A primary stage in understanding a pure phenomenon is to divide it into steps and provides issues labels. That offers us a approach to speak concerning the phenomenon. However in nature, there are seldom clear divisions between processes. Your entire Universe is a long-running collection of intertwined causes and results set in movement by the Massive Bang.
One of many phenomena scientists are working arduous to know is how compact photo voltaic methods kind. Up till now, the dominant considering was that first a star kinds, then planets kind. They have been thought-about separate, discrete levels in photo voltaic system formation. Name it the “star first, planets second” mannequin. However there are issues with that mannequin, they usually change into extra obtrusive as astronomers research different photo voltaic methods.
One of many issues is the mass distribution puzzle introduced by compact photo voltaic methods. If stars kind first after which planets, why do compact photo voltaic methods have so many planets with such comparable lots? Within the well-known TRAPPIST-1 system, all seven planets are bigger than Mars, and 5 of them are inside 15% of Earth’s diameter.
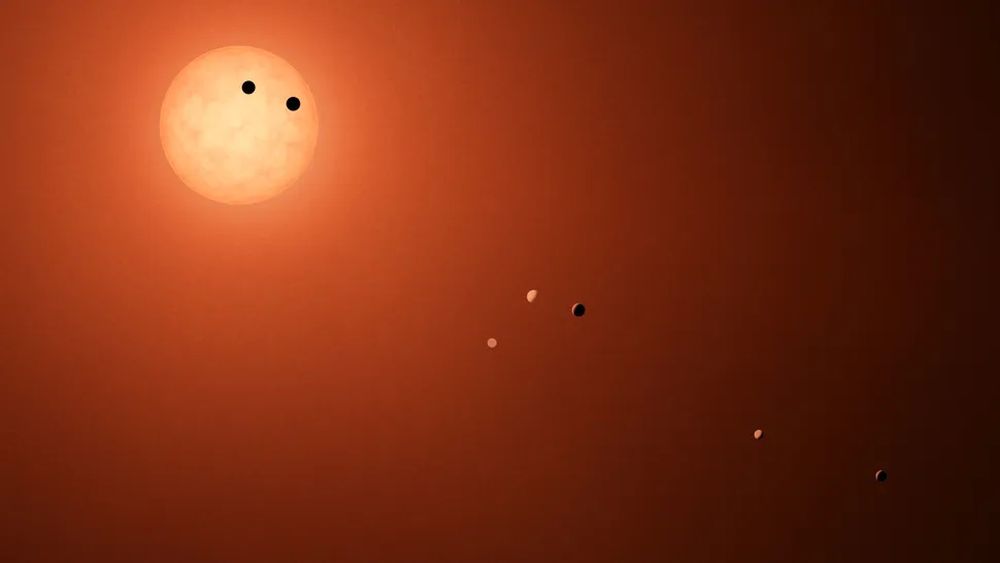 This artist’s illustration reveals the crimson dwarf star TRAPPIST-1 and the seven planets in its compact system. Picture Credit score: NASA
This artist’s illustration reveals the crimson dwarf star TRAPPIST-1 and the seven planets in its compact system. Picture Credit score: NASA
Researchers on the Southwest Analysis Institute (SwRI) could have found out how compact methods kind. Their new analysis is titled “Origin of compact exoplanetary systems during disk infall,” and it is revealed in Nature Communications. The authors are Raluca Rufu and Robin Canup, each from the Photo voltaic System Science and Exploration Division at SwRI.
“Exoplanetary methods that comprise a number of planets on short-period orbits seem like prevalent within the present noticed exoplanetary inhabitants, but the processes that give rise to such configurations stay poorly understood,” the researchers write of their article. “A typical prior assumption is that planetary accretion commences after the infall of gasoline and solids to the circumstellar disk ends.”
The traditional knowledge says that planets kind after the star kinds. Every photo voltaic system kinds from a photo voltaic nebula, and as a younger star kinds, a circumstellar disk of fabric kinds round it. That is the fabric that younger stars draw from. Ultimately, materials stops falling into the circumstellar disk and its mass is fastened. After a couple of million years, this disk is dispersed. However earlier than it’s, planets begin forming within the disk by collisions, mergers, and accretion. On this understanding, planets begin forming solely after materials has stopped falling into the disk.
“Compact methods are one of many nice mysteries of exoplanet science,” mentioned Rufu, a Sagan Fellow and lead creator of a Nature Communications article describing this analysis. “They comprise a number of rocky planets of comparable dimension, like peas in a pod, and a standard mass ratio that could be very totally different than that of our photo voltaic system’s planets.”
“Intriguingly, the widespread mass ratio seen in compact exoplanetary methods is much like that of the satellite tv for pc methods of our gasoline planets. These moons are thought to have developed as gasoline planets finalized their formation. This appears a strong clue that compact methods could replicate an identical underlying course of,” mentioned Canup.
The Atacama Large Millimeter Array (ALMA) telescope is astronomers’ greatest software for observing younger, still-forming photo voltaic methods as a result of it could possibly see by the gasoline and dirt that shrouds them. As ALMA examines increasingly more younger methods, it finds that planets start forming early. How can this be understood?
“Conventionally, it has been assumed that planetary meeting began after stellar infall ends. Nonetheless, current ALMA observations present sturdy proof that planetary accretion, or formation, could start earlier,” mentioned Rufu. “We suggest that compact methods are surviving remnants of planet accretion that occurred through the remaining phases of infall.”
The researchers used simulations to check the concept. They developed a mannequin that may clarify compact photo voltaic methods that is partly primarily based on ALMA observations. It reveals that planets start forming whereas the star remains to be accreting, and {that a} planet migrates inward because it positive aspects mass. This creates methods like TRAPPIST-1.
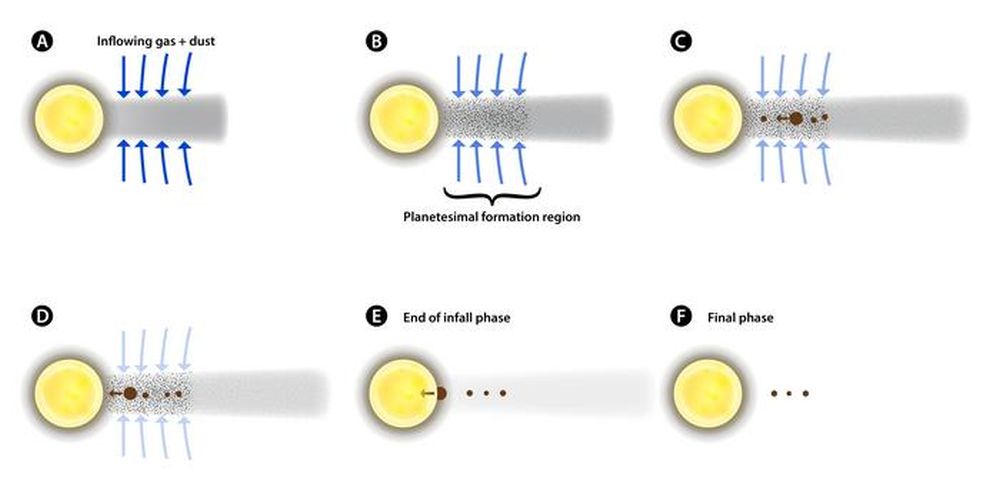 This determine reveals the formation course of for compact methods of rocky planets in accordance with the brand new mannequin. Planets start forming in areas of a disk round a younger star which might be fed by an ongoing infall of gasoline and small grains. Rising planets gather rocky materials whereas progressively spiraling inward by interactions with surrounding gasoline. As a planet positive aspects mass, its inward migration accelerates. This course of creates a compact planetary system with a planets-to-star mass ratio in line with noticed compact exoplanetary methods. Picture Credit score: Rufu and Canup 2025. Nature Communications
This determine reveals the formation course of for compact methods of rocky planets in accordance with the brand new mannequin. Planets start forming in areas of a disk round a younger star which might be fed by an ongoing infall of gasoline and small grains. Rising planets gather rocky materials whereas progressively spiraling inward by interactions with surrounding gasoline. As a planet positive aspects mass, its inward migration accelerates. This course of creates a compact planetary system with a planets-to-star mass ratio in line with noticed compact exoplanetary methods. Picture Credit score: Rufu and Canup 2025. Nature Communications
“We discover that planets that accrete throughout infall can survive till the gasoline disk disperses and orbital migration ends,” mentioned Canup. “Importantly, throughout a broad vary of circumstances, the mass of surviving methods is proportional to the mass of the host star, offering the primary rationalization for the same mass ratios of noticed multi-planet compact methods.”
The method introduced of their mannequin is considerably parallel with the moon-forming course of round gasoline giants like Jupiter. As a gasoline large kinds, a hoop of fabric kinds round it, fed from the circumstellar disk. Identical to planets forming round a star, moons kind within the disk across the gasoline large. The 2 processes aren’t precisely the identical, although. The planet-forming disks round stars can persist for thousands and thousands of years, whereas the moon-forming disks rapidly disperse as soon as infall from the circumstellar disk ceases.
“It’s thrilling to see that the method of early meeting in younger disks may go in an identical method throughout very totally different scales,” the group notes.
“Predictions of our mannequin must be more and more testable by observations,” the SwRI researchers clarify of their article. “Accretion throughout infall implies a standard compact system mass ratio unbiased of stellar mass, and that methods with considerably decrease estimated mass ratios would possibly host but undetected planets.”
There are, after all, excellent questions. For instance, how bigger planets kind on this mannequin remains to be unclear. The authors write that planets that survive whereas forming throughout infall, and their traits, rely largely on the radial extent of disk infall (rc) and the ratio of the gasoline disk lifetime to the infall timescale (β). Nonetheless, their simulations solely concerned small rc and small β circumstances, in line with compact methods.
“Most broadly, our outcomes counsel that the long-standing assumption that planet accretion commences solely after infall has ended is probably not legitimate for all methods, and consideration of this early accretionary part is warranted,” the authors conclude.

