Fuel clouds within the Milky Approach’s Galactic Heart (GC) include copious quantities of star-forming fuel. However for some purpose, few large stars type there, regardless that comparable fuel clouds elsewhere within the galaxy simply type large stars. The clouds additionally type fewer stars general. Are they a brand new sort of molecular cloud?
The star-forming areas are referred to as Big Hii areas, that means the hydrogen is ionized by UV radiation from close by stars. These clouds of fuel can span a whole bunch of light-years whereas typical star forming clouds are solely dozens of sunshine years throughout. These giants maintain sufficient fuel to spawn hundreds of stars. Some have a luminosity equal to hundreds of thousands of Suns and in different elements of the galaxy they’re powered by star clusters with a whole bunch of sizzling, large stars.
Nevertheless, within the GC, these Big Hii areas battle to type large stars. New analysis in The Astrophysical Journal examined three of those areas within the GC, additionally referred to as the Central Molecular Zone (CMZ).
The analysis is titled “Surveying the Giant H ii Regions of the Milky Way with SOFIA. VII. Galactic Center Regions Sgr B1, Sgr B2, and Sgr C.” The lead writer is James M. De Buizer from the Carl Sagan Heart for Analysis on the SETI Institute.
“Big H ii (GH ii) areas are house to extraordinarily large younger and forming OB stellar clusters,” the authors write. “They include a major fraction of essentially the most large stars in a galaxy and subsequently can dominate a galaxy’s thermal emission.” Finding out these areas can assist astronomers perceive the best way to interpret observations of different galaxies and the way large stars type and evolve within the areas.
“Understanding how large stars type and evolve can make clear the preliminary mass operate and star formation theories,” the researchers clarify.
The examine is concentrated on 77 large young stellar objects (MYSO) discovered within the three GH ii areas within the CMZ. Throughout their formation, they’re extraordinarily influential objects as a result of they’ll dramatically reshape their environment by emitting highly effective UV radiation. Their highly effective outflows can both set off or stifle star formation in close by areas. They will excavate cavities of their molecular clouds and disperse star-forming materials. Observing them helps astronomers perceive their energetic processes and the way they affect galactic evolution. Sadly, they’re buried inside dense clouds and are tough to watch. This analysis used SOFIA observations to probe them inside their obscuring clouds.
The researchers discovered that there are similarities between all three GH ii areas, and likewise some important variations.
 This determine from the analysis reveals Sgr B1 and B2. MYSOs are marked in letters and numbers. Letters characterize MYSOs recognized as radio continuum sources and numbers characterize MYSOs recognized as infrared sources. Picture Credit score: De Buizer et al. 2025. The Astrophysical Journal.
This determine from the analysis reveals Sgr B1 and B2. MYSOs are marked in letters and numbers. Letters characterize MYSOs recognized as radio continuum sources and numbers characterize MYSOs recognized as infrared sources. Picture Credit score: De Buizer et al. 2025. The Astrophysical Journal.
After they in contrast the three GH ii areas within the GC, they discovered that the star formation charge is beneath common. Additionally they discovered that regardless of the dense clouds of fuel, they battle to type large stars and should not have sufficient materials to type multiple technology of stars. This units the areas other than different star-forming areas elsewhere within the Milky Approach.
“Current research have concluded that star formation is probably going depressed close to the Galactic Heart, and even that there could also be no current star formation occurring there,” mentioned lead writer De Buizer in a press release. “Since presently-forming large stars are brightest at lengthy infrared wavelengths, we obtained the very best decision infrared pictures of our Galaxy’s central-most star-forming areas. The info present that, contrarily, large stars are presently forming there, however affirm at a comparatively low charge.”
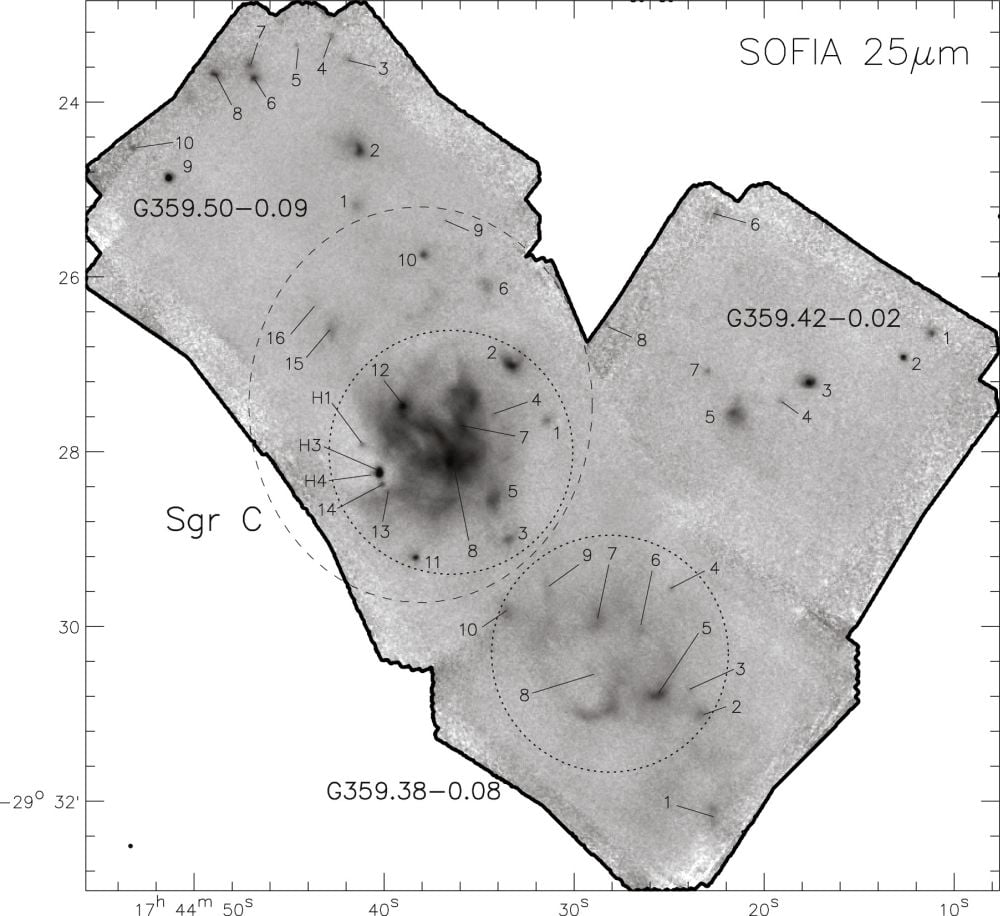 This determine reveals Sgr C and its three sub-regions. The numbers point out MYSO candidates recognized by SOFIA. Picture Credit score: De Buizer et al. 2025. The Astrophysical Journal.*
This determine reveals Sgr C and its three sub-regions. The numbers point out MYSO candidates recognized by SOFIA. Picture Credit score: De Buizer et al. 2025. The Astrophysical Journal.*
Sgr B2 appears to host the youngest of the MYSOs and likewise essentially the most large ones. The most important MYSO in Sgr B2 is about 64 photo voltaic lots, which is “… per a number of of the opposite GH ii areas now we have studied farther out within the Galactic aircraft,” the authors write. Nevertheless, the most important MYSOs in Sgr B1 and Sgr C are solely half as large at about 32 photo voltaic lots.
Sgr C stands aside for various causes. “Sgr C has fewer confirmed MYSOs, and it appears to have a better fraction of low-mass younger stellar objects and contamination from extra advanced interloper/foreground stars,” the authors write. “Moreover, in contrast to typical GH ii areas, Sgr B1 and Sgr C are considerably ionized by advanced interloper stars, which doubtless didn’t type inside these areas,” the researchers clarify.
&t=32s
Our Photo voltaic System is 26,000 light-years from the GC, however the three HII areas within the examine orbit the GC at about 300 mild years. This places them in extraordinarily shut proximity to the energetic chaos that defines the area. There are intense tidal forces from the supermassive black gap that resides there, highly effective stellar winds from large stars, excessive temperatures, and highly effective magnetic fields. This all disrupts the star formation course of.
“These Galactic Heart star-forming areas are in some ways similar to the large star-forming areas within the comparatively calm backwaters of our galaxy,” mentioned examine co-author Wanggi Lim from IPAC at Caltech. “Nevertheless, essentially the most large stars we’re discovering in these Galactic Heart areas, although nonetheless remarkably massive, fall brief in each dimension and amount in comparison with these present in comparable areas elsewhere in our Galaxy. Moreover, such star-forming areas usually cling on to massive reservoirs of star-forming materials and proceed to provide a number of epochs of stars, however that seems to not be the case for these Galactic Heart areas.”
One of many three areas is completely different, although. Sgr B2 has a low star formation charge (SFR) like the opposite H ii areas, however it seems to have held onto its reservoir of star forming materials. Doubtlessly, this implies one other future star cluster might be fashioned there. The authors clarify that the close by Sgr B1 might be extra advanced and has “had time to disperse a lot of its molecular materials.”
Although there are distinct variations between the three GH ii areas, all of them have comparable MYSO stellar densities. They’re all throughout the vary of GH ii areas elsewhere within the galaxy, however are all beneath the common. “This result’s per the notion that CMZ star-forming areas don’t look like as prolific as one would possibly anticipate, however they’re certainly presently producing MYSOs at a charge per GH ii areas farther out within the Galactic aircraft, albeit at a charge beneath the common,” the authors write. However what’s shocking is that MYSO stellar densities are comparable for all three GH ii areas, regardless that Sgr B2 is a way more prolific star-forming setting.
Astronomers suppose that typical GH ii areas host large star clusters which are nonetheless embedded of their fuel clouds. However two of the areas on this examine, Sgr B1 and Sgr C, do not match into this definition. They might be a brand new sort of area.
“In these methods, Sgr B1 and Sgr C deviate from classical GH ii area habits, thus doubtlessly representing a brand new class of GH ii area or difficult their classification as GH ii areas,” the authors write.
Alternatively, they could not correctly be referred to as GH ii areas in any respect. “Alternatively, for the reason that naive assumption is that GH ii areas are the results of clusters of large stars forming from, and nonetheless residing inside, their natal big molecular clouds, one might argue that, as an alternative of being a brand new class of GH ii area, Sgr B1 and Sgr C should not reliable GH ii areas in any respect,” the authors conclude.

