Think about scanning the evening sky for indicators of alien know-how utilizing the identical programs that hunt for exploding stars. That is precisely what researchers are actually doing, reworking astronomical alert programs initially designed to catch supernovae into highly effective instruments for detecting potential technosignatures, the proof of superior civilisations past Earth.
 The Crab Nebula is a supernova remnant within the constellation Taurus (Credit score : NASA/ESA)
The Crab Nebula is a supernova remnant within the constellation Taurus (Credit score : NASA/ESA)
Each evening, the Zwicky Transient Facility (ZTF) generates as much as 1 million alerts because it displays the sky for altering objects. These alerts movement via 9 completely different “alert brokers,” that are refined software program programs that course of and distribute details about something that brightens, dims, or seems within the sky. The upcoming Legacy Survey of House and Time (LSST) will enhance this quantity by an order of magnitude, creating an unprecedented flood of astronomical knowledge.
Whereas these programs had been constructed to catch explosive occasions like supernovae and observe asteroids, a brand new paper by researchers Eleanor Gallay, James Davenport, and Steve Croft demonstrates their untapped potential for SETI (Seek for Extraterrestrial Intelligence). Their work reveals how we will repurpose these astronomical programs to seek for the delicate signatures that may point out synthetic buildings or applied sciences round distant stars.
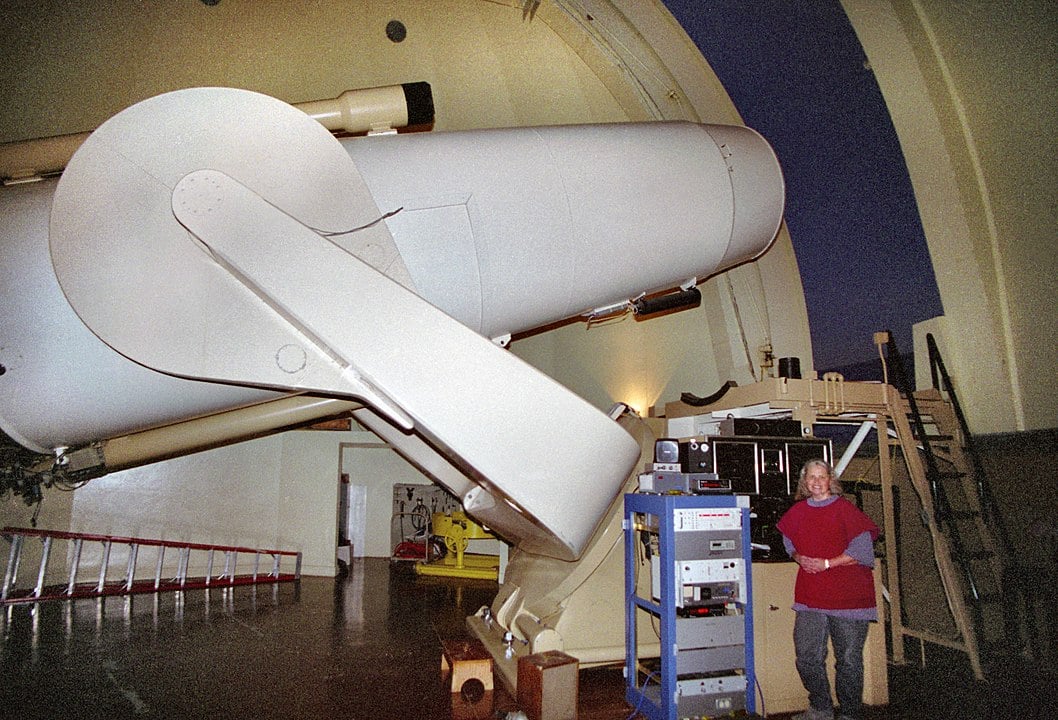 The Samuel Oschin Telescope, a part of the Zwicky Transient Facility
The Samuel Oschin Telescope, a part of the Zwicky Transient Facility
The inspiration for this method comes partly from “Boyajian’s Star,” in any other case generally known as “Tabby’s Star” and with the official designator KIC 8462852, which puzzled astronomers with its mysterious dimming patterns. The researchers word that analysing close by stars for comparable behaviour over time was accomplished within the case of Boyajian’s Star, although pure explanations like mud clouds finally proved most certainly. Nevertheless, the research highlighted how uncommon stellar behaviour might probably point out synthetic megastructures like Dyson spheres, hypothetical constructs that superior civilisations may construct round their stars.
The brand new analysis takes this idea additional, creating automated programs to determine “stellar dippers,” stars that instantly and dramatically dim with out apparent pure causes. These objects are stars with a traditionally fixed luminosity that drop instantly in brightness for a motive unexplained by classical stellar variability or different astrophysical phenomena.
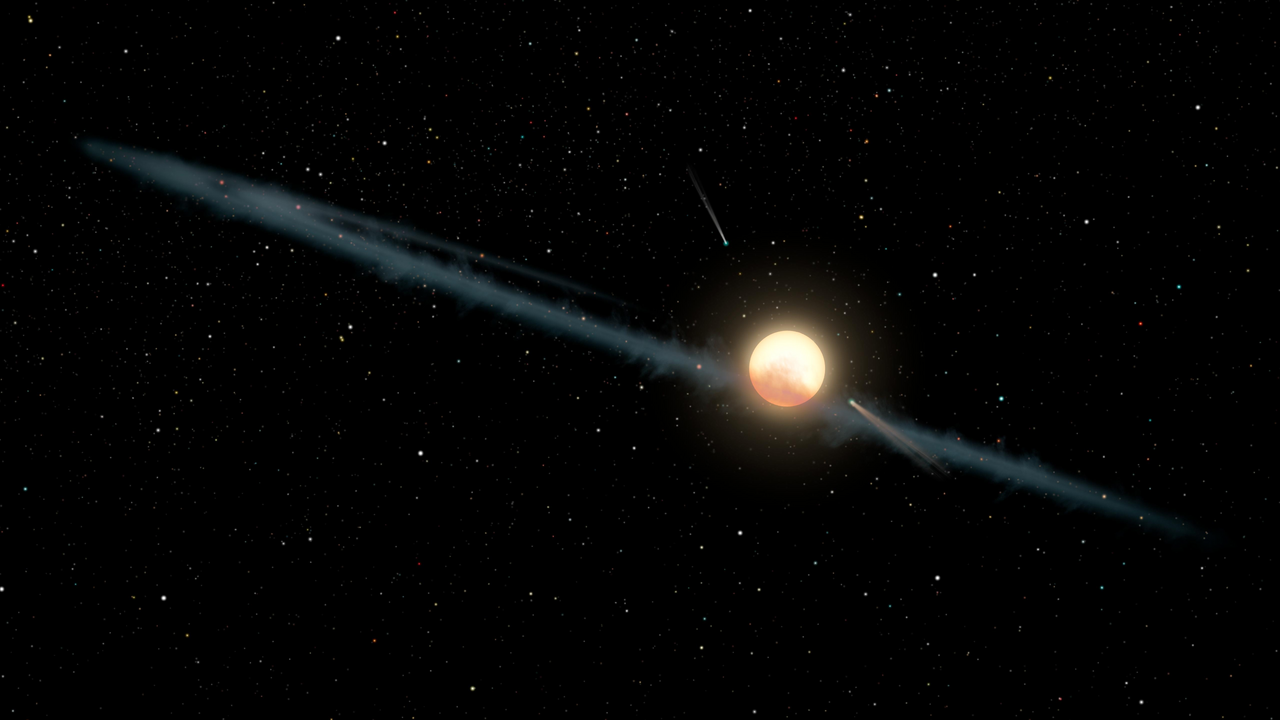 Artist’s idea of an “uneven ring of mud” orbiting Tabby’s Star (Credit score : NASA/JPL-Caltech)
Artist’s idea of an “uneven ring of mud” orbiting Tabby’s Star (Credit score : NASA/JPL-Caltech)
The problem is immense: filtering hundreds of thousands of nightly alerts to seek out the handful that may signify one thing genuinely anomalous. The researchers developed a two-stage method. First, they use the alert dealer’s built-in filtering capabilities to slender down candidates. Then they apply extra evaluation utilizing historic knowledge to determine stars exhibiting unprecedented dimming behaviour.
The staff has deployed optical SETI methods, reminiscent of planetary transit zone geometries and the SETI Ellipsoid. The SETI Ellipsoid is a very intelligent idea that identifies the zone in house the place hypothetical alien observers would have seen Earth transit throughout the Solar, probably prompting them to ship indicators in our route.
The researchers are sincere about present constraints. Although the SETI strategies that alert brokers can execute are at present restricted, they supply recommendations that will improve future technosignature and anomaly searches within the period of the Vera C. Rubin Observatory. The present programs weren’t designed with SETI in thoughts, so some modifications and new approaches might be wanted to totally realise their potential.
Nevertheless, the inspiration is stable. Alert brokers already possess refined instruments for figuring out uncommon astronomical occasions, and the researchers discover some SETI initiatives are doable utilizing options instantly within the brokers. The Lasair alert dealer, for example, gives a “watchmap” function that may monitor particular areas of sky for anomalous indicators.
Because the Vera C. Rubin Observatory comes on-line with LSST, the quantity of astronomical alerts will enhance dramatically. This creates each alternatives and challenges for technosignature analysis. Extra knowledge means higher possibilities of catching uncommon, anomalous occasions, but it surely additionally means creating much more refined filtering methods to keep away from being overwhelmed.
 Artist impression of the finished LSST (Credit score : LSST Venture Workplace)
Artist impression of the finished LSST (Credit score : LSST Venture Workplace)
The researchers’ work represents a wise method to SETI that makes use of current infrastructure reasonably than requiring devoted alien looking telescopes. By utilising programs already scanning the complete seen sky each few nights, they’re basically getting a free journey on some of the complete surveillance networks ever pointed on the sky.
The staff concludes that their preliminary outcomes clarify the promising alternative for future anomaly and technosignature searches utilizing alert brokers on knowledge from ZTF and the upcoming LSST. Whereas we should not look forward to finding alien megastructures subsequent week, this analysis establishes the groundwork for a brand new technology of SETI that might function constantly, scanning hundreds of thousands of stars for the indicators that we aren’t alone within the universe.
Supply : Technosignature Searches with Real-time Alert Brokers

