky Approach galaxy in an ultraviolet wavelength, revealing particulars within the area round our photo voltaic system.
What’s it?
This spectrograph map, generated from information collected by NASA’s New Horizons probe, depicts the comparatively uniform brightness of the ultraviolet (UV) “Lyman-alpha” background surrounding the solar and its space of affect.
“Understanding the Lyman-alpha background helps make clear close by galactic constructions and processes,” stated Dr. Randy Gladstone with the Southwest Analysis Institute (SwRI) in Colorado. “This analysis means that scorching interstellar gasoline bubbles just like the one our photo voltaic system is embedded inside may very well be areas of enhanced hydrogen gasoline emissions at a wavelength referred to as Lyman alpha.”
Lyman-alpha is a particular wavelength of UV mild emitted and scattered by hydrogen atoms. It’s helpful when learning distant stars, galaxies and the interstellar medium, as it may assist detect the composition, temperature and motion of those distant objects.
On this spectrograph map, the black dots characterize roughly 90,000 identified UV-bright stars in our galaxy.
The place is it?
New Horizons, which started as the primary mission to flyby Pluto, collected baseline information about Lyman-alpha emissions throughout its preliminary journey to the small, icy world.
After the spacecraft’s main aims at Pluto have been accomplished, New Horizons’ ultraviolet spectrograph (named “Alice”) was used to make extra frequent surveys of Lyman-alpha emissions as New Horizons traveled farther from the solar. These observations included an intensive set of scans in 2023 that mapped roughly 83% of the sky.
Why is it superb?
Earlier than this map was launched, scientists theorized {that a} wall of interstellar hydrogen atoms would accumulate as they reached the sting of our heliosphere — the area of our galaxy the place the photo voltaic wind from our solar reaches and interacts with the interstellar medium. New Horizons information noticed nothing to point that this “wall” was an vital supply of Lyman-alpha emissions.
“These are actually landmark observations, in giving the primary clear view of the sky surrounding the photo voltaic system at these wavelengths, each revealing new traits of that sky and refuting older concepts that the Alice New Horizons information simply does not help,” stated Dr. Alan Stern. the mission’s principal investigator at SwRI. “This Lyman-alpha map additionally offers a strong basis for future investigations to study much more.”
Need to know extra?
Learn extra about New Horizons’ mission after leaving Pluto and different latest analysis based mostly on Lyman-alpha emissions. You may as well discover the scientific paper describing the SwRI map and its findings in The Astronomical Journal.

