Exploding stars come in several sorts, and these various kinds of supernovae present astronomers various things in regards to the cosmos. There is a scientific urge for food to search out extra of them and enhance our information about these unique occasions. The Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope ought to be capable to feed that urge for food.
The Roman is because of launch in about two years, and can make its option to its station on the Solar-Earth L2 orbit. After commissioning, it’s going to start operations. One among its three main surveys is the High-Latitude Time-Domain Survey. In that survey, the highly effective house telescope will picture the identical part of sky past the Milky Manner each 5 days for 2 years. The staff behind the Roman will sew these scenes collectively into one complete film, a type of cosmic cinema.
These films will reveal the presence of Sort 1a supernovae. These happen in binary star techniques the place one star is a white dwarf. White dwarfs have immense gravitational pressure as a result of they’re extraordinarily dense objects. They draw materials away from their companion stars, which may very well be something from one other white dwarf to a large star. That materials builds up on the white dwarf’s floor, and when it reaches a vital mass, it triggers a runaway response and a supernova explosion.
Sort 1a are completely different from what we will name commonplace supernovae. These are core-collapse supernovae, the place an enormous star collapses right into a neutron star or a black gap, or is totally destroyed and leaves behind solely a diffuse nebula.
Since Sort 1a supernovae explode at a set mass, their peak luminosity is thought. For that purpose, they function commonplace candles, instruments astronomers use to precisely gauge the space to their dwelling galaxies. These correct distances permit cosmologists to hint the growth of the Universe.
The Roman’s Excessive-Latitude Time-Area Survey is a vital a part of its mission and is aimed toward discovering Sort 1a supernovae and different transients. In line with new analysis and simulations, it ought to discover about 27,000 of them, a stunning quantity that is about ten instances better than the present variety of recognized Sort 1a SN. This complete knowledge set ought to assist cosmologists of their quest to map the growth of the Universe, a vital a part of understanding darkish vitality.
“Proof is mounting that darkish vitality has modified over time, and Roman will assist us perceive that change by exploring cosmic historical past in methods different telescopes can’t.” – Dr. Ben Rose – Dept. of Physics and Astronomy, Baylor College
The 27,000 quantity comes from new analysis printed in The Astrophysical Journal titled “The Hourglass Simulation: A Catalog for the Roman High-latitude Time-domain Core Community Survey.” The lead writer is Dr. Ben Rose, an assistant Professor of Physics within the Division of Physics and Astronomy at Baylor College.
The Roman will discover these explosions by observing gentle from distant galaxies and searching again in time. The Roman will push that point boundary and permit astronomers to see Sort 1a SN additional again than ever. Many of the T1a SN noticed thus far exploded within the final 8 billion years. The Roman’s Excessive-Latitude Time-Area Survey (HLTDS) will uncover hundreds that exploded longer than 10 billion years in the past, and dozens that exploded even sooner than that. These commonplace candles will fill a lacking hole and are vital proof of the Universe’s growth in its early age.
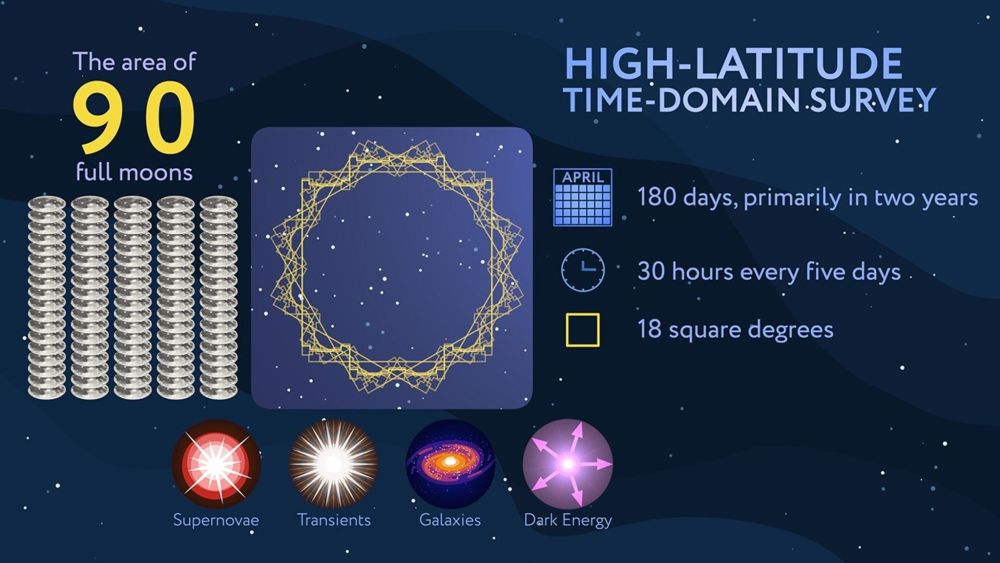 This graphic outlines the Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope’s Excessive-Latitude Time Area Survey. The survey’s major element will cowl over 18 sq. levels — a area of sky as giant as 90 full moons — and can detect supernovae that occurred as much as about 8 billion years in the past. Smaller areas throughout the survey can look even additional again in time, probably again to when the universe was round a billion years outdated. The survey will likely be break up between the northern and southern hemispheres, positioned in areas of the sky that will likely be repeatedly seen to Roman. The majority of the survey will encompass 30-hour observations each 5 days for 2 years in the course of Roman’s five-year main mission. Picture Credit score: NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle
This graphic outlines the Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope’s Excessive-Latitude Time Area Survey. The survey’s major element will cowl over 18 sq. levels — a area of sky as giant as 90 full moons — and can detect supernovae that occurred as much as about 8 billion years in the past. Smaller areas throughout the survey can look even additional again in time, probably again to when the universe was round a billion years outdated. The survey will likely be break up between the northern and southern hemispheres, positioned in areas of the sky that will likely be repeatedly seen to Roman. The majority of the survey will encompass 30-hour observations each 5 days for 2 years in the course of Roman’s five-year main mission. Picture Credit score: NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle
“Filling these knowledge gaps might additionally fill in gaps in our understanding of darkish vitality,” lead writer Rose mentioned in a press release. “Proof is mounting that darkish vitality has modified over time, and Roman will assist us perceive that change by exploring cosmic historical past in methods different telescopes can’t.”
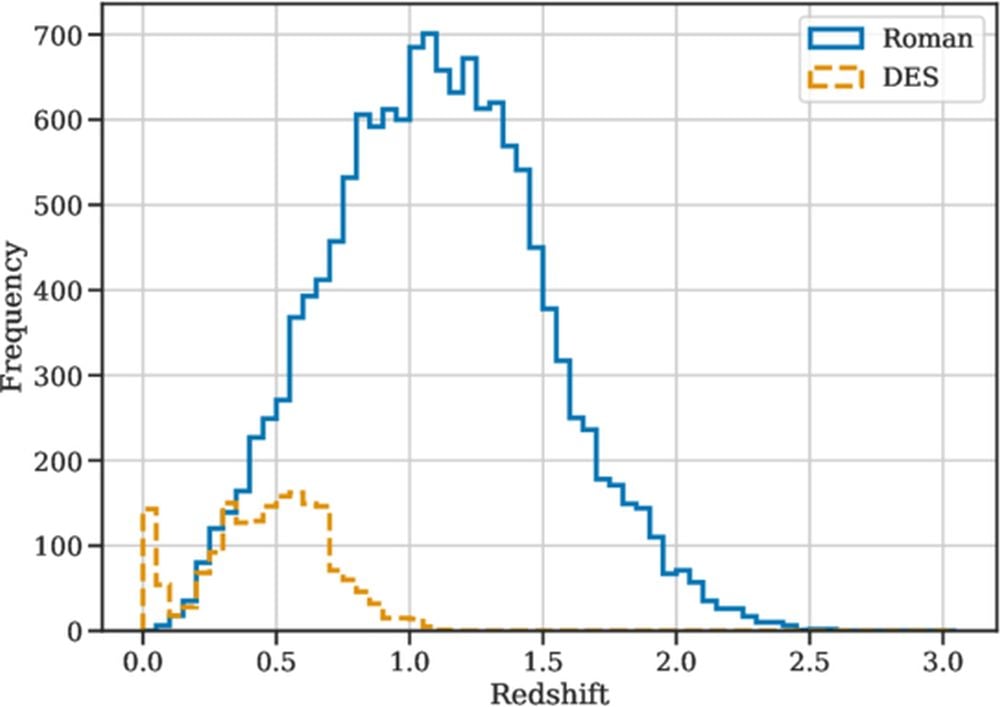 This determine compares the Roman’s anticipated haul of Sort 1a SN with the Darkish Power Survey’s cosmological pattern of the identical. “DES has over 1500 SNe in its cosmological pattern with only a few at z > 1. Nevertheless, we anticipate Roman to have practically 19,000 SN Ia, with the bulk above z > 1,” the authors write. Picture Credit score: Rose et al. 2025. TApJ
This determine compares the Roman’s anticipated haul of Sort 1a SN with the Darkish Power Survey’s cosmological pattern of the identical. “DES has over 1500 SNe in its cosmological pattern with only a few at z > 1. Nevertheless, we anticipate Roman to have practically 19,000 SN Ia, with the bulk above z > 1,” the authors write. Picture Credit score: Rose et al. 2025. TApJ
Each supernova is basically a flash within the cosmos, and dissecting the sunshine from the flash reveals what kind of occasion launched it. Core collapse SN and T1a SN aren’t simple to differentiate at such nice distances, however the gentle modifications over time, and may be break up aside with spectroscopy to be taught extra about it. The Roman carries two devices, and one among them, the Extensive-Discipline Instrument (WFI), permits the telescope to do large-scale spectroscopic surveys.
“By seeing the best way an object’s gentle modifications over time and splitting it into spectra — particular person colours with patterns that reveal details about the thing that emitted the sunshine—we will distinguish between all of the various kinds of flashes Roman will see,” mentioned Rebekah Hounsell, examine co-author and assistant analysis scientist on the College of Maryland-Baltimore County working at NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle.
The Hourglass Simulation “makes use of essentially the most up-to-date spectral vitality distribution fashions and charge measurements for 10 extragalactic time-domain sources,” the authors clarify of their analysis. “We simulate these fashions by the design reference Roman Area Telescope survey.”
“In complete, Hourglass has over 64,000 transient objects, 11,000,000 photometric observations, and 500,000 spectra,” the authors write. Hourglass confirmed that the Roman can look forward to finding “roughly 21,000 Sort Ia supernovae, 40,000 core-collapse supernovae, round 70 superluminous supernovae, ∼35 tidal disruption occasions, three kilonovae, and presumably pair-instability supernovae.”
This spectacular knowledge set will drive the examine and understanding not solely of darkish vitality, however of many different transient occasions too. As of 2024, for instance, astronomers knew of solely about 260 superluminous supernovae (SLSNe). These explosions may be 10p instances as luminous as different SN. Solely large stars better than 40 photo voltaic lots are anticipated to blow up as SLSNe, but astrophysicists aren’t sure what causes them. Discovering an extra 70 might present solutions to some excellent questions.
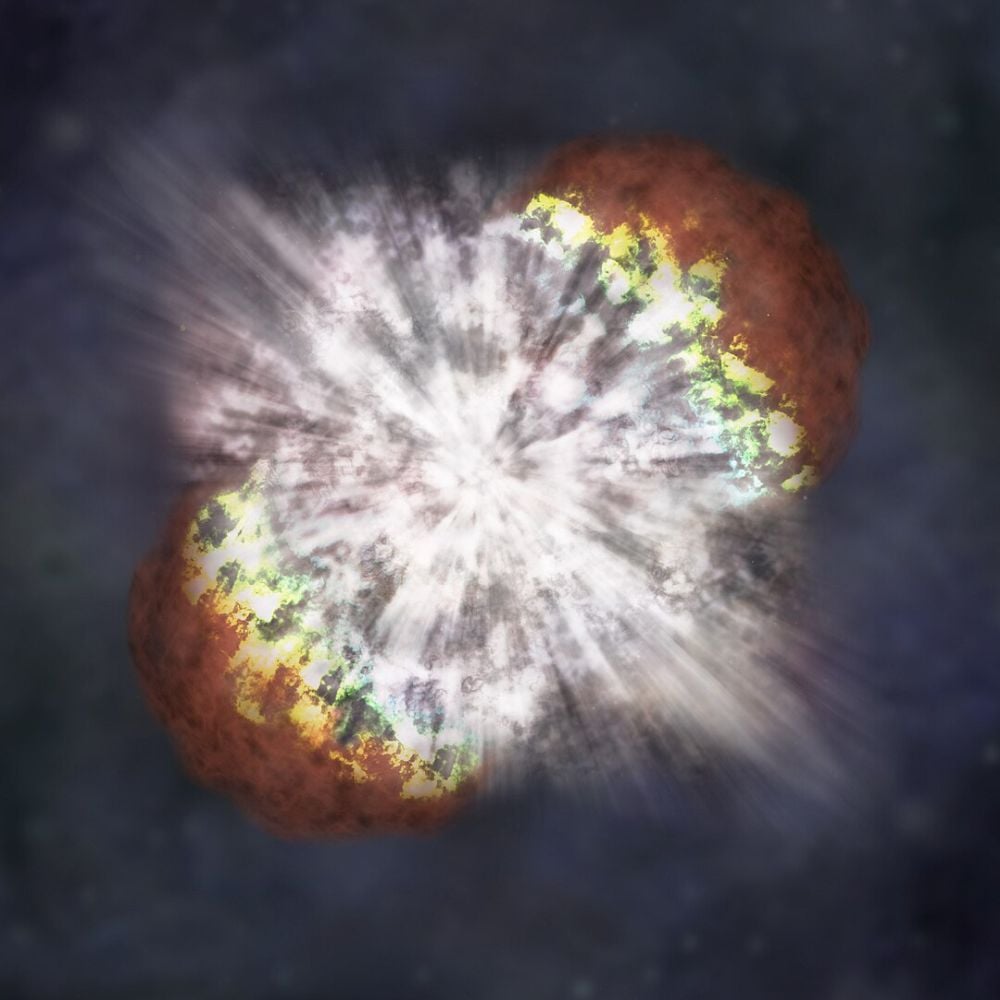 This artist’s illustration reveals the explosion of SN 2006gy, a superluminous supernova about 238 million light-years away. Picture Credit score: By Credit score: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss – Public Area,
This artist’s illustration reveals the explosion of SN 2006gy, a superluminous supernova about 238 million light-years away. Picture Credit score: By Credit score: NASA/CXC/M.Weiss – Public Area,
The Hourglass Simulation is designed to arrange the science neighborhood for the Roman’s deluge of knowledge. With its tens of hundreds of transients, hundreds of thousands of photometric observations, and lots of of hundreds of spectra, Hourglass will function a coaching instrument. “Moreover, Hourglass is a helpful knowledge set to coach machine studying classification algorithms.”
“With the dataset we’ve created, scientists can practice machine-learning algorithms to differentiate between various kinds of objects and sift by Roman’s downpour of knowledge to search out them,” Hounsell added within the press launch. “Whereas trying to find kind Ia supernovae, Roman goes to gather quite a lot of cosmic ‘bycatch’—different phenomena that aren’t helpful to some scientists, however will likely be invaluable to others.”
Amongst these different phenomena are Tidal Disruption Events (TDE), which happen when a black gap consumes a star. Astronomers know of about 100 of them, and so they can reveal the presence of black holes which might be in any other case dormant and undetectable. If the Roman can discover an extra 35, that may undoubtedly assist them reply a few of their questions. Not solely are their excellent questions on black holes’ lots and spina, however there are additionally questions on how stars behave within the dense areas close to galactic facilities.
Kilonovae are one other kind of cosmic explosion and happen when two neutron stars or a neutron star and a black gap collide. Although they’re fainter than SN, Kilonovae launch gravitational waves and in addition produce substantial quantities of heavy parts like gold, platinum, and uranium. There’s just one confirmed kilonova explosion, and there are lots of excellent questions on them. Astrophysicists wish to perceive the composition of those parts of their ejecta, and the way usually they happen and if there are a number of sorts. If the Roman can discover three extra, that is an enormous enhance within the dataset scientists need to work with.
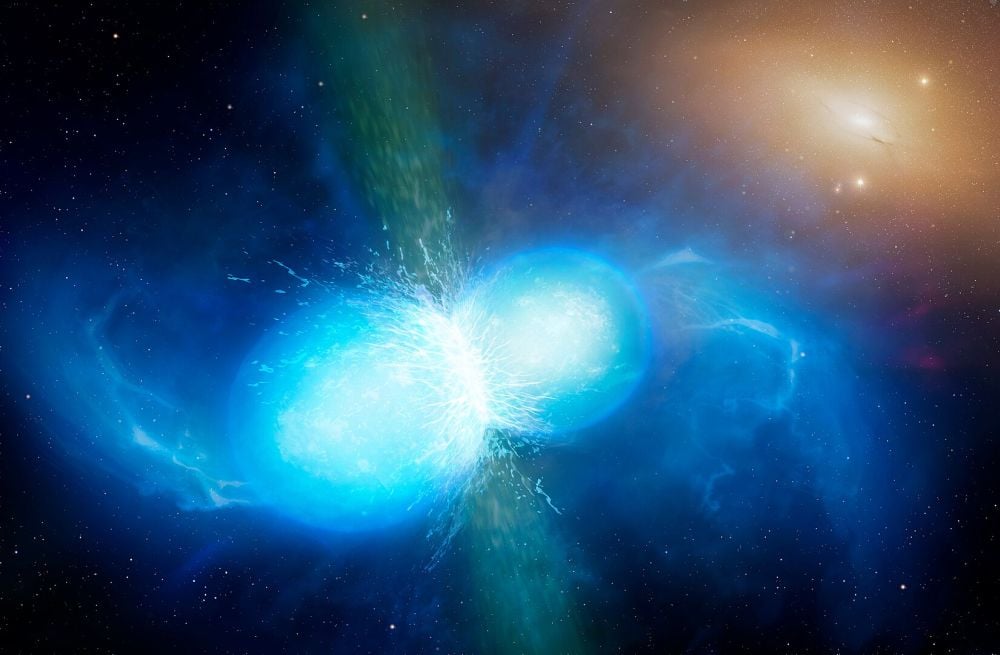 This artist’s illustration reveals two neutron stars merging, releasing gravitational waves and exploding as a kilonova. There’s just one confirmed kilonova, so if the Roman can discover three extra, that is an enormous soar in knowledge. Picture Credit score: By College of Warwick/Mark Garlick, CC BY 4.0
This artist’s illustration reveals two neutron stars merging, releasing gravitational waves and exploding as a kilonova. There’s just one confirmed kilonova, so if the Roman can discover three extra, that is an enormous soar in knowledge. Picture Credit score: By College of Warwick/Mark Garlick, CC BY 4.0
Pair-instability supernovae are one other unique kind of stellar explosion that scientists wish to know extra about. Solely extraordinarily large stars between about 130 to 250 photo voltaic lots can explode as pair-instability supernovae (PISNe), and so they do not go away neutron stars or black holes behind. The progenitor stars is totally destroyed, and solely an increasing nebula of gasoline and mud, together with heavy parts synthesized within the explosion, is left behind. Astrophysicists wish to know the precise stellar mass of their progenitors and what function metallicity performs.
Because it stands now, astrophysicists have solely a small handful of candidate PISNe, and if the Roman can discover ten of them just like the simulation suggests, researchers can have much more knowledge to work with.
“I believe Roman will make the primary confirmed detection of a pair-instability supernova,” Rose mentioned. “They’re extremely far-off and really uncommon, so that you want a telescope that may survey quite a lot of the sky at a deep publicity degree in near-infrared gentle, and that’s Roman.”
As NASA’s subsequent flagship astrophysics mission, the Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope will make an unlimited contribution to our understanding of various kinds of cosmic explosions. By stitching collectively its observations into films that present how completely different cosmic explosions happen, it would advance our scientific information significantly.
“Whether or not you wish to discover darkish vitality, dying stars, galactic powerhouses, or in all probability even fully new issues we’ve by no means seen earlier than, this survey will likely be a gold mine,” mentioned Rose.
Every time a brand new telescope mission is launched, it is after years and even many years of preliminary work, together with determining what questions should be requested and what devices are wanted to search out the solutions. Simulations just like the Hourglass simulation have gotten extra frequent, because the astronomy neighborhood anticipates and prepares for brand new knowledge from upcoming missions.
However every mission additionally produces surprises, and although they’re unpredictable, scientists usually point out how excited they’re to search out shocking new issues.
“Roman’s going to discover a entire bunch of extraordinary issues out in house, together with some we haven’t even considered but,” Hounsell mentioned. “We’re undoubtedly anticipating the sudden.”
 An illustration the Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope, set to launch in 2027, if it could possibly survive funds cuts. Picture Credit score: NASA/GSFC/SVS
An illustration the Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope, set to launch in 2027, if it could possibly survive funds cuts. Picture Credit score: NASA/GSFC/SVS
Sadly, the present US administration has taken intention at NASA’s funds and introduced that the Roman’s funding will likely be lower. For the reason that present administration has gained a repute for complicated bulletins which might be generally later rescinded, the mission’s future is unclear.
Whether it is permitted and launched, its valuable dataset will likely be a feast for astrophysicists around the globe and can assist drive a deeper understanding of Nature and a few of its most excessive objects and occasions.

