Astronomers have discovered one other super-Earth. It is about 10 occasions extra large than Earth, and orbits within the liveable zone of a Solar-like star 2475 light-years away. These large Earth-like planets maintain key details about how planets kind and evolve.
The planet is known as Kepler-725c, and regardless of being 10 occasions extra large than Earth, it is nonetheless thought-about a low-mass exoplanet. Tremendous-Earths like this are intriguing objects as a result of our Photo voltaic System has none, although they’re the commonest sort of exoplanet discovered, with greater than 1500 confirmed thus far. They’re bigger than Earth, smaller than Neptune, and are usually 1.25 to 2 Earth radii.
The invention is in a brand new analysis article in Nature Astronomy titled “A temperate 10-Earth-mass exoplanet around the Sun-like star Kepler-725.” The lead writer is L. Solar from the Chinese language Academy of Sciences.
What’s outstanding about this discovery is that astronomers used the Transit Timing Variation (TTV) methodology to detect it. Sometimes, low-mass exoplanets like this are discovered utilizing the transit or radial velocity strategies.
The transit methodology can solely be used when an exoplanet blocks starlight from our perspective, so the photo voltaic methods must be edge-on from our perspective. Because the methodology depends on blocked gentle, bigger planets are preferentially detected since they block extra gentle. Planets on shut orbits are additionally preferentially detected as a result of they full extra transits in much less statement time.
Radial velocity, or Doppler spectroscopy, can be biased towards extra large planets nearer to the star. It really works by sensing the shifting wavelengths of sunshine from a star because the planet induces a slight wobble within the star. Since smaller planets induce smaller wobbles than large planets, large planets are preferentially detected.
The TTV methodology makes use of the presence of a identified exoplanet to detect an extra planet. On this case, astronomers already knew of 1 planet within the system named Kepler-725b. It is a fuel big exoplanet about 1/4 the mass of Jupiter. Astronomers watched it orbiting its star and seemed for variations within the timing of its orbit. Any adjustments sign the presence of an extra planet, on this case, its super-Earth sibling Kepler-725c. Because the exoplanet Kepler-725b is way much less large than the star, it is affected by its sibling greater than the star is. That makes the impact simpler to watch.
Every methodology has strengths and weaknesses, however the transit and radial velocity strategies are biased in direction of bigger planets with brief orbital durations of about 100 days or much less. However Kepler-725c has an orbital interval of 207.5 days.
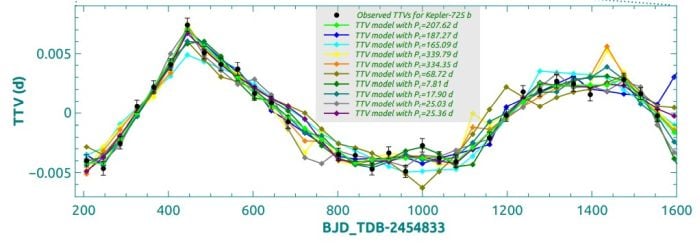
This determine from the analysis exhibits a number of the outcomes. Black strong dots characterize the noticed TTVs for the identified exoplanet Kepler-725b. The road with brilliant inexperienced diamonds represents the most effective orbital interval for Kepler-725c of 207.5 days. Picture Credit score: Solar et al. 2025. Nature Astronomy.
TTV reveals extra than simply the presence of an extra planet. The astronomers additionally extracted necessary data because it tugged on its sibling. “By way of evaluation of the transit timing variations of the comparatively short-period (39.64 days) heat Jupiter Kepler-725 b, we discover that Kepler-725 c has a interval of 207.5 days and travels in an eccentric orbit (with an eccentricity of 0.44 ± 0.02 and an orbital semi-major axis of 0.674 ± 0.002 au), receiving a time-averaged insolation of 1.4 occasions the Earth’s worth,” the researchers clarify.
The planet’s eccentric orbit means it spends solely a part of its time within the liveable zone, the place liquid water might persist on its floor. With solely this information to go by, its habitability is an open query. Relying on its ambiance and different elements, it is potential that some sort of life might survive, however that is solely speculative.
“This discovery demonstrates that the transit timing variation methodology allows the detection and correct mass measurement of a super-Earth/mini-Neptune inside a solar-like star’s liveable zone,” the authors write of their article.
The truth that TTV efficiently discovered this planet is a optimistic growth. By combining TTV observations with different strategies, astronomers can get a a lot clearer image of a distant photo voltaic system. TTV observations are notably sturdy at figuring out photo voltaic system architectures, whereas radial velocity excels at revealing planetary lots, and the transit methodology determines planet sizes.
Exoplanet science is shifting from an emphasis on detection to a concentrate on characterizing exoplanets and their photo voltaic methods. The TTV methodology exhibits promise for filling within the gaps in photo voltaic methods already identified to host exoplanets. When the strategy is mixed with an upcoming mission just like the ESA’s PLATO spacecraft, our seek for super-Earths and Earth-size worlds will take an enormous step ahead.
Quotation: Solar, L., Gu, S., Wang, X. et al. A temperate 10-Earth-mass exoplanet across the Solar-like star Kepler-725. Nat Astron (2025).

