Since Galileo first noticed them by way of his telescope within the early 1600s, sunspots have fascinated scientists. These darkish patches on the Solar’s floor can persist for days and even months, however till now, researchers could not absolutely clarify why they remained secure for such prolonged intervals.
A examine revealed in Astronomy & Astrophysics has lastly solved this centuries-old puzzle. A global group of scientists, led by researchers from Germany’s Institute of Photo voltaic Physics, developed a revolutionary new technique for analyzing sunspot stability that reveals the fragile stability preserving these photo voltaic options intact.
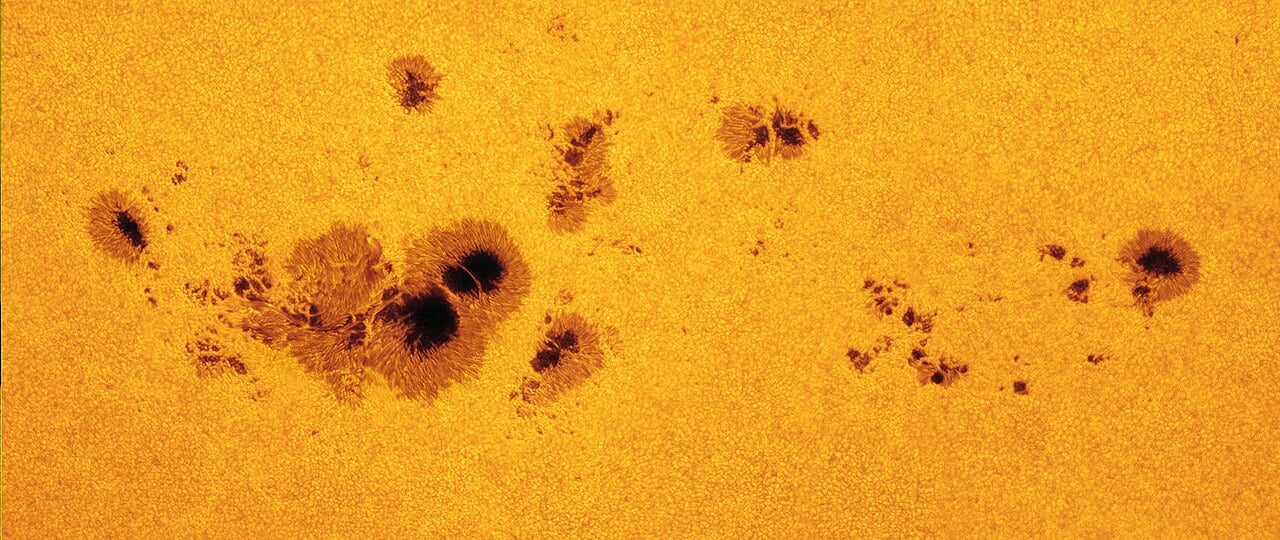 A gaggle of sunspots, labeled as Energetic Area 1520 rotated into view over the left aspect of the solar on July 7, 2012. (Credit score : NASA/Goddard House Flight Centre)
A gaggle of sunspots, labeled as Energetic Area 1520 rotated into view over the left aspect of the solar on July 7, 2012. (Credit score : NASA/Goddard House Flight Centre)
Sunspots are areas the place the Solar’s magnetic discipline is powerful, akin to the magnetic discipline in a hospital MRI machine, however protecting an space bigger than Earth itself. These magnetic discipline concentrations seem as darkish spots as a result of they’re cooler than the encircling photo voltaic floor however in actuality, a sunspot on the distance of the Solar however remoted from the remainder of the disc would shine brighter than the complete Moon!
The variety of sunspots follows an 11 12 months cycle, reaching peak exercise when photo voltaic storms are more than likely to happen. Throughout these intervals, unstable magnetic configurations close to sunspots can set off explosive occasions referred to as coronal mass ejections and photo voltaic flares. These area climate occasions can disrupt satellite tv for pc communications and, in excessive instances, trigger energy grid failures on Earth.
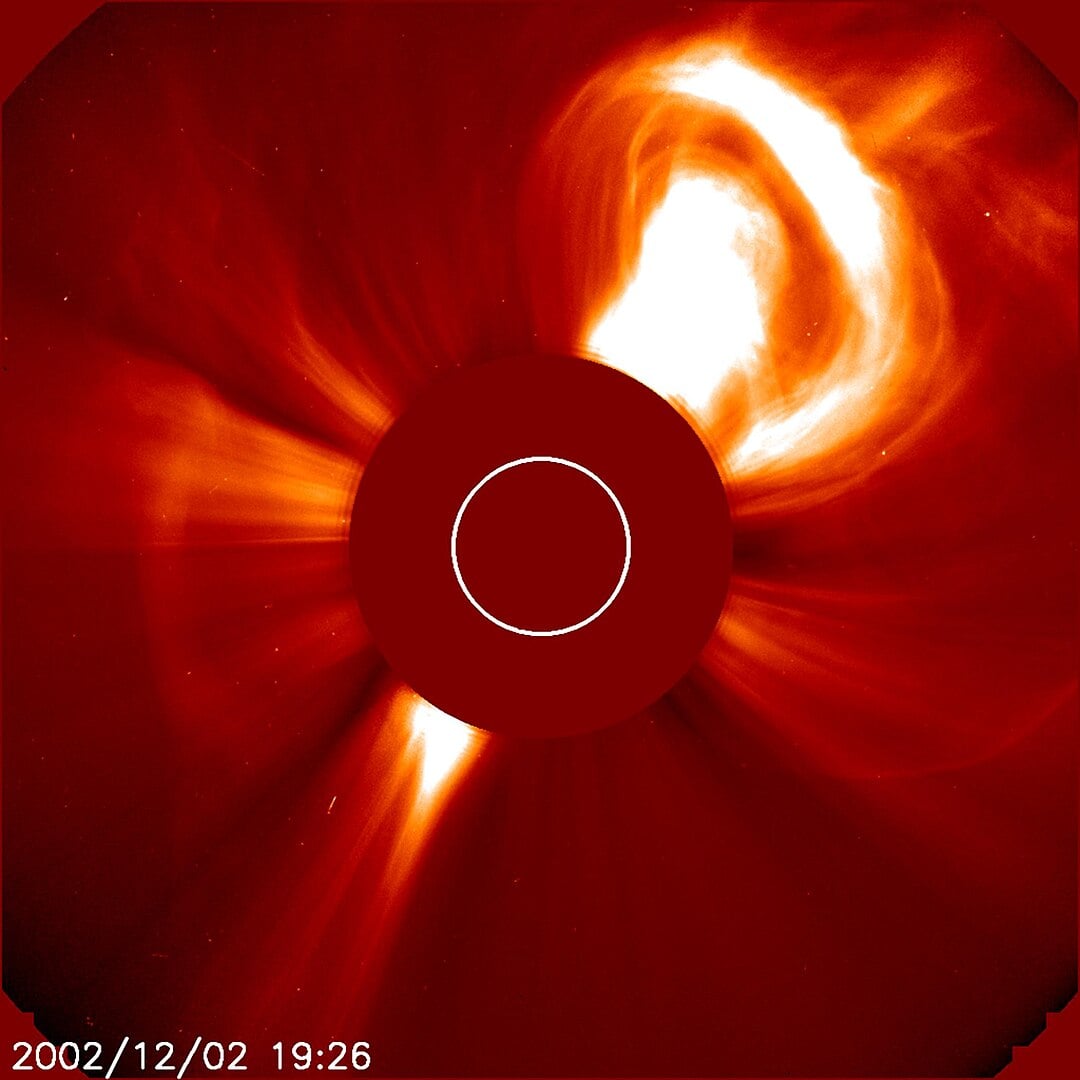 When noticed in white-light coronagraph imagery, CMEs generally resemble a lightweight bulb, possessing a shiny bulb-like outer shell surrounding a darkish void and compact internal construction. (Credit score : NASA)
When noticed in white-light coronagraph imagery, CMEs generally resemble a lightweight bulb, possessing a shiny bulb-like outer shell surrounding a darkish void and compact internal construction. (Credit score : NASA)
It’s lengthy been suspected that sunspots stay secure due to an equilibrium between fuel strain and magnetic forces. Nevertheless, proving this stability has been difficult attributable to atmospheric disturbances that intrude with floor primarily based observations of the Solar’s magnetic discipline.
The analysis group made a vital breakthrough by enhancing a method initially developed at Germany’s Max Planck Institute for Photo voltaic System Analysis. Their enhanced technique removes the blurring results of Earth’s environment from observations made with the German GREGOR photo voltaic telescope.
Utilizing this refined method, the researchers analysed polarised gentle emitted by the Solar to measure magnetic forces inside sunspots with unprecedented precision. Their measurements now obtain satellite tv for pc high quality outcomes from floor primarily based telescopes at a fraction of the fee.
The evaluation revealed that magnetic forces inside sunspots are completely balanced by strain forces, sustaining strict equilibrium. This delicate stability explains why sunspots can survive for such prolonged intervals on the Solar’s turbulent floor.
This discovery has vital sensible functions. By understanding the exact mechanisms that maintain sunspots secure, scientists might be able to predict when these photo voltaic options turn into unstable and extra more likely to produce harmful area climate occasions.
Higher prediction of photo voltaic storms may assist shield satellites, energy grids, and astronauts from dangerous radiation. As our society turns into more and more depending on satellite tv for pc know-how and digital infrastructure, this analysis offers essential insights for safeguarding fashionable life in opposition to photo voltaic threats. It additionally represents a significant step ahead in photo voltaic physics, combining superior floor primarily based observations with subtle evaluation methods to unravel considered one of astronomy’s oldest mysteries.
Supply : A new method for analyzing the stability of sunspots

